Abstract
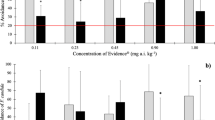
The risk element accumulation ability of two groups of epigeic species, insects from families Coleoptera and Hymenoptera (namely Formicidae), was determined and related to soil risk element content and bioaccessibility. The study was conducted in the district of Příbram, Czech Republic, which was characterised by extremely high aged pollution in the soils, including risk elements, especially As, Pb, Zn and Cd, due to the former mining and smelting activity. Four sampling sites differing in their pseudo-total risk element contents were selected and composite samples of individuals representing either Coleoptera or Formicidae were sampled at the individual sampling points. The results indicate the ability of Coleoptera and Formicidae organisms to accumulate risk elements, especially at the location with extremely high soil risk element content. In soil containing up to 841 mg As kg−1, 84.6 mg Cd kg−1, 4250 mg Pb kg−1 and 8542 mg Zn kg−1, contents in insect bodies reached 239 mg As kg−1 As, 24.2 mg Cd kg−1, 70.4 mg Pb kg−1 and 335 mg Zn kg−1 in beetles and up to 20.9 mg As kg−1, 29.9 mg Cd kg−1, 111 mg Pb kg−1 and 657 mg Zn kg−1 in ants. Therefore, bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) varied between 0.02 and 0.55. Increasing Cd content in Coleoptera bodies with increasing soil pseudo-total element content was observed only among the investigated elements. However, the results indicate increasing BAF values with decreasing soil element levels, especially for Cd, Pb and Zn, indicating limited uptake of elements by the organisms living in contact with extremely contaminated soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous. (2016). Public notice no. 153/2016 about the conditions for the protection of the agricultural soil quality. Legal code of The Czech Republic, 2692–2699.
Babin-Fenske, J., & Anand, M. (2011). Patterns of insect communities along a stress gradient following decommissioning of a cu-Ni smelter. Environmental Pollution, 159, 3036–3043.
Bednarska, A. J., & Stachowicz, I. (2013). Costs of living in metal polluted areas: Respiration rate of the ground beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus from two gradients of metal pollution. Ecotoxicology, 22, 118–124.
Bednarska, A. J., Swiatek, Z. M., Paciorek, K., & Kubinska, N. (2017). Effect of cadmium bioavailability in food on its compartmentalisation in carabids. Ecotoxicology, 26, 1259–1270.
Beeby, A., & Richmond, L. (2010). Magnesium and the regulation of lead in three populations of the garden snail Cantareus aspersus. Environmental Pollution, 158, 2288–2293.
Belskaya, E., Gilev, A., & Belskii, E. (2017). Ant (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) diversity along a pollution gradient near the middle Ural copper smelter, Russia. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 10768–10777.
Berger, B., & Dallinger, R. (1993). Terrestrial snails as quantitative indicators of environmental metal pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 25, 65–84.
Bernard, F., Brulle, F., Douay, F., Lemiere, S., Demuynck, S., & Vandenbulcke, F. (2010). Metallic trace element body burdens and gene expression analysis of biomarker candidates in Eisenia fetida, using an "exposure/depuration" experimental scheme with field soils. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 1034–1045.
Boyle, S., & Kakouli-Duarte, T. (2018). The behaviour of the nematode, Steinernema feltiae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) in sand contaminated with the industrial pollutant chromium VI. Ecotoxicology, 27, 590–604.
Butovsky, R. O. (2011). Heavy metals in carabids (Coleoptera, Carabidae). ZooKeys, 100, 215.
Button, M., Moriarty, M. M., Watts, M. J., Zhang, J., Koch, I., & Reimer, K. J. (2011). Arsenic speciation in field-collected and laboratory-exposed earthworms Lumbricus terrestris. Chemosphere, 85, 1277–1283.
Cao, C., Zhang, Q., Ma, Z. B., Wang, X. M., Chen, H., & Wang, J. J. (2018). Fractionation and mobility risks of heavy metals and metalloids in wastewater-irrigated agricultural soils from greenhouses and fields in Gansu, China. Geoderma, 328, 1–9.
