Abstract
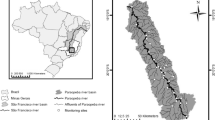
Surface water quality monitoring networks are usually deployed and rarely re-evaluated with regard to their effectiveness. In this sense, this work sought to evaluate and to guide optimization projects for the water quality monitoring network of the Velhas river basin, using multivariate statistical methods. The cluster, principal components, and factorial analyses, associated with non-parametric tests and the analysis of violation to the standards set recommended by legislation, identified the most relevant water quality parameters and monitoring sites, and evaluated the sampling frequency. Thermotolerant coliforms, total arsenic, and total phosphorus were considered the most relevant parameters for characterization of water quality in the river basin. The monitoring sites BV156, BV141, BV142, BV150, BV137, and BV153 were considered priorities for maintenance of the network. The multivariate statistical analysis showed the importance of a monthly sampling frequency, specifically the parameters considered most important.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achieng, A. O., Raburu, P. O., Kipkorir, E. C., Ngodhe, S. O., Obiero, K. O., & Ani-Sabwa, J. (2017). Assessment of water quality using multivariate techniques in river Sosiani, Kenya. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(280), 1–13.
Almeida, K. C. B. (2013). Avaliação da rede de monitoramento de qualidade das águas superficiais da Bacia do Rio das Velhas utilizando o método da entropia. Master’s thesis. Federal University of Minas Gerais, Postgraduate program in Sanitation, Environment and Water Resources, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais. 98 p.
APHA, AWWA, WEF. (2012). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (22nd ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association 1360p.
Borba, R., Figueiredo, P., Rawlins, B. R., Matschullat, B., & J. (2000). Arsenic in water and sediment in the Iron Quadrangle, state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Geociencias, 30(3), 558–561.
Chen, Q., Wu, W., Blanckaert, K., Ma, J., & Huang, G. (2012). Optimization of water quality monitoring network in a large river by combining measurements, a numerical model and matter-element analyses. Journal of Environmental Management, 110, 116–124.
Chow, M. F., Shiah, F. K., Lai, C. C., Kuo, H. Y., Wang, K. W., Lin, C. H., Chen, T. Y., Kobayashi, C., & Ko, Y. (2016). Evaluation of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Fei-Tsui reservoir basin, Taiwan. Environment and Earth Science, 75(6), 1–15.
Christofaro, C., & Leão, M. M. D. (2009). Caracterização temporal do arsênio nos cursos d’água da bacia hidrográfica do Rio das Velhas, MG, Brasil, ao longo de uma década (1998-2007). Ambiente e Água – An Interdisciplinar. Journal of Applied Science, 4(3), 54–66.
Comitê da bacia hidrográfica do rio das Velhas – CBH Velhas. (2014). Análise integrada, articulação e compatibilização dos interesses internos e externos, cenários e prognósticos: relatório 03, revisão 02 – atualização do plano diretor de recursos hídricos da bacia hidrográfica do rio das Velhas. 397 p.
Costa, E. P., Pinto, C. C., Soares, A. L. C., Melo, L. D. V., & Oliveira, S. C. (2017). Evaluation of violations in water quality standards in the monitoring network of São Francisco River basin, the third largest in Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 2–16.
Ferraz, H. D. A. (2012). Associação da ocorrência de cianobactérias às variações de parâmetros de qualidade da água em quatro bacias hidrográficas de Minas Gerais. Federal University of Minas Gerais. http://www.bibliotecadigital.ufmg.br/dspace/bitstream/handle/1843/BUOS-97HH3W/disserta__o_hanna_ferraz.pdf?sequence=1. Accessed 20 June 2017.
Finotti, A. R., Finkler, R., Silva, M. D., & Cemim, G. (2009). Monitoramento de Recursos Hídricos em Áreas Urbanas (272p). Caxias do Sul: Educs.
Gamble, A., & Babbar-Sebens, M. (2012). On the use of multivariate statistical methods for combining in-stream monitoring data and spatial analysis to characterize water quality conditions in the White River Basin, Indiana, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 845–875.
