Abstract
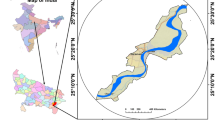
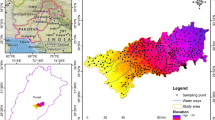
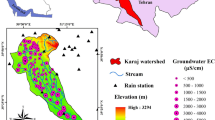
Arsenic (As) is one of the most important dangerous elements as more than 100 million of people are exposed to risk, globally. The permissible threshold of As for drinking water is 10 μg/L according to both the WHO’s drinking water guidelines and the Iranian national standard. However, several studies have indicated that As concentrations exceed this threshold value in several regions of Iran. This research evaluates an As-susceptible region, the Tajan River watershed, using the following data-mining models: multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS), functional data analysis (FDA), support vector machine (SVM), generalized linear model (GLM), multivariate discriminant analysis (MDA), and gradient boosting machine (GBM). This study considers 12 factors for elevated As concentrations: land use, drainage density, profile curvature, plan curvature, slope length, slope degree, topographic wetness index, erosion, village density, distance from villages, precipitation, and lithology. The susceptibility mapping was conducted using training (70%) and validation (30%). The results of As contamination in sediment showed that classifications into 4 levels of concentration are very similar for two models of GLM and FDA. The GBM calculated the areas of highest arsenic contamination risk by MARS and SVM with percentages of 30.0% and 28.7%, respectively. FDA, GLM, MARS, and MDA models calculated the areas of lowest risk to be 3.3%, 23.0%, 72.0%, 25.2%, and 26.1%, respectively. The results of ROC curve reveal that the MARS, SVM, and MDA had the highest accuracies with area under the curve ROC values of 84.6%, 78.9%, and 79.5%, respectively. Land use, lithology, erosion, and elevation were the most important predictors of contamination potential with a value of 0.6, 0.59, 0.57, and 0.56, respectively. These are the most important factors. Finally, these data-mining methods can be used as appropriate, inexpensive, and feasible options to identify As-susceptible areas and can guide managers to reduce contamination in sediment of the environment and the food chain.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla, F., & Khalil, R. (2018). Potential effects of groundwater and surface water contamination in an urban area, Qus City, Upper Egypt. Journal of the African Earth Sciences, 141, 164–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.02.016.
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Arsenic. In Trace elements in terrestrial environments (pp. 219–261). Springer.
Ahmad, A., & Bhattacharya, P. (2019). Arsenic in drinking water: is 10 μg/L a safe limit? Curr. Pollut. Reports, 5, 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-019-0102-7.
Akgun, A., Sezer, E. A., Nefeslioglu, H. A., Gokceoglu, C., & Pradhan, B. (2012). An easy-to-use MATLAB program (MamLand) for the assessment of landslide susceptibility using a Mamdani fuzzy algorithm. Computational Geosciences, 38, 23–34.
Al-Abadi, Alaa M., Hamid Reza Pourghasemi, Shamsuddin Shahid, & Hussain B Ghalib. (2017). “Spatial mapping of groundwater potential using entropy weighted linear aggregate novel approach and GIS.” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 42(3), 1185–99.
Ali, M. M., Ali, M. L., Islam, M. S., & Rahman, M. Z. (2016). Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag., 5, 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.01.002.
Alidadi, H., Ramezani, A., Davodi, M., Peiravi, R., Paydar, M., Dolatabadi, M., & Rafe, S. (2015). Determination of total arsenic in water resources: a case study of Rivash in Kashmar City. Heal. Scope, 4, 14–16. https://doi.org/10.17795/jhealthscope-25424.
Atkinson, P., Jiskoot, H., Massari, R., Murray, T. (1998). Generalized linear modelling in geomorphology 1195, 1185–1195.
Barzegar, R., Moghaddam, A. A., Deo, R., Fijani, E., & Tziritis, E. (2018). Mapping groundwater contamination risk of multiple aquifers using multi-model ensemble of machine learning algorithms. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 697–712.
Belkin, H. E., Warwick, P. D., Finkelman, R. B., Zheng, B., & Zhou, D. (1998). High arsenic coals related to sedimentary rock-hosted gold deposition in southwestern Guizhou Province, Peoples Republic of China. In Pittsburgh Coal Conference, Pittsburgh, PA (United States).
Bhattacharya, P. C. (2002). Rural‐to‐urban migration in LDCs: A test of two rival models. Journal of International Development, 14(7), 951–972.
Bhattacharya, R., & Patrangenaru, V. (2002). Nonparametic estimation of location and dispersion on Riemannian manifolds. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 108(1-2), 23–35.
