Abstract
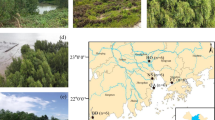
Mangrove forests are widely located along coastlines. They have been identified to be inimitable and dynamic ecosystems. This study investigated the trace metals in mangrove water and surface sediments of Nansha, Guangzhou, China. Zn (148.42 ± 247.47 μg L−1) was the most abundant metal in waters, followed by As (82.34 ± 118.95 μg L−1), Pb (22.96 ± 120.50 μg L−1), and Ni (19.42 ± 47.84 μg L−1). In sediments, the most abundant metal was Fe (27.04 ± 1.91 g kg−1), followed by Mn (1049.04 ± 364.11 mg kg−1), Zn (566.33 ± 244.37 mg kg−1), and Cr (106.9 ± 28.51 mg kg−1). Higher contents of trace metals were detected in vicinity areas of the river mouth. The results of pollution indexes, including contamination factor, enrichment factor, and geo-accumulation index, indicated the pollution of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in sediments. The Spearman correlation and cluster analysis were used to evaluate the metal sources. In water, the significant correlations among Zn and water chemical parameters (Na, Mg, K, Ca, conductivity, pH, and Cl) might indicate the natural source of Zn from the seawater. Water sampling sites in estuaries and coastal areas were clustered separately, which might indicate the influences of upstream water and the seawater, respectively. In sediments, the significant relationships among Cd, Pb, and Zn concentrations were likely to imply the emissions from industries and exploitation of the Pb-Zn mine. The occurrence of Cr and Cu in sediments can be attributed to the spills of lubricants or oil. Cd in sediments could cause serious ecological risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, L. E., Melville, F., & Jolley, D. (2008). An assessment of an oil spill in Gladstone, Australia - impacts on intertidal areas at one month post-spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57(6–12), 607–615.
Andrade, L., Marcet, P., Feal, L. F., Feal, C. F., Covelo, E. F., & Vega, F. A. (2004). Impact of the prestige oil spill on marsh soils: Relationship between heavy metal, sulfide and total petroleum hydrocarbon contents at the Villarrube and Lires marshes (Galicia, Spain). Ciencias Marinas, 30(3), 477–487.
Botté, S. E., Hugo, R. F., & Marcovecchio, J. E. (2007). Dissolved heavy metal (cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations in surface water and porewater from Bahía Blanca estuary tidal flats. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 79(4), 415–421.
Cao, H. Y., Liang, T., Wang, L. J., Ding, S. M., Ding, L. Q., & Yan, X. (2006). Contents and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in water and sediment of intertidalite. Environmental Science, 27(1), 126–131.
Castro, I., Teixeira, J. A., Salengke, S., Sastry, S. K., & Vicente, A. A. (2004). Ohmic heating of strawberry products: Electrical conductivity measurements and ascorbic acid degradation kinetics. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 5(1), 27–36.
Chen, W. W., Zhang, J. X., Abass, O. K., Wen, X. Y., Huang, H. F., Qu, C. K., & Qi, S. H. (2016). Distribution characteristics, concentrations, and sources of cd and Pb in Laoxiawan Channel sediments from Zhuzhou, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 96(6), 797–803.
China, M. O. E. P. (2005) China environmental state bulletin.
Cline, J. T., & Upchurch, S. B. (1973) Mode of heavy metal migration in the upper strata of lake sediment.
Costa-Böddeker, S., Hoelzmann, P., Thuyên, L. X., Huy, H. D., Nguyen, H. A., Richter, O., & Schwalb, A. (2017). Ecological risk assessment of a coastal zone in southern Vietnam: Spatial distribution and content of heavy metals in water and surface sediments of the Thi Vai estuary and can Gio mangrove Forest. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(2), 1141–1151.
Ennouri, R., Chouba, L., Magni, P., & Kraiem, M. M. (2010). Spatial distribution of trace metals (cd, Pb, hg, cu, Zn, Fe and Mn) and oligo-elements (mg, ca, Na and K) in surface sediments of the Gulf of Tunis (northern Tunisia). Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 163(1–4), 229–239.