Chen, Y. Y., Dong, B. B., & Xin, J. (2017). Occurrence and fractionation of Cr along the Loushan River affected by a chromium slag heap in East China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 15655–15666.
Creamer, R. E., Rimmer, D. L., & Black, H. I. J. (2008). Do elevated soil concentrations of metals affect the diversity and activity of soil invertebrates in the long-term? Soil Use and Management, 24, 37–46.
Dallinger, R. (1994). Invertebrate organisms as biological indicators of heavy-metal pollution. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 48, 27–31.
Dallinger, R., Berger, B., & Birkel, S. (1992). Terrestrial isopods - useful biological indicators of urban metal pollution. Oecologia, 89, 32–41.
Dvořák, T., Száková, J., Kroulíková, S., Košnář, Z., Holečková, Z., Najmanová, J., & Tlustoš, P. (2017). Content of inorganic and organic pollutants and their mobility in bottom sediment from the Orlík water reservoir (Vltava river, Czech Republic). Soil & Sediment Contamination, 26, 584–604.
Eeva, T., Sorvari, J., & Koivunen, V. (2004). Effects of heavy metal pollution on red wood ant (Formica s. str.) populations. Environmental Pollution, 132, 533–539.
Ernst, G., Zimmermann, S., Christie, P., & Frey, B. (2008). Mercury, cadmium and lead concentrations in different ecophysiological groups of earthworms in forest soils. Environmental Pollution, 156, 1304–1313.
Ettler, V., Rohovec, J., Navratil, T., & Mihaljevic, M. (2007). Mercury distribution in soil profiles polluted by lead smelting. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 78, 13–17.
Filipek-Mazur, B., Mazur, K., & Gondek, K. (2001). The effect of organic fertilisers on distribution of heavy metals among fractions in soil. Rostlinná Výroba, 47, 123–128.
Fröhlichová, A., Száková, J., Najmanová, J., & Tlustoš, P. (2018). An assessment of the risk of element contamination of urban and industrial areas using Taraxacum sect. Ruderalia as a bioindicator. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 150.
Fuksova, Z., Szakova, J., & Tlustos, P. (2009). Effects of co-cropping on bioaccumulation of trace elements in Thlaspi caerulescens and Salix dasyclados. Plant, Soil and Environment, 55, 461–467.
Ghannem, S., Khazri, A., Sellami, B., & Boumaiza, M. (2016). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and Chlaenius (Chlaeniellus) olivieri (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the vicinity of a textile factory near Ras Jbel (Bizerte, Tunisia). Environmental Earth Science, 75.
Ghannem, S., Touaylia, S., & Boumaiza, M. (2018a). Beetles (Insecta: Coleoptera) as bioindicators of the assessment of environmental pollution. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 24, 456–464.
Ghannem, S., Touaylia, S., & Mustapha, B. (2018b). Assessment of trace metals contamination in soil, leaf litter and leaf beetles (Coleoptera, Chrysomelidae) in the vicinity of a metallurgical factory near Menzel Bourguiba, (Tunisia). Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 24, 991–1002.
Gongalsky, K. B., Filimonova, Z. V., Pokarzhevskii, A. D., & Butovsky, R. O. (2007). Differences in responses of herpetobionts and geobionts to impact from the Kosogorsky metallurgical plant (Tula region, Russia). Russian Journal of Ecology, 38, 52–57.
Gramigni, E., Calusi, S., Gelli, N., Giuntini, L., Massi, M., Delfino, G., Chelazzi, G., Baracchi, D., Frizzi, F., & Santini, G. (2013). Ants as bioaccumulators of metals from soils: Body content and tissue-specific distribution of metals in the ant Crematogaster scutellaris. European Journal of Soil Biology, 58, 24–31.
