Abstract
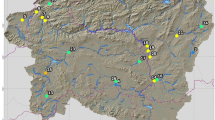
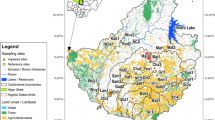
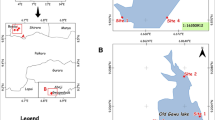
A macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index was developed for River Chanchaga, North Central Nigeria. Macroinvertebrates and physicochemical variables were sampled seasonally between March 2017 and February 2018 from four stations: station 1 (least impacted control station) and three downstream stations 2, 3 and 4. A total of 29 macroinvertebrate metrics in four categories, richness, abundance, composition and diversity, were evaluated for their potential to discriminate between the stations, seasonal stability and redundancy. Of the 29 metrics, only 13 fulfilled all criteria and were then integrated into the final Chanchaga multimeric index (MMIchanchaga). Application of the newly developed multimetric index revealed that water quality at stations 2 and 3 was fair and that of station 4 was poor. Water quality deteriorated slightly during the rainy season compared with the dry season. In terms of the individual component metrics, EPT richness, EPT (%) and Shannon diversity were highly sensitive to water quality impairment. The Bray–Curtis similarity measure revealed that stations 2 and 3 were more similar compared with the similarity between other stations. Overall, the newly developed multimetric index proved useful and represents the first important step in such index development in Nigeria.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association). (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). USA: WEF and AWWA 1213Pp.
Arimoro, F. O., & Ikomi, R. B. (2008). Response of macroinvertebrate communities to abattoir wastes and other anthropogenic activities in a municipal stream in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environmentalist, 28, 85–98.
Arimoro, F. O., & Ikomi, R. B. (2009). Ecological integrity of Upper Warri River, Niger Delta using aquatic insects as bioindicators. Ecological Indicators, 9, 455–461.
Arimoro, F. O., Odume, O. N., Uhunoma, S. I., & Edegbene, A. O. (2015). Anthropogenic impact on water chemistry and benthic macroinvertebrate associated changes in a southern Nigeria stream. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 1–14.
Baptista, D. F., Buss, D. F., Egler, M., Giovanelli, A., Silveira, M. P., & Nessimian, J. L. (2007). A multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for evaluation of Atlantic Forest streams at Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 575, 83–94.
Barber-James, H. M., Gattolliat, J., Sartori, M., & Hubbard, M. D. (2008). Global diversity of mayflies (Ephemeroptera, Insecta) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia, 595, 339–350.
Barbour, M. T., Gerritsen, J., Snyder, B. D., & Stribling, J. B. (1999). Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic macroinvertebrates and fish (2nd ed.. EPA 841–13–99-002). Washington, D.C: Environmental Protection Agency; Office of water.
Bonada, N., Prat, N., Resh, V. H., & Statzner, B. (2006). Development in aquatic insect biomonitoring: a comparative analysis of recent approaches. Annual Review of Entomology, 51, 495–523.
Camargo, J. A., Alonso, A., & De la Puente, M. (2004). Multimetric assessment of nutrient enrichment in impounded rivers based on bethic macroinvertebrates. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96, 233–249.
Clarke, K. R., & Warwick, R. M. (1994). Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. UK: Plymouth marine laboratory.
Cranston, P. S. (2000). Electronic guide to the Chironomidae of Australia. http://www.entomologyucdavis.edu/chiropage. 29/08/2013.
Dallas, H. F., Lowe, S., Kennedy, M. P., Saili, K., & Murphy, K. J. (2018). Zambian invertebrate scoring system (ZISS): a macroinvertebrate-based biotic index for rapid bioassessment of southern tropical African river systems. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 43(4), 325–344.
Edegbene, A. O. (2018). Invasive grass (Typha domingensis): A potential menace on the assemblage and abundance of migratory/water related birds in Hadejia-Nguru wetlands, Yobe State, Nigeria. Tropical Freshwater Biology, 27(2), 13–30.
Edegbene, A. O., & Arimoro, F. O. (2012). Ecological status of Owan River, southern Nigeria using aquatic insects as bioindicators. Journal of Aquatic Sciences, 27, 99–111.
Edegbene, A. O., Arimoro, F. O., Odoh, O., & Ogidiaka, E. (2015). Effect of anthropogenicity on the composition and diversity of aquatic insects of a municipal river in North Central Nigeria. Biosciences Research in Today’s World, 1, 69–80.
Gerber, A., & Gabriel, M. J. M. (2002). Aquatic invertebrates of South African Rivers—field guide. In Resource quality services. Pretoria: Department of Water Affairs.