Fu, J., Zhao, C., Luo, Y., Liu, C., Kyzas, G. Z., Luo, Y., Zhao, D., An, S., & Zhu, H. (2014). Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 270(3), 102–109.
Gasparson, M., & Burgess, J. S. (2000). Human impacts in Antarctica: Trace-element geochemistry of freshwater lakes in the Larsemann Hills, East Antarctica. Environmental Geology, 39(9), 963–976.
Gil, P. L., Paulo, T., Stefano, C., Luis, N., & José, P. (2011). Monitoring anthropogenic sewage pollution on mangrove creeks in southern Mozambique: A test of Palaemon concinnus Dana, 1852 (Palaemonidae) as a biological indicator. Environmental Pollution, 159(2), 636–645.
Giri, S., Mukhopadhyay, A., Hazra, S., Mukherjee, S., Roy, D., Ghosh, S., Ghosh, T., & Mitra, D. (2014). A study on abundance and distribution of mangrove species in Indian Sundarban using remote sensing technique. Journal of Coastal Conservation, 18(4), 359–367.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Hassan, S. M., Garrison, A. W., Allen, H. E., Toro, D. M. D., & Ankley, G. T. (2010). Estimation of partition coefficients for five trace metals in sandy sediments and application to sediment quality criteria. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 15(12), 2198–2208.
Hu, X., Nai, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, C., Wei, T., Jiang, W., et al. (2011). Seasonal characteristics of cadmium content and distribution in Pearl River estuary. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(3), 629–635.
Huang, W. W., Martin, J. M., Seyler, P., Zhang, J., & Zhong, X. M. (1988). Distribution and behaviour of arsenic in the Huang he (yellow river) estuary and Bohai Sea. Marine Chemistry, 25(1), 75–91.
Huang, L., Bai, J., Xiao, R., Gao, H., & Liu, P. (2012). Spatial distribution of Fe, cu, Mn in the surface water system and their effects on wetland vegetation in the Pearl River estuary of China. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 40(10), 1085–1092.
Jin, W. (2018). Coastal land use/land cover change and the ecological environmental effects in Pearl River estuary. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Lau, S. S. S., & Chu, L. M. (2000). The significance of sediment contamination in a coastal wetland, Hong Kong, China. Water Research, 34(2), 379–386.
Li, J., Ming, H., Wei, H., & Gu, Y. (2009). Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2–3), 976–981.
Li, L., Mo, L., & Lu, Y. (2014). Heavy metal content studies in sediments of Qinzhou port mangrove wetlands. Western China Communication Science & Technology, 5, 76–80.
Li, R., Li, R., Chai, M., Shen, X., Xu, H., & Qiu, G. (2015). Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Futian mangrove forest sediment in Shenzhen Bay, South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(1), 448–456.
Liang, P., Wu, S. C., Zhang, J., Cao, Y., Yu, S., & Wong, M. H. (2016). The effects of mariculture on heavy metal distribution in sediments and cultured fish around the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Chemosphere, 148, 171–177.
Liu, X., & Qin, G. (2016). Study on status and countermeasures on ecological environment compensation of mineral resources regions in Guangdong Province. Coal Economic Research, 36(3), 21–26.
Liu, J., Wu, H., Feng, J., Li, Z., & Lin, G. (2014). Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk assessments in the sediments and zoobenthos of selected mangrove ecosystems, South China. Catena, 119(1), 136–142.
Liu, J., Ma, K., & Qu, L. (2017). Relative influence of sediment variables on mangrove community assembly in Leizhou peninsula, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 117(1–2), 429–435.
Ma, Y., Li, T., Gao, Q., Jiang, J., Shi, H., & Wang, A. (2014). Background values and contamination of heavy metals in sediments from the Pearl River estuary. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 34(3), 712–719.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, 2(108), 108–118.
Protano, C., Zinnà, L., Giampaoli, S., Romano, S. V., Chiavarini, S., & Vitali, M. (2014). Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks in rivers: A case study from southern Italy. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 92(1), 75–80.
Saha, M., Sarkar, S. K., & Bhattacharya, B. (2006). Interspecific variation in heavy metal body concentrations in biota of Sunderban mangrove wetland, Northeast India. Environment International, 32(2), 203–207.