Green, I. D., & Walmsley, K. (2013). Time-response relationships for the accumulation of cu, Ni and Zn by seven-spotted ladybirds (Coccinella septempunctata L.) under conditions of single and combined metal exposure. Chemosphere, 93, 184–189.
Grzes, I. M. (2010). Ants and heavy metal pollution - a review. European Journal of Soil Biology, 46, 350–355.
Grzes, I. M. (2012). Zinc kinetics in the ant Myrmica rubra originating from a metal pollution gradient. Chemosphere, 88, 1015–1018.
Grzes, I. M., & Okrutniak, M. (2016). Pre-adaptive cadmium tolerance in the black garden ant. Chemosphere, 148, 316–321.
Heikens, A., Peijnenburg, W. J., & Hendriks, A. J. (2001). Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Environmental Pollution, 113, 385–393.
Hlava, J., Krupauerová, A., & Barták, M. (2013). Arthropod diversity in agrosystems under different management. Scientia Agriculturae Bohemica, 44, 85–89.
Hlava, J., Szakova, J., Vadlejch, J., Cadkova, Z., Balik, J., & Tlustos, P. (2017). Long-term application of organic matter based fertilisers: Advantages or risks for soil biota? A review. Environmental Reviews, 25, 408–414.
Hůrka, K., (2005). Beetles of Czech and Slovak Republic. Kabourek. 390 pp. (in Czech & English).
Jiang, M. B., Wang, X. H., Liusui, Y. H., Sun, X. Q., Zhao, C. Y., & Liu, H. (2015). Diversity and abundance of soil animals as influenced by long-term fertilization in Grey Desert soil, China. Sustainability-Basel, 7, 10837–10853.
Judd, T. M., & Fasnacht, M. P. (2007). Distribution of micronutrients in social insects: A test in the termite Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera : Rhinotermitidae) and the ant Myrmica punctiventris (Hymenoptera : Formicidae). Annals of Entomological Society of America, 100, 893–899.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2010). Trace elements in soils and plants (Vol. 548). CRC press.
Kasemodel, M. C., Lima, J. Z., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B., Trofino, J. C., & Rodrigues, V. G. (2016). Soil contamination assessment for Pb, Zn and cd in a slag disposal area using the integration of geochemical and microbiological data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 698.
Kavehei, A., Hose, G. C., & Gore, D. B. (2018). Effects of red earthworms (Eisenia fetida) on leachability of lead minerals in soil. Environmental Pollution, 237, 851–857.
Kheirallah, D. A., & El-Samad, L. M. (2019). Oogenesis anomalies induced by heavy metal contamination in two tenebrionid beetles (Blaps polycresta and Trachyderma hispida). Folia Biologica, 67, 9–23.
Komulainen, M., & Mikola, J. (1995). Soil processes as influenced by heavy-metals and the composition of soil Fauna. Journal of Applied Ecology, 32, 234–241.
Lagisz, M. (2008). Changes in morphology of the ground beetle Pterostichus oblongopunctatus (Coleoptera; Carabidae) from vicinities of a zinc and lead smelter. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1744–1747.
Lair, G. J., Gerzabek, M. H., & Haberhauer, G. (2007). Retention of copper, cadmium and zinc in soil and its textural fractions influenced by long-term field management. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 1145–1154.
Lindqvist, L., Block, M., & Tjalve, H. (1995). Distribution and excretion of cd, hg, methyl-hg and Zn in the predatory beetle Pterostichus niger (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 14, 1195–1201.
Liu, M., Xu, J., Krogh, P. H., Song, J., Wu, L., Luo, Y., & Ke, X. (2018). Assessment of toxicity of heavy metal-contaminated soils toward Collembola in the paddy fields supported by laboratory tests. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 16969–16978.
Lock, K., Janssens, F., & Janssen, C. R. (2003). Effects of metal contamination on the activity and diversity of springtails in an ancient Pb-Zn mining area at Plombieres, Belgium. European Journal of Soil Biology, 39, 25–29.