Bhattacharya, P., Chatterjee, D., & Jacks, G. (1997). Occurrence of arsenic-contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from Delta Plains, Eastern India: options for safe drinking water supply. International Journal of Water Resources Development, 13, 79–92.
Bickel, P. J., Chen, A., & Levina, E. (2011). The method of moments and degree distributions for network models. The Annals of Statistics, 39(5), 2280–2301.
Buschmann, J., Berg, M., Stengel, C., & Sampson, M. L. (2007). Arsenic and manganese contamination of drinking water resources in Cambodia: coincidence of risk areas with low relief topography. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 2146–2152.
Centeno, J. A., Mullick, F. G., Martinez, L., Page, N. P., Gibb, H., Longfellow, D., ... & Ladich, E. R. (2002). Pathology related to chronic arsenic exposure. Environmental health perspectives, 110(suppl 5), 883–886.
Chen, Y., Jia, Z., Mercola, D., & Xie, X. (2013, 2013). A gradient boosting algorithm for survival analysis via direct optimization of concordance index. Comput. Math. Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/873595.
Choubin, B., Darabi, H., Rahmati, O., Sajedi-Hosseini, F., & Kløve, B. (2018). River suspended sediment modelling using the CART model: a comparative study of machine learning techniques. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 272–281.
Couto, C., Vicente, H., Machado, J., Abelha, A., & Neves, J. (2012). Water quality modeling using artificial intelligence-based tools. International Journal of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics, 7(3), 300–309.
Egan, J. P. (1975). Signal detection theory and ROC analysis academic press series in cognition and perception. London: Academic.
Elias, M. S., Hamzah, M. S., Rahman, S. A., Salim, N. A. A., Siong, W. B., & Sanuri, E. (2014). Ecological risk assessment of elemental pollution in sediment from Tunku Abdul Rahman National Park. Sabah. AIP Conf. Proc., 1584, 196–206. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4866131.
Erdik, T., & Pektas, A. O. (2017). Rock slope damage level prediction by using multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS). Neural Computing and Applications, 31, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3186-2.
Ezemonye, L. I., Adebayo, P. O., Enuneku, A. A., Tongo, I., & Ogbomida, E. (2019). Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicology Reports, 6, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.11.010.
Febrero-Bande, M., & Oviedo de la Fuente, M. (2012). Statistical computing in functional data analysis: the R package fda.usc. Journal of Statistical Software, 51, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v051.i04.
Friedman, J. H. (1991). Multivariate adaptive regression splines. The Annals of Statistics, 19, 1–67.
Friedman, J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 1189–1232.
Ghanbarpour, M. R., Zolfaghari, S., Geiss, C., & Darvari, Z. (2013). Investigation of river flow alterations using environmental flow assessment and hydrologic indices: Tajan River watershed, Iran. Int. J. River Basin Manag., 11, 311–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2013.823978.
Gutiérrez, Á. G., Schnabel, S., & Lavado Contador, J. F. (2009). Using and comparing two nonparametric methods (CART and MARS) to model the potential distribution of gullies. Ecological Modelling, 220, 3630–3637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.06.020.
Haghiabi, A. H. (2016). Prediction of longitudinal dispersion coefficient using multivariate adaptive regression splines. Journal of Earth System Science, 125, 985–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0708-8.
Harper, T. R., & Kingham, N. W. (1992). Removal of arsenic from wastewater using chemical precipitation methods. Water Environment Research, 64, 200–203.
Hassan, E., Zainuddin, Z., & Nordin, S. (2017). A review of financial distress prediction models: logistic regression and multivariate discriminant analysis. Indian-Pacific Journal of Accounting and Finance, 1, 13–23.
Hutton, M., & Symon, C. (1986). The quantities of cadmium, lead, mercury and arsenic entering the UK environment from human activities. Sci Total Environ, 57, 129–150.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Raknuzzaman, M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Islam, M. K. (2015). Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecological Indicators, 48, 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016.
Jamshidi-Zanjani, A., & Saeedi, M. (2017). Multivariate analysis and geochemical approach for assessment of metal pollution state in sediment cores. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 16289–16304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9248-2.
Jiang, X., Teng, A., Xu, W., & Liu, X. (2014). Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in the Yellow Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 83, 366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.020.
Kalantar, B., Pradhan, B., Naghibi, S. A., Motevalli, A., & Mansor, S. (2018). Assessment of the effects of training data selection on the landslide susceptibility mapping: a comparison between support vector machine (SVM), logistic regression (LR) and artificial neural networks (ANN). Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk, 5705, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2017.1407368.