Gu, Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., Li, J., Wang, K., Zheng, K., Zhang, X., & Sheng, L. (2016). Assessment of reservoir water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Qiandao Lake, China. Sustainability, 8(243), 1–17.
Güler, C., Kurt, M. A., Alpaslan, M., & Akbulut, C. (2012). Assessment of the impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater hydrology and chemistry in Tarsus coastal plain (Mersin, SE Turkey) using fuzzy clustering, multivariate statistics and GIS techniques. Journal of Hydrology, 414-415, 435–451.
Hunt, C. D., Rust, S. W., & Sinnott, L. (2008). Application of statistical modeling to optimize a coastal water quality monitoring program. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137(1–3), 505–522.
Instituto Mineiro de Gestão das Águas – Igam. (2013). Identificação de municípios com condição crítica para a qualidade de água na bacia do rio das Velhas. Belo Horizonte: Igam 48p.
Instituto Mineiro de Gestão das Águas – Igam. (2018). Monitoramento da Qualidade das Águas. Available at: http:www.igam.mg.gov.br/igam. Accessed in June/2018.
İşçen, C. F., Altin, A., Şenoğlu, B., & Yavuz, H. S. (2009). Evaluation of surface water quality characteristics by using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Euphrates river basin, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151, 259–264.
Jardim, B. F. M. (2011). Variação dos parâmetros físicos e químicos das águas superficiais da bacia do rio das Velhas - MG e sua associação com as florações de cianobactérias. Federal University of Minas Gerais. http://www.bibliotecadigital.ufmg.br/dspace/bitstream/handle/1843/ENGD-8KDPVL/disserta__o_b_rbara_fernanda_de_melo_jardim.pdf?sequence=1. Accessed 20 June 2017.
Kennish, M. J., Fertig, B. M., & Lathrop, R. G. (2012). Assessment of nutrient loading and eutrophication in Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor, New Jersey in support of nutrient management planning. Technical report (Institute of Marine and Coastal Sciences, Rutgers University) to the New England interstate water pollution control commission, Lowell, Massachusetts. 258 p.
Khalil, B., Ouarda, T. B. M. J., ST-Hilaire, A., & Chebana, F. (2010). A statistical approach for the rationalization of water quality indicators in surface water quality monitoring networks. Journal of Hydrology, 386, 173–185.
Khalil, B., Ou, C., Proulx-McInnis, S., St-Hilaire, A., & Zanacic, E. (2014). Statistical assessment of the surface water quality monitoring network in Saskatchewan. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225(2128), 1–22.
Krishna, A. K., Satyanarayanan, M., & Govil, P. K. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 15(167), 366–373.
Krogmann, D. W., Butalla, K., & Sprinkle, J. (1986). Blooms of cyanobacteria on the Potomac River. Plant Physiology, 80, 667–671.
Lattin, J., Carroll, J. D., & Green, P. E. (2011). Análise de Dados Multivariados. São Paulo: Cengage Learning 455 p.
Ling, T. Y., Soo, C. L., Liew, J. J., Nyanti, L., Sim, S. F., & Grinang, J. (2017). Application of multivariate statistical analysis in evaluation of surface river water quality of a tropical river. Journal of Chemistry, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5737452.
Liu, Y., Zheng, B. H., Wang, M., Xu, Y. X., & Qin, Y. W. (2014). Optimization of sampling frequency for routine river water quality monitoring. SCIENCE CHINA Chemistry, 57(5), 772–778.
Luo, K., Hu, X., He, Q., Wu, Z., Cheng, H., Hu, Z., & Mazumder, A. (2017). Using multivariate techniques to assess the effects of urbanization on surface water quality: a case study in the Liangjiang New Area, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(174), 1–11.
Macdonald, D. D., Clark, M. J. R., Whitfield, P. H., & Wong, M. P. (2009). Designing monitoring programs for water quality based on experience in Canada I: theory and framework. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 28(2), 204–213.
