Abstract
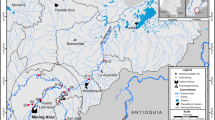
Recognizing the pollution characteristics and potential risks of trace metals in sediments are important to protect water ecosystem safety. In the present study, a systematic investigation was performed to assess the pollution and risk level of trace metals in river sediments located in the greatest gold production base in China. The geo-accumulation index was used to assess the contamination degree. The sediment quality guidelines and potential ecological risk index were employed to complete an ecological risk assessment. A non-carcinogenic health risk assessment was also carried out to evaluate potential adverse health risks. Correlations and principal component analyses were applied to check relationships among trace metals and ascertain potential pollution sources. The results suggested that the sediments in the river were most polluted by As, Cd, and Hg followed by Cu, Pb, and Zn. The assessment of potential human health risk revealed that there was no significant non-carcinogenic risk to the inhabitants. Gold mining and smelting activities and the long-term excessive application of fertilizers and agrochemicals were identified as the main anthropogenic releases. This study contributed an understanding that possible sources, contamination degree, and ecological risk level of trace metals in riverine surface sediments in a gold mining area.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, P., Ghorbani, M. R., Coltorti, M., Kuritani, T., Cai, Y., Fioretti, A. M., Braschi, E., Giacomoni, P. P., Aghabazaz, F., Babazadeh, S., & Conticelli, S. (2019). High-Nb hawaiite-mugearite and high-Mg calc-alkaline lavas from northeastern Iran: Oligo-Miocene melts from modified mantle wedge. International Geology Review, 61, 150–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2017.1416502.
Birch, G. F., & Apostolatos, C. (2013). Use of sedimentary metals to predict metal concentrations in black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) tissue and risk to human health (Sydney estuary, Australia). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 5481–5491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1538-8.
Caeiro, S., Costa, M. H., Ramos, T. B., Fernandes, F., Silveira, N., Coimbra, A., Medeiros, G., & Painho, M. (2005). Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: an index analysis approach. Ecological Indicators, 5, 151–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2005.02.001.
Cai, L., Xu, Z., Bao, P., He, M., Dou, L., Chen, L., Zhou, Y., & Zhu, Y. G. (2015). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source of arsenic and heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunde, Southeast China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148, 189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.09.010.
Cai, Y. B., Mi, Y. T., Yu, J., & Zhang, H. (2016). Arsenic speciation and kinetic release simulation of stream sediment contaminated by gold mining. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16, 1121–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1334-9.
Cai, Y. B., Zhang, H., Yuan, G. D., & Li, F. Y. (2017). Sources, speciation and transformation of arsenic in the gold mining impacted Jiehe River, China. Applied Geochemistry, 84, 254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.07.001.
CEPA. (1995). Environmental quality standard for soils. (GB15618-1995), first edition. Beijing: Chinese Environmental Protection Administration.
Chen, H., Chen, R., Teng, Y., & Wu, J. (2016). Contamination characteristics, ecological risk and source identification of trace metals in sediments of the Le’an River (China). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 125, 85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.042.
Chen, L., Zhou, S., Wu, S., Wang, C., Li, B., Li, Y., & Wang, J. (2018). Combining emission inventory and isotope ratio analyses for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Chemosphere, 204, 140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.002.
Darwish, M. A. G. (2017). Reconnaissance geochemical survey in the Marahiq area, Wadi Allaqi region, south Egypt: a preliminary assessment of stream sediments for gold placer and environmental hazard. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 493–516. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7152-1.
Esdaile, L. J., & Chalker, J. M. (2018). The mercury problem in artisanal and small-scale gold mining. Chemistry-A Europen Journal, 24, 6905–6916. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201704840.
Feng, D., Aldrich, C., & Tan, H. (2000). Treatment of acid mine water by use of heavy metal precipitation and ion exchange. Minerals Engineering, 13, 623–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(00)00045-5.
Fu, J., Zhao, C., Luo, Y., Liu, C., Kyzas, G. Z., Luo, Y., Zhao, D., An, S., & Zhu, H. (2014). Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: Their relations to environmental factors. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 270, 102–109. https://doi.org/10.1010/j.jhazmat.2014.01.044.
