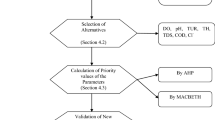
Abstract
Water quality indices are mathematical equations that transform water quality data into a particular number which describe the status of water. A number of water quality indices have been developed by various researchers for categorizing the water quality for different uses. These indices are developed based on classification criteria, sub-indices, and aggregation function. In the present study, a generalized Composite Water Quality Index (CWQI) is developed to classify the water into five categories, viz excellent, good, fair, poor, and polluted. For this purpose, the concentration ranges have been categorized on the basis of the Indian Standards (IS) and Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) standards and considering International standards of World Health Organization (WHO) and European Commission (EC). Twenty-five water quality parameters are selected based on the social and environmental impacts, and weights are computed using the Saaty’s Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) tool. These parameters are selected such that the same indices can be used to assess the quality of both surface and ground water. The computed weights minimize the subjectivity in assigning the parameter weights. The proposed index improves understanding of water quality issues by integrating complex data and generates a score which describes the status of water quality. The index will be very useful for the water management authorities to maintain good health of surface water resources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, S. A. (1999). Water quality indices, a state-of-the art. Journal of the Institution of Public Health Engineers, 1, 13–24.
Bharti, N., & Katyal, D. (2011). Water quality indices used for surface water vulnerability assessment. International Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2(1), 154–173.
Boyacioglu, H. (2007). Development of a water quality index based on a European classification scheme. Water SA, 33(1), 101–106.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index: do we dare? Water & Sewage Works, 117(10), 339–343.
Bureau of Indian Standards (1991)Specifications for Drinking Water, IS:10500: 1991 Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi, India.
Bureau of Indian Standards. (2012). Indian standard drinking water specification, IS:10500: 2012. Drinking water sectional committee, FAD (p. 25). New Delhi: India.
Central Ground Water Board (2014) District groundwater brochure of Junagadh district, Gujarat. Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India.
Davis, J. C. (1986). Statistics and data analysis in geology. New York: John Willey and Sons, 2nd ed.
Dee, N., Baker, J., Drobny, N., Duke, K. M., Whitman, I., & Fahringer, D. (1973). An environmental evaluation system for water resource planning. Water Resources Research, 9(3), 523–535.
Deininger, R., & Landwehr, J. M. (1971). A water quality index for public water supplies. School of Public Health. Ann Arbor: Univ. of Michigan.
Dhiman, S. D. (2014). Hydro-chemistry and multivariate analysis of the groundwater quality parameters of Rajkot district, Gujarat. Hydrology Journal, 37, 26–34.
Dinius, S. H. (1972). Social accounting system for evaluating water. Water Resources Research, 8(5), 1159–1177.
Douglas, E. B. & Leo, W. N. (1977). Hydrogeochemical relationships using partial correlation coefficient. Water Resources Bulletin, 13, 843–846.
Fritz, S. J. (1994). A survey of charge-balance errors on published analyses of potable ground and surface waters. Groundwater, NGWA, 32(4), 539–546. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1994.tb00888.x.
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of Water Pollution Control Administration, 37(3), 300.
Javanbarg, M. B., Scawthorn, C., Junji, K., & Shahbodghkhan, B. (2012). Fuzzy AHP-based multicriteria decision making systems using particle swarm optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 39, 960–966.
Khan AA, Paterson R, Khan H (2003) Modification and application of the CCME WQI for the communication of drinking water quality data in Newfoundland and Labrador. In: 38th Central Symposium on Water Quality Research, Canadian Association on Water Quality, Burlington, Canada.
Krishan, G., Singh, S., Gurjar, G., Kumar, C. P., & Ghosh, N. C. (2016a). Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index (WQI) using GIS in Ballia district, Uttar Pradesh. India. J Environ Anal Toxicol, 6, 366.
Krishan, G., Singh, S., Khanna, A., Singh, R. P., & Ghosh, N. C. (2016b). Water quality index of groundwater in Haridwar district, Uttarakhand. Water and Energy International, 58, 55–58.