Sharma, M., Balakrishna, K., Hofmann, A. W., & Shankar, R. (2007). The transport of osmium and strontium isotopes through a tropical estuary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(20), 4856–4867.
Sinex, S. A., & Wright, D. A. (1988). Distribution of trace metals in the sediments and biota of Chesapeake Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 19(9), 425–431.
Song, M. (2014) Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in water and sediments of the Pearl River estuary., Jinan University.
Sundaramanickam, A., Shanmugam, N., Cholan, S., Kumaresan, S., Madeswaran, P., & Balasubramanian, T. (2016). Spatial variability of heavy metals in estuarine, mangrove and coastal ecosystems along Parangipettai, southeast coast of India. Environmental Pollution, 218, 186–195.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Yao, M. W. Y. (1998). Normalisation and heavy metal contamination in mangrove sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 216(1–2), 33–39.
Tao, F., Xiangdong, L., & Gan, Z. (2005). Acid volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals in the sediment cores of the Pearl River estuary, South China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 61(3), 420–431.
Thuong, N. T., Yoneda, M., Shimada, Y., & Matsui, Y. (2015). Assessment of trace metal contamination and exchange between water and sediment systems in the to Lich River in inner Hanoi, Vietnam. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(7), 3925–3936.
Wu, Q., Tam, N. F., Leung, J. Y., Zhou, X., Fu, J., Yao, B., et al. (2014). Ecological risk and pollution history of heavy metals in Nansha mangrove, South China. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 104(1), 143–151.
Wu, Q., Leung, J. Y. S., Yuan, X., Huang, X., Li, H., Huang, Z., & Li, Y. (2015). Biological risk, source and pollution history of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in the sediment in Nansha mangrove, South China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 96(1–2), 57–64.
Xu, S., Lin, C., Qiu, P., Song, Y., Yang, W., Xu, G., Feng, X., Yang, Q., Yang, X., & Niu, A. (2015). Tungsten- and cobalt-dominated heavy metal contamination of mangrove sediments in Shenzhen, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 100(1), 562–566.
Xu, S., Xu, G., & Liao, B. (2016). Evaluationand analysis on heavy Metals' pollution in mangrove Wetland's seawater of the Pearl River estuary. Journal of South China Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 48(5), 44–51.
Yan, P. L. I., Pan, X. H., & Liu, X. Q. (2010). Determination of K,Na,Ca,Mg,Li,Sr and Mn in Seawater by ICP-AES. China Water & Wastewater, 26(4), 86–88.
Yang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2012). The research Progress on heavy metal pollution in the Pearl River estuary. Ocean and Fishery, (7), 55–57.
Zhang, Y. (2013). Heavy metals’ process in water and pollution risk assessment in surface sediments of the Yellow River estuary, Yangtze estuary and Pearl River Estuary. Third Institute Of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration.
Zhang, Z. W., Xu, X. R., Sun, Y. X., Yu, S., Chen, Y. S., & Peng, J. X. (2014). Heavy metal and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems of China: A review. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 21(20), 11938–11950.
Zhang, Y., Chu, C., Li, T., Xu, S., Liu, L., & Ju, M. (2017). A water quality management strategy for regionally protected water through health risk assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metal pollution in 3 marine reserves. Science of the Total Environment, 599, 721.
Zhao, L., Xu, Y., Hou, H., Shangguan, Y., & Li, F. (2014). Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 468-469, 654–662.
Zhuang, Y., & Shi, X. (2003). Standard free energy of transferring heavy metals from aquatic phase to sedimentary phase. Shanghai Environmental Science, (11), 776–778.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the valuable field work and laboratory assistance of Xiaoyu Jiang, Tingyu Lan, Hongyan Xiang, and Guangdong Hydrogeology Battalion. We genuinely thank Tianpeng Hu and Damao Xu for the data analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41473095) and the Research Fund of The Guangxi Key Laboratory of Theory and Technology for Environmental Pollution Control (Grant No. Guikeneng 1701K008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 70 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Huang, H., Ding, Y. et al. Trace metals in aquatic environments of a mangrove ecosystem in Nansha, Guangzhou, South China: pollution status, sources, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 191, 629 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7732-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7732-5