Khan, Y., & See, C. S. (2016). Predicting and analyzing water quality using machine learning: a comprehensive model. In 2016 IEEE Long Island Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Keesstra, S. D., Bouma, J., Wallinga, J., Tittonell, P., Smith, P., Cerdà, A., & Bardgett, R. D. (2016). The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Soil., 2, 11–128.
Keesstra, S., Mol, G., de Leeuw, J., Okx, J., de Cleen, M., & Visser, S. (2018). Soil-related sustainable development goals: four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land, 7(4), 133.
Khound, N. J., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2017). Multivariate statistical evaluation of heavy metals in the surface water sources of Jia Bharali River basin, north Brahmaputra plain, India. Applied Water Science, 7, 2577–2586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0453-9.
Kumar, G. P., Yadav, S. K., Thawale, P. R., Singh, S. K., & Juwarkar, A. A. (2008). Growth of Jatropha curcas on heavy metal contaminated soil amended with industrial wastes and Azotobacter—a greenhouse study. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2078–2082.
Li, C., Wang, J., Han, L., & Dong, D. (2012). A simulation model validation method based on functional data analysis * 516–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34384-1_61.
Luoto, M., & Hjort, J. (2004). Generalized linear modelling in periglacial studies: terrain parameters and patterned ground. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 338, 327–338. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.482.
Marjanovic, M., Kovačević, M., Bajat, B., & Voženílek, V. (2011). Landslide susceptibility assessment using SVM machine learning algorithm. Engineering Geology, 123, 225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.09.006.
Marmion, M., Hjort, J., Thuiller, W., & Luoto, M. (2009). Computers & geosciences statistical consensus methods for improving predictive geomorphology maps 35, 615–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2008.02.024.
Mehrdadi, N., Ghobadi, M., & Hoveidi, H. (2006). Evaluation of the quality and self purification potential. Iranian J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng., 3, 199–204.
Mihalovič, M. (2016). Performance comparison of multiple discriminant analysis and logit models in bankruptcy prediction. Econ. Sociol., 9, 101–118. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-789X.2016/9-4/6.
Model, T. E., Encoder-decoder, N., & Tessellation, V. (2004). Learning vector quantization (LVQ) what is a vector quantization ? Neural Networks, 1–12.
Moore, J. W., & Ramamoorthy, S. (2012). Heavy metals in natural waters: applied monitoring and impact assessment. Springer Science & Business Media.
Morin, G., & Calas, G. (2006). Arsenic in soils, mine tailings, and former industrial sites. Elements, 2, 97–101.
Motevalli, A., Pourghasemi, H. R., & Zabihi, M. (2018). 2.12. Assessment of GIS-based machine learning algorithms for spatial modeling of landslide susceptibility: case study in Iran A2 - Huang, Bo BT - Comprehensive Geographic Information Systems. In Comprehensive geographic information systems (pp. 258–280). Oxford: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10461-0.
Motevalli, A., Naghibi, S. A., Hashemi, H., Berndtsson, R., Pradhan, B., & Gholami, V. (2019a). Inverse method using boosted regression tree and k-nearest neighbor to quantify effects of point and non-point source nitrate pollution in groundwater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 228, 1248–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.293.
Motevalli, A., Pourghasemi, H. R. Hashemi, H. & Gholami, V. (2019b). “Assessing the Vulnerability of Groundwater to Salinization Using GIS-Based Data-Mining Techniques in a Coastal Aquifer.” In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences, 547–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815226-3.00025-9.
Murugesan, G. S., Sathishkumar, M., & Swaminathan, K. (2006). Arsenic removal from groundwater by pretreated waste tea fungal biomass. Bioresource Technology, 97, 483–487.
Naghibi, S. A., Ahmadi, K., & Daneshi, A. (2017). Application of support vector machine, random forest, and genetic algorithm optimized random forest models in groundwater potential mapping. Water Resources Management, 31, 2761–2775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1660-3.
Naghibi, S. A., Pourghasemi, H. R., Pourtaghi, Z. S., & Rezaei, A. (2015). Groundwater qanat potential mapping using frequency ratio and Shannon’s entropy models in the Moghan watershed, Iran. Earth Science Informatics, 8, 171–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-014-0145-7.
Nandi, A., & Shakoor, A. (2010). A GIS-based landslide susceptibility evaluation using bivariate and multivariate statistical analyses. Engineering Geology, 110, 11–20.
Natekin, A., & Knoll, A. (2013). Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2013.00021.