Golfieri, B., Surian, N., & Hardersen, S. (2018). Towards a more comprehensive assessment of river corridor conditions: a comparison between the morphological quality index and three biotic indices. Ecological Indicators, 84, 525–534.
Gordon, N. D., McMahon, T. A., & Finlayson, B. L. (1994). Stream hydrology, an introduction for ecologists. New York: Wiley 526pp.
Hammer, Ø., Harper, D. A. T., & Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica, 4(1) 9Pp. http://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm. Accessed 1 July 2015.
Hawkins, C. P., Norris, R. H., Hogue, J. N., & Feminella, J. W. (2000). Development and evaluation of predictive models for measuring the biological integrity of streams. Ecological Applications, 10, 1456–1477.
Helson, J. E., & Williams, D. D. (2013). Development of a macroinvertebrate multimetric index for the assessment of low-land streams in the neotropics. Ecological Indicators, 29, 167–178.
Kaaya, L. T., Day, J. A., & Dallas, H. F. (2015). Tanzania River Scoring System (TARISS): a macroinvertebrate-based biotic index for rapid bioassessment of river. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 40(2), 109–117.
Mereta, S. T., Boets, P., De Meester, L., & Goethals, P. L. M. (2013). Development of multimetric index based on benthic macroinvertebrates for the assessment of natural wetlands in southwest Ethiopia. Ecological Indicators, 29, 510–521.
Merritt, R. W., Wallace, J. R., Higgins, M. J., Alexander, M. K., Berg, M. B., Morgan, W. T., Cummins, K. W., & Vandeneeden, B. (1996). Procedures for the functional analysis of invertebrate communities of the Kissimmee river-floodplain ecosystem. Florida Scientist, 59, 216–274.
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005). Ecosystems and human well-being: Wetlands and water synthesis. Washington, DC.
Monaghan, K., & Soares, A. M. V. M. (2012). Bringing new knowledge to an old problem: building a biotic index from lotic macroinvertebrates traits. Ecological Indicators, 20, 213–220.
Odume, O. N. (2014). An evaluation of macroinvertebrate-based biomonitoring and ecotoxicological assessments of deteriorating environmental water quality in the Swartkops River, South Africa. Unpublsihed Ph. D thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of Rhodes University. 373Pp.
Odume, O. N., Muller, W. J., Arimoro, F. O., & Palmer, C. G. (2012). The impact of water quality deterioration on macroinvertebrate communities in the Swartkops River, South Africa: a multimetric approach. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 37, 191–200.
Ogbeibu, A.E. (2005). Biostatistics: a practical approach to research and data handling. Benin City: Mindex publishing, 264Pp.
Rosenberg, D. M., & Resh, V. H. (Eds.). (1993). Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates (Vol. 10119). New York: Chapman and Hall one penn plaza.
Shull, D. R., Smith, Z. M., & Selckmann, G. M. (2019). Development of a benthic macroinvertebrate multimeric index for large semiwadeable rivers in the Mid-Atlantic region of the USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7153-x.
Smith, M. J., Key, W. R., & Edward, D. H. D. (1999). AUSRIVAS: using macroinvertebrates to assess ecological condition of rivers in Western Australian. Freshwater Biology, 41, 269–282.
Suriano, M. T., Gessener, A. A., Roque, F. O., & Froehlich, C. G. (2011). Choice of macroinvertebrate metrics to evaluate stream conditions in Atlantic Forest, Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175, 87–101.
UN-(United Nations) Water. (2011). Water quality http://www.unwater.org/donwloads/waterquality policybrief.pdf. Accessed: 1 July, 2015.
Vlek, H. E., Sporka, F., & Krno, I. (2006). Influence of macroinvertebrate sample size on bio assessment of streams. Hydrobiologia, 566, 523–542.
Zamora-Muniz, C., Sainz-Cantero, C. E., Sanchez-Ortega, A., & Alba-Tercedor, J. (1995). Are biological indices BMPW and APT and their significance regarding water quality seasonally dependent? Factor explaining their variations. Water Research, 29, 285–290.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the doctoral research grant awarded to the first author (grant no. 110894) by the South African National Research Foundation (NRF) and the World Academy of Science (TWAS). We thank Mr. Obinnah Odoh, Mr. Prince Ossai, Helen Adekunle, Meshack Sanda, Hassana and Mrs. Edegbene Ovie Tega for their field, laboratory and technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edegbene, A.O., Elakhame, L.A., Arimoro, F.O. et al. Development of macroinvertebrate multimetric index for ecological evaluation of a river in North Central Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 191, 274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7438-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7438-8