Krishan, G., Singh, S., Kumar, C. P., Gurjar, S., & Ghosh, N. C. (2016c). Assessment of water quality index (WQI) of groundwater in Rajkot district, Gujarat. India. J Earth Sci Clim Change, 7, 341.
Landwehr, J. M. (1976). A statistical view of a class of water quality indices. Water Resources Research, 15(2), 460–468.
Lee, A. H. I., Chen, W. C., & Chang, C. J. (2008). A fuzzy AHP and BSC approach for evaluating performance of IT department in the manufacturing industry in Taiwan. Expert Systems with Applications, 34, 96–107.
Majumdar, A., Sarkar, B., & Majumdar, P. K. (2004). Application of analytic hierarchy process for the selection of cotton fibers. Fibers and Polymers, 5(4), 297–302.
Mc Duffie, B., & Haney, J. T. (1973). A proposed river pollution index. American Chemical Society, Division of Water. New York, NY: Air and Waste Chemistry.
Nemerow NL, Sumitomo H (1970) Benefits of water quality enhancement. Syracuse, University, Syracuse, NY, Report No. 16110 DAJ.
O’Cornor FM (1972) The application of multi-attribute scaling procedures to the development of indices of water quality. Ph.D Dissertation, University of Michigan.
Parti, L., Pavanello, R., & Pesarin, F. (1971). Assessment of surface water quality by single index of pollution. Water Research, 5, 741–751.
Rao, S. C., Rao, S. N. V, & Chandu, S. N. (1996). Characterisation of ground water contamination using factor analysis. Environmental Geology, 28, 175–180.
Saaty TL (1980) Fundamentals of decision making and priority theory with analytical hierarchical process. Vol VI, RWS Publications, University of Pittsburgh, Pittusburgh USA, pp 3–95.
Sargaonkar, A., & Deshpande, V. (2003). Development of an overall index of pollution for surface water based on a general classification scheme in Indian context. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 89, 43–67.
Singh, S., Kumar, B., Thakural, L. N., & Galkate, R. V. (2009). A comprehensive study on water balance, sedimentation and physico-chemical characteristics of Sagar Lake in India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 148(1–4), 265–276.
Singh, S., Ghosh, N. C., Krishan, G., Galkate, R., Thomas, T., & Jaiswal, R. K. (2015). Development of an overall water quality index (OWQI) for surface water in Indian context. Current World Environment: An International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 10, 813–822.
Smith DG (1987) Water quality indexes for use in New Zealand’s rivers and streams. Water Quality Centre Publication No. 12, Water Quality Centre, Ministry of Works and Development, Hamilton, New Zealand.
Srivastava, A. K. (2015). Water pollution assessment of Azamgarh Mandal of Ballia district, Uttar Pradesh, India. International Journal on Environmental Sciences, 6, 4–8.
Stoner, J. D. (1978). Water quality indices for specific water use. U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, Y.A. Circular, 140–770.
Triantaphyllou, E., & Mann, S. H. (1995). Using the analytic hierarchy process for decision making in engineering applications: some challenges. International journal of industrial engineering. Applications and Practice, 2(1), 35–44.
Viet, N. T., & Bhargava, D. S. (1998). Water quality and management Saigon river in Hochi Minch city, Vietnam. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 31, 321.
Voudouris, K., Panagopoulos, A., & Koumantakis, J. (2000). Multivariate statistical analysis in the assessment of hydrochemistry of the Northern Korinthia prefecture alluvial aquifer system (Peloponnese, Greece). Natural Resources Research, 9(2), 135–146.
Walski, T. M., & Parker, F. L. (1974). Consumers water quality index. Journal of Environmental Engineering, ASCE, 100, 593–611.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Director, National Institute of Hydrology (NIH), Roorkee (India), for granting necessary administrative support, technical guidance, and kind permission to carry out the present work and publish this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Ghosh, N.C., Krishan, G. et al. Development of indices for surface and ground water quality assessment and characterization for Indian conditions. Environ Monit Assess 191, 182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7276-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7276-8