Nico, P. S., Fendorf, S. E., Lowney, Y. W., Holm, S. E., & Ruby, M. V. (2004). Chemical structure of arsenic and chromium in CCA-treated wood: implications of environmental weathering. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 5253–5260.
Nordstrom, D.K., Archer, D.G., 2003. Arsenic thermodynamic data and environmental geochemistry, in: Arsenic in ground water. Springer, pp. 1–25.
Nriagu, J. O., Bhattacharya, P., Mukherjee, A. B., Bundschuh, J., Zevenhoven, R., & Loeppert, R. H. (2007). Arsenic in soil and groundwater: an overview. Trace Met. Other Contam. Environ., 9, 3–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-1121(06)09001-8.
Ozdemir, A., & Altural, T. (2013). A comparative study of frequency ratio, weights of evidence and logistic regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping: Sultan Mountains, SW Turkey. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 64, 180–197.
Park, S., Hamm, S. Y., Jeon, H. T., & Kim, J. (2017). Evaluation of logistic regression and multivariate adaptive regression spline models for groundwater potential mapping using R and GIS. Sustain., 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071157.
Pejman, A., Nabi Bidhendi, G., Ardestani, M., Saeedi, M., & Baghvand, A. (2015). A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: a case study. Ecological Indicators, 58, 365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.06.012.
Peprah, M. S., Mensah, I. O., & Akresi, J. A. (2017). Performance evaluation of multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) and multiple linear regression (MLR) for forward conversion of geodetic, λ, h to Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, Z) coordinates ϕ 5, 109–118. https://doi.org/10.12691/jgg-5-3-2.
Pourghasemi, H. R., Moradi, H. R., Fatemi Aghda, S. M., Gokceoglu, C., & Pradhan, B. (2014). GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping with probabilistic likelihood ratio and spatial multi-criteria evaluation models (north of Tehran, Iran). Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7, 1857–1878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0825-x.
Pourghasemi, H. R., Gayen, A., Panahi, M., Rezaie, F., & Blaschke, T. (2019). Multi-hazard probability assessment and mapping with emphasis on landslides, floods, and earthquakes in Iran. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.203.
Quirós, E., Felicísimo, Á. M., & Cuartero, A. (2009). Testing multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) as a method of land cover classification of TERRA-ASTER satellite images. Sensors, 9, 9011–9028. https://doi.org/10.3390/s91109011.
Rajaei, F., Sari, A. E., Salmanmahiny, A., Delavar, M., Bavani, A. R. M., & Srinivasan, R. (2017). Surface drainage nitrate loading estimate from agriculture fields and its relationship with landscape metrics in Tajan watershed. Paddy Water Environ, 15, 541–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-016-0570-y.
Rahmati, O., Pourghasemi, H. R., & Melesse, A. M. (2016). Application of GIS-based data driven random forest and maximum entropy models for groundwater potential mapping: a case study at Mehran Region, Iran. Catena, 137, 360–372.
Rezaei, A., Hassani, H., Hayati, M., Jabbari, N., & Barzegar, R. (2018). Risk assessment and ranking of heavy metals concentration in Iran’s Rayen groundwater basin using linear assignment method. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 32, 1317–1336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1477-x.
Richardson, C. W., Price, J. D., & Burnett, E. (1978). Arsenic concentrations in surface runoff from small watersheds in Texas 1. Journal of Environmental Quality, 7, 189–192.
Roy, S.S., Pratyush, C., Barna, C., 2018. Soft computing applications 634. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-62524-9.
Ruokolainen, M., Pantsar-Kallio, M., Haapa, A., & Kairesalo, T. (2000). Leaching, runoff and speciation of arsenic in a laboratory mesocosm. Sci Total Environ, 258, 139–147.
Sadeghi, F., Nasseri, S., Mosaferi, M., Nabizadeh, R., Yunesian, M., & Mesdaghinia, A. (2017). Statistical analysis of arsenic contamination in drinking water in a city of Iran and its modeling using GIS. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5912-8.
Samui, P., Kim, D., & Viswanathan, R. (2015). Spatial variability of rock depth using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS). Environment and Earth Science, 73, 4265–4272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3711-x.
Sanders, J. G., & Cibik, S. J. (1985). Adaptive behavior of euryhaline phytoplankton communities to arsenic stress. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldend., 22, 199–205.
Singh, R., Singh, S., Parihar, P., Singh, V. P., & Prasad, S. M. (2015). Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: a review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 247–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.009.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Smith, A. H., Marshall, G., Yuan, Y., Ferreccio, C., Liaw, J., von Ehrenstein, O., Steinmaus, C., Bates, M. N., & Selvin, S. (2006). Increased mortality from lung cancer and bronchiectasis in young adults after exposure to arsenic in utero and in early childhood. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 1293.