Gao, Z. X. (2018). Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and its ecological risk in one river reach of a gold mine in Inner Mongolia, Northern China. International Biodeterioration, 128, 94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.001.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Iqbal, J., Tirmizi, S. A., & Shah, M. H. (2013). Statistical apportionment and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Rawal Lake (Pakistan). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 729–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2588-y.
Jahan, S., & Strezov, V. (2018). Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of seaports of NSW, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 128, 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.036.
Ji, H., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Gao, Y., & Xing, Y. (2017). Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in overlying water, porewater, and sediments of Yongding River in a coal mine brownfield. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18, 624–639.
Kalaivanan, D., & Ganeshamurthy, A. N. (2016). Abiotic stress physiology of horticultural crops. In Mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity in plants (1st ed., pp. 85–102). New Delhi: Springer India.
Khalil, M. K., Draz, S. E. O., El Zokm, G. M., & El-Said, G. F. (2015). Apportionment of geochemistry, texture’s properties, and risk assessment of some elements in surface sediments from Bardawil Lagoon, Egypt. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 22, 775–791. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2015.1107714.
Kim, L., Vasile, G.G., Stanescu, B., Dinu, C., Ene, C. (2016). Distribution of Trace Metals in Surface Water and Streambed Sediments in the Vicinity of an Abandoned Gold Mine from Hunedoara County, Romania. Revista De Chimie, 67, 1441-1446.
Kükrer, S., Şeker, S., Abacı, Z. T., & Kutlu, B. (2014). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of northern littoral zone of Lake Çıldır, Ardahan, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 3847–3857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3662-4.
Kusin, F. M., Azani, N. N. M., Hasan, S. N. M. S., & Sulong, N. A. (2018). Distribution of heavy metals and metalloid in surface sediments of heavily-mined area for bauxite ore in Pengerang, Malaysia and associated risk assessment. Catena, 165, 454–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.02.029.
Lachance, G. R., & Traill, R. J. (1966). Practical solution to the matrix problem in X-ray analysis, I. Method: Canadian. Spectroscopy, 11, 43–48.
Li, H., Gao, X., Gu, Y., Wang, R., Xie, P., Liang, M., Ming, H., & Su, J. (2018). Comprehensive large-scale investigation and assessment of trace metal in the coastal sediments of Bohai Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 129, 126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.022.
Liu, H. Q., Liu, G. J., Wang, S. S., Zhou, C. C., Yuan, Z. J., & Da, C. N. (2018a). Distribution of heavy metals, stable isotope ratios (delta C-13 and delta N-15) and risk assessment of fish from the Yellow River Estuary, China. Chemosphere, 208, 731–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.028.
Liu, Q., Wang, F., Meng, F., Jiang, L., Li, G., & Zhou, R. (2018b). Assessment of metal contamination in estuarine surface sediments from Dongying City, China: Use of a modified ecological risk index. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 126, 293–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.11.017.
Liu, Y. F., et al. (2018c). Comprehensive risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediment of the Yangtze River Anqing section, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7621-1.
Long, E. R., & Macdonald, D. D. (1998a). Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 4, 1019–1039.
Long, E. R., & Macdonald, D. D. (1998b). Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 4, 1019–1039.
Ma, X. L., et al. (2016). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the Yellow River using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere, 144, 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.026.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002440010075.
Marrugo-Negrete, J., Pinedo-Hernández, J., & Díez, S. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environmental Research, 154, 380–388.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.016.
Morton-Bermea, O., Gómez-Bernal, J. M., Armienta, M. A., Lozano, R., Hernández-Álvarez, E., Romero, F., & Castro-Larragoitia, J. (2014). Metal accumulation by plant species growing on a mine contaminated site in Mexico. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 5207–5213.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, 2, 108–118.
Natali, C., & Bianchini, G. (2018). Natural vs anthropogenic components in sediments from the Po River delta coastal lagoons (NE Italy). Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 25, 2981–2991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0986-y.
Nemati, K., Bakar, N. K. A., Abas, M. R., & Sobhanzadeh, E. (2011). Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 192, 402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.039.
Obrist, D., Kirk, J. L., Zhang, L., Sunderland, E. M., Jiskra, M., & Selin, N. E. (2018). A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio, 47, 116–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-017-1004-9.
Pan, K., & Wang, W. X. (2012). Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Science of the Total Environment, 421, 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.013.