Mavukkandy, M. O., Karmakar, S., & Harikumar, P. S. (2014). Assessment and rationalization of water quality monitoring network: a multivariate statistical approach to the Kabbini River (India). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 10045–10066.
Minas Gerais. Conselho Estadual de Política Ambiental; Conselho Estadual de Recursos Hídricos de Minas Gerais. (2008). Normative Deliberation COPAM/CERH-MG n. 01, de 05 de maio de 2008. Provides for the classification of water bodies and environmental guidelines for their classification and establishes the conditions and standards for effluents dicharge and other measures.
Mingoti, S. A. (2005). Análise de Dados Através de Métodos de Estatística Multivariada: uma abordagem aplicada. Belo Horizonte: Editora UFMG 297 p.
Monica, N., & Choi, K. S. (2016). Temporal and spatial analysis of water quality in Saemangeum watershed using multivariate statistical techniques. Paddy and Water Environment, 14(3), 3–17.
Naddeo, V., Scannapieco, D., Zarra, T., & Belgiorno, V. (2012). River water quality assessment: implementation of non-parametric tests for sampling frequency optimization. Land Use Policy, 30, 197–205.
Park, S. Y., Choi, J. H., Wang, S., & Park, S. S. (2006). Design of a water quality monitoring network in a large river system using the genetic algorithm. Ecological Modelling, 199(3), 289–297.
Ruzdjak, A. M., & Ruzdjak, D. (2015). Evaluation of river water quality variations using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(215), 1–14.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22, 464–475.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., Sofoniou, M., & Kouimtzis, T. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northen Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India) – a case sudy. Water Research, 38, 3980–3992.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., & Sinha, S. (2005). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques – a case study. Analytica Chimica Acta, 538, 355–374.
Taoufik, G., Khouni, I., & Ghrabi, A. (2017). Assessment of physico-chemical and microbiological surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Wadi El-Bey River, Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 10(181), 1–19.
Tavakol, M., Arjmandi, R., Shayeghi, M., Monavari, S. M., & Karbassi, A. (2017). Application of multivariate statistical methods to optimize water quality monitoring network with emphasis on the pollution caused by fish farms. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 46(1), 83–92.
Telci, I. T., Nam, K., Guan, J., & Aral, M. M. (2009). Optimal water quality monitoring network design for river systems. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 2987–2998.
Trindade, A. L. C., Almeida, K. C. B, Barbosa, P. E., & Oliveira, S. M. A. C. (2017). Tendências temporais e espaciais da qualidade das águas superficiais da sub-bacia do Rio das Velhas, estado de Minas Gerais. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 22(1), 13–24.
Vieira, J. S., Pires, J. C. M., Martins, F. G., Vilar, V. J. P., Boaventura, R. A. R., & Botelho, C. M. S. (2012). Surface water quality assessment of Lis River using multivariate statistical methods. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 5549–5561.
Wang, J., Liu, G., Liu, H., Lam, P. K., & S. (2017). Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe river, Anhui, China. Science of the Total Environment, 583, 421–431.
Ye, R., Liu, L., Wang, Q., Ye, X., Cao, Q., He, Q., & Cai, Y. (2017). Identification of coastal water quality by multivariate statistical techniques in two typical bays of northern Zhejiang Province, East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(2), 1–10.
Zhang, Q., Li, Z., Zeng, G., Li, J., Fang, Y., Yan, Q., Wang, Y., & Ye, F. (2009). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques in red soil hilly region: a case study of Xiangjiang watershed, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152, 123–131.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Institute of Water Management of Minas Gerais (Igam) and its technical team for providing the monitoring data and for the constant support and service.
Funding
This study received financial supports from the National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq), the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), and the Foundation of Support Research of the State of Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calazans, G.M., Pinto, C.C., da Costa, E.P. et al. Using multivariate techniques as a strategy to guide optimization projects for the surface water quality network monitoring in the Velhas river basin, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 190, 726 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7099-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7099-z