Sohel, N., Persson, L. Å., Rahman, M., Streatfield, P. K., Yunus, M., Ekström, E.-C., & Vahter, M. (2009). Arsenic in drinking water and adult mortality: a population-based cohort study in rural Bangladesh. Epidemiology, 824–830.
Stout, W. L., Sharpley, A. N., & Landa, J. (2000). Effectiveness of coal combustion by-products in controlling phosphorus export from soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 1239–1244.
Tangahu, B. V., Abdullah, S., Rozaimah, S., Basri, H., Idris, M., Anuar, N., & Mukhlisin, M. (2011). A review on heavy metals (As, Pb, and Hg) uptake by plants through phytoremediation. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011.
Tehrany, M. S., Pradhan, B., & Jebur, M. N. (2015). Flood susceptibility analysis and its verification using a novel ensemble support vector machine and frequency ratio method. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 29, 1149–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1021-9.
Tehrany, M. S., Pradhan, B., & Jebur, M. N. (2014). Flood susceptibility mapping using a novel ensemble weights-of-evidence and support vector machine models in {GIS}. Journal of Hydrology, 512, 332–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.008.
Tenebe, I. T., Emenike, C. P., & Daniel Chukwuka, C. (2019). Prevalence of heavy metals and computation of its associated risk in surface water consumed in Ado-Odo Ota, South-West Nigeria. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. An Int. J., 25, 882–904. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1454824.
Tien Bui, D., Pradhan, B., Lofman, O., & Revhaug, I. (2012a). Landslide susceptibility assessment in Vietnam using support vector machines, decision tree, and nave bayes models. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/974638.
Tien Bui, D., Pradhan, B., Lofman, O., Revhaug, I., & Dick, O. B. (2012b). Landslide susceptibility mapping at Hoa Binh province (Vietnam) using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and GIS. Computational Geosciences, 45, 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.10.031.
Touzani, S., Granderson, J., & Fernandes, S. (2018). Gradient boosting machine for modeling the energy consumption of commercial buildings. Energy and Buildings, 158, 1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.11.039.
Vaclavikova, M., Gallios, G. P., Hredzak, S., & Jakabsky, S. (2008). Removal of arsenic from water streams: an overview of available techniques. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 10, 89–95.
Van der Bruggen, B., & Vandecasteele, C. (2003). Removal of pollutants from surface water and groundwater by nanofiltration: overview of possible applications in the drinking water industry. Environmental Pollution, 122, 435–445.
Van Geen, A., Bostick, B. C., Trang, P. T. K., Lan, V. M., Mai, N.-N., Manh, P. D., Viet, P. H., Radloff, K., Aziz, Z., & Mey, J. L. (2013). Retardation of arsenic transport through a Pleistocene aquifer. Nature, 501, 204.
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051.
Wang, Y., Deng, Y., 2009. Environmental geochemistry of high-arsenic aquifer systems. Heavy Met. Environ.
Yang, C. C., Prasher, S. O., Lacroix, R., & Kim, S. H. (2003). A multivariate adaptive regression splines model for simulation of pesticide transport in soils. Biosystems Engineering, 86, 9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1537-5110(03)00099-0.
Yesilnacar, E. K. (2005). The application of computational intelligence to landslide susceptibility mapping in Turkey (p. 200). University of Melbourne, Department.
Zabihollah, Y., Ahmad, T., Kamran, N., Younes, Y., & Aliakbar, Y. (2013). Assessment of the surface water quality in Tajan river basin, Iran. Life Science Journal, 10(3), 775-780.
Zhang, C., Shan, B., Tang, W., Dong, L., Zhang, W., & Pei, Y. (2017). Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 139, 263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.047.
Zhang, H., Jiang, Y., Yang, T., Wang, M., Shi, G., & Ding, M. (2016). Heavy metal concentrations and risk assessment of sediments and surface water of the Gan River, China. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 25, 1529–1540. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/62100.
Zhu, H. N., Yuan, X. Z., Zeng, G. M., Jiang, M., Liang, J., Zhang, C., Yin, J., Huang, H. J., Liu, Z. F., & Jiang, H. W. (2012). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed.), 22, 1470–1477. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61343-5.
Funding
The study was supported by the College of Agriculture, Shiraz University (Grant No. 96GRD1M271143).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirchooli, F., Motevalli, A., Pourghasemi, H.R. et al. How do data-mining models consider arsenic contamination in sediments and variables importance?. Environ Monit Assess 191, 777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7979-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7979-x