Pandey, M., Tripathi, S., Pandey, A. K., & Tripathi, B. D. (2014). Risk assessment of metal species in sediments of the river Ganga. Catena, 122, 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.06.012.
Rai, R., Agrawal, M., & Agrawal, S. B. (2016). Impact of heavy metals on physiological processes of plants: with special reference to photosynthetic system (pp. 127–140). New Delhi: Springer India.
Rovira, J., Mari, M., Schuhmacher, M., Nadal, M., & Domingo, J. L. (2011). Monitoring environmental pollutants in the vicinity of a cement plant: A temporal study. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 60, 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9628-9.
Ruzickova, S., Remeteiova, D., Mickova, V., & Dirner, V. (2018). Sediment matrix characterization as a tool for evaluating the environmental impact of heavy metals in metal mining, smelting, and ore processing areas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6551-4.
Shi, C. (2016). Average background values of 39 chemical elements in stream sediments of China. Earth Science, 14, 234–258 (in chinese).
Sierra, C., Ruiz-Barzola, O., Menendez, M., Demey, J. R., & Vicente-Villardon, J. L. (2017). Geochemical interactions study in surface river sediments at an artisanal mining area by means of canonical (MANOVA)-Biplot. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 175, 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.01.002.
Simpson, S. L., & Batley, G. E. (2007). Predicting metal toxicity in sediments: a critique of current approaches. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 3, 18–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.5630030103.
Strzebońska, M., Jarosz-Krzemińska, E., & Adamiec, E. (2017). Assessing historical mining and smelting effects on heavy metal pollution of river systems over span of two decades. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228, 141–152.
Suresh, G., Ramasamy, V., Meenakshisundaram, V., Venkatachalapathy, R., & Ponnusamy, V. (2011). Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 69, 1466–1474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2011.05.020.
Taiwo, A. M., & Awomeso, J. A. (2017). Assessment of trace metal concentration and health risk of artisanal gold mining activities in Ijeshaland, Osun state Nigeria— Part 1. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 177, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.01.009.
Tessier, A., & Campbell, P. G. C. (1987). Partitioning of trace metals in sediments: relationships with bioavailability. Hydrobiologia, 149(1), 43–52.
Turekian, K. K. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72, 175–182.
USEPA. (1989). Risk assessment guidance for superfund, volume 1, human health evaluation manual (part A). ReportEPA/540/1-89/002. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
USEPA. (2004). Risk assessment guidance for superfund, volume1, human health evaluation manual (part E, supplemental guidance for dermal risk assessment). Report EPA/540/R/99/005. Washington, DC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Vallejo Toro, P. P., Vasquez Bedoya, L. F., Dario Correa, I., et al. (2016). Impact of terrestrial mining and intensive agriculture in pollution of estuarine surface sediments: spatial distribution of trace metals in the Gulf of Uraba, Colombia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 111, 311–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.093.
Varol, M. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195, 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051.
Vianello, G., et al. (2014). Critical evaluation of an intercalibration project focused on the definition of new multi-element soil reference materials (AMS-MO1 AND AMS-ML1) Eqa. International Journal of Environmental Quality, 15, 41–64.
Wang, XL., Sato, T., Xing, BS., Tao, S. (2005). Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Science of The Total Environment, 350, 28-37.
Wang, Y. B., Liu, C. W., & Wang, S. W. (2015). Characterization of heavy-metal-contaminated sediment by using unsupervised multivariate techniques and health risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 113, 469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.036.
Xia, F., Qu, L., Wang, T., Luo, L., Chen, H., Dahlgren, R. A., Zhang, M., Mei, K., & Huang, H. (2018). Distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollutants in sediments of a rapid developing urban river system. Chemosphere, 207, 218–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.090.
Zhang, H., Yu, J., & Zhou, S. (2014). Spatial distribution of As, Cr, Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn in the water and sediment of a river impacted by gold mining. Mine Water and the Environment, 33, 206–216.
Funding
This study was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA23050203) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41373100). Additional support was provided by the CAS Key Technology Talent Program and the Instrument Developing Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. Y728021021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Liu, Q. & Sheng, Y. Distribution and risk assessment of trace metals in riverine surface sediments in gold mining area. Environ Monit Assess 191, 191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7311-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7311-9