Lodenius, M., Josefsson, J., Heliovaara, K., Tulisalo, E., & Nummelin, M. (2009). Cadmium in insects after ash fertilization. Insect Sci., 16, 93–98.
Marrugo-Negrete, J., Pinedo-Hernandez, J., & Diez, S. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinu River basin, Colombia. Environmental Research, 154, 380–388.
Meloun, M., & Militký, J. (2004). Statistical analysis of the experimental data. Academia, Praha. in Czech.
Nahmani, J., & Rossi, J. P. (2003). Soil macroinvertebrates as indicators of pollution by heavy metals. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 326, 295–303.
Nuorteva, P., & Elberg, K. (1999). Levels of cadmium and some other metals in insects. In Proceedings of the XXIV Nordic congress of entomology (pp. 125–137).
Osman, W., & Shonouda, M. (2017). X-ray metal assessment and ovarian ultrastructure alterations of the beetle, Blaps polycresta (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae), inhabiting polluted soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 14867–14876.
Pedrini-Martha, V., Sager, M., Werner, R., & Dallinger, R. (2012). Patterns of urban mercury contamination detected by bioindication with terrestrial isopods. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 63, 209–219.
Pisanello, F., Marziali, L., Rosignoli, F., Poma, G., Roscioli, C., Pozzoni, F., & Guzzella, L. (2016). In situ bioavailability of DDT and hg in sediments of the Toce River (Lake Maggiore basin, northern Italy): Accumulation in benthic invertebrates and passive samplers. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 10542–10555.
Quevauviller, P., Ure, A., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Improvement of analytical measurements within the Bcr-program - single and sequential extraction procedures applied to soil and sediment analysis. International Journal of Environmental Chemistry, 51, 129–134.
Rabitsch, W. B. (1997). Seasonal metal accumulation patterns in the red wood ant Formica pratensis (Hymenoptera) at contaminated and reference sites. Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 1455–1461.
Růžička, J. (2005). Icones insectorum europae centralis. Coleoptera: Agyrtidae, Silphidae. Folia Heyrovskyana Serie B, 3, 1–9.
Salamun, P., Kucanova, E., Brazova, T., Miklisova, D., Renco, M., & Hanzelova, V. (2014). Diversity and food web structure of nematode communities under high soil salinity and alkaline pH. Ecotoxicology, 23, 1367–1376.
Salamun, P., Renco, M., Kucanova, E., Brazova, T., Papajova, I., Miklisova, D., & Hanzelova, V. (2012). Nematodes as bioindicators of soil degradation due to heavy metals. Ecotoxicology, 21, 2319–2330.
Shonouda, M., & Osman, W. (2018). Ultrastructural alterations in sperm formation of the beetle, Blaps polycresta (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) as a biomonitor of heavy metal soil pollution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 7896–7906.
Scheifler, R., Gomot-de Vaufleury, A., Toussaint, M. L., & Badot, P. M. (2002). Transfer and effects of cadmium in an experimental food chain involving the snail Helix aspersa and the predatory carabid beetle Chrysocarabus splendens. Chemosphere, 48, 571–579.
Schipper, A. M., Wijnhoven, S., Leuven, R. S., Ragas, A. M., & Hendriks, A. J. (2008). Spatial distribution and internal metal concentrations of terrestrial arthropods in a moderately contaminated lowland floodplain along the Rhine River. Environmental Pollution, 151, 17–26.
Simon, E., Harangi, S., Baranyai, E., Braun, M., Fabian, I., Mizser, S., Nagy, L., & Tothmeresz, B. (2016). Distribution of toxic elements between biotic and abiotic components of terrestrial ecosystem along an urbanization gradient: Soil, leaf litter and ground beetles. Ecological Indicators, 60, 258–264.
Skalski, T., Kędzior, R., Kolbe, D., & Knutelski, S. (2015). Different responses of epigeic beetles to heavy metal contamination depending on functional traits at the family level. Baltic Journal of Coleopterology, 15, 81–90.
Smetana, A., (1958). Fauna ČSR. Staphylinidae. I. ČSAV, Praha. 435 pp. (in Czech, German and Russian abstract).
Smith, P., Cotrufo, M. F., Rumpel, C., Paustian, K., Kuikman, P. J., Elliott, J. A., McDowell, R., Griffiths, R. I., Asakawa, S., Bustamante, M., House, J. I., Sobocká, J., Harper, R., Pan, G., West, P. C., Gerber, J. S., Clark, J. M., Adhya, T., Scholes, R. J., & Scholes, M. C. (2015). Biogeochemical cycles and biodiversity as key drivers of ecosystem services provided by soils. SOIL Discussions, 2, 537–586.
Sorvari, J., & Eeva, T. (2010). Pollution diminishes intra-specific aggressiveness between wood ant colonies. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 3189–3192.
Soto-Jimenez, M. F., & Olvera-Balderas, D. (2018). Geochemical fractionation and potential ecological risk of cadmium and Lead in soils impacted by secondary Lead refinery. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 101, 372–379.
Stary, P., & Kubiznakova, J. (1987). Content and transfer of heavy-metal air-pollutants in populations of Formica spp. wood ants (Hym, Formicidae). Journal of Applied Entomology, 104, 1–10.
Stone, D., Jepson, P., & Laskowski, R. (2002). Trends in detoxification enzymes and heavy metal accumulation in ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) inhabiting a gradient of pollution. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 132, 105–112.
Talarico, F., Brandmayr, P., Giulianini, P. G., Ietto, F., Naccarato, A., Perrotta, E., Tagarelli, A., & Giglio, A. (2014). Effects of metal pollution on survival and physiological responses in Carabus (Chaetocarabus) lefebvrei (Coleoptera, Carabidae). European Journal of Soil Biology, 61, 80–89.
van der Fels-Klerx, H. J., Camenzuli, L., van der Lee, M. K., & Oonincx, D. G. (2016). Uptake of cadmium, Lead and arsenic by Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens from contaminated substrates. PLoS One, 11, e0166186.
Vanek, A., Boruvka, L., Drabek, O., Mihaljevic, M., & Komarek, M. (2005). Mobility of lead, zinc and cadmium in alluvial soils heavily polluted by smelting industry. Plant, Soil and Environment, 51, 316–321.
Vyslouzilova, M., Tlustos, P., Szakova, J., & Pavlikova, D. (2003). As, cd, Pb and Zn uptake by Salix spp. clones grown in soils enriched by high loads of these elements. Plant, Soil and Environment, 49, 191–196.
Weeks, J. M., Spurgeon, D. J., Svendsen, C., Hankard, P. K., Kammenga, J. E., Dallinger, R., Kohler, H. R., Simonsen, V., & Scott-Fordsmand, J. (2004). Critical analysis of soil invertebrate biomarkers: A field case study in Avonmouth. UK. Ecotoxicology, 13, 817–822.
Yang, K., Zhang, T., Shao, Y., Tian, C., Cattle, S. R., Zhu, Y., & Song, J. (2018). Fractionation, bioaccessibility, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of an urban recreational area amended with composted sewage sludge. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 613.
Zygmunt, P. M., Maryanski, M., & Laskowski, R. (2006). Body mass and caloric value of the ground beetle (Pterostichus oblongopunctatus) (Coleoptera, Carabidae) along a gradient of heavy metal pollution. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25, 2709–2714.
Acknowledgements
Correction and improvement of language were provided by Proof-Reading-Service.com Ltd., Devonshire Business Centre, Works Road, Letchworth Garden City SG6 1GJ, United Kingdom.
Funding
Financial support was from the GAČR 17-00859S project, and and European Regional Development Fund-Project No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 284 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhtorova, D., Hlava, J., Száková, J. et al. Risk element accumulation in Coleoptera and Hymenoptera (Formicidae) living in an extremely contaminated area—a preliminary study. Environ Monit Assess 191, 432 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7584-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7584-z