Abstract
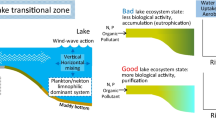
In lakes, the littoral habitat and its invertebrate communities are often exposed to water-level fluctuations. We examined the effects of seasonal changes on water level, substrata availability and benthic fauna in the littoral zone of Peri Lake, a shallow lake that has experienced a strong reduction in water level due to changes in rainfall. In this study, we also examined whether the abundance and composition of aquatic invertebrates differed among the four substrata. Our main objective was to assess the effect of seasonal changes on water level and benthic invertebrates inhabiting the different types of substrata. Benthic invertebrates were sampled four different substrata (Schoenoplectus californicus, sand and stones, allochthonous leaf litter, and macrophyte stands), and we also measured meteorological, physical and chemical variables. We found that complex habitats, such as allochthonous leaf litter and aquatic macrophyte, stand to be colonised by a larger number of macroinvertebrates because they provide more habitats or potential niches for colonisation by different species. In addition, we observed that during periods of low water level, the presence of substrata in the littoral zone decreased, as did the associated biota. Therefore, our results suggest that water level changes have a major functional impact on the littoral zone of the lake, and can affect substratum availability, which also impacts invertebrate communities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, C., Coelho, R., Silva, M., Bentes, M. L., Monteiro, P., Ribeiro, J., Erzini, K., & Gonçalves, J. M. S. (2008). Use of different intertidal habitats by faunal communities in a temperate coastal lagoon. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 80, 357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2008.08.017.
Anderson, M. J. (2001). A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology, 26, 32–46.
Aroviita, J., & Hämäläinen, H. (2008). The impact of water level regulation on littoral macroinvertebrate assemblages in boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia, 613, 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-008-9471-4.
Batista-Silva, V. F., Boneto, D. D., Bailly, D. A. M. C. F., & Kashiwaqui, E. A. L. (2011). Invertebrates associated to Eichhornea azurea Kunth in a lagoon of the Upper Paraná River: composition, community attributes and influence of abiotic factors. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000016.
Brauns, M., Garcia, X. F., & Pusch, M. T. (2008). Potential effects of water-level fluctuations on littoral invertebrates in lowland lakes. Hydrobiologia, 613, 5–12.
Cai, Y. J., Lu, Y. J., Wu, Z. S., Chen, Y. W., Zhang, L., & Lu, Y. (2014). Community structure and decadal changes in macrozoobenthic assemblages in Lake Poyang, the largest freshwater lake in China. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 414, 09.
Carmignani, J. R., & Roy, A. H. (2017). Ecological impacts of winter water level drawdowns on lake littoral zones: a review. Aquatic Sciences, 79, 803–824.
Carvalho, C., Hepp, L. H., Palma-Silva, C., & Albertoni, E. F. (2015). Decomposition of macrophytes in a shallow subtropical lake. Limnologica, 53, 1–9.
Casartelli, M. R., & Ferragut, C. (2015). Influence of seasonality and rooted aquatic macrophyte on periphytic algal community on artificial substratum in a shallow tropical reservoir. International Review of Hydrobiology, 100, 158–168.
Clarke, K. R., & Gorley, R. N. (2006). PRIMER v6: User manual/tutorial. Plymouth: PRIMER-E.
Coops, H., & Hosper, S. H. (2002). Water-level management as a tool for the restoration of shallow lakes in the Netherlands. Lake and Reservoir Management, 18, 293–298.
Covich, A. P., Margaret, A. P., & Crowl, T. A. (1999). The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems: zoobenthic species influence energy flows and nutrient cycling. BioScience, 49, 119–127.
Dalu, T., Clegg, B., & Nhiwatiwa, T. (2012). Macroinvertebrate communities associated with littoral zone habitats and the influence of environmental factors in Malilangwe Reservoir, Zimbabwe. Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems, 406, 06.
Dinka, M., Agoston-Szabo, E., Bercik, A., & Kutrucz, G. (2004). Influence of water level fluctuation on the spatial dynamic of the water chemistry at lake Ferto/Neusiedler See. Limnologica, 334, 48–56.
Dufrêne, M., & Legendre, P. (1997). Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs, 67, 345–366.
Esteves, F. A., Caliman, A., Santangelo, J. M., Guariento, R. D., Farjalla, V. F., & Bozelli, R. L. (2008). Neotropical coastal lagoons: an appraisal of their biodiversity, functioning, threats and conservation management. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 68, 967–981. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842008000500006.
Evtimova, V. V., & Donohue, I. (2014). Quantifying ecological responses to amplified water level fluctuations in standing waters: an experimental approach. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51, 1282–1291. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12297.
Evtimova, V. V., & Donohue, A. (2016). Water-level fluctuations regulate the structure and functioning of natural lakes. Freshwater Biology, 61, 251–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12699.
Fernández, H. R., & Domíngues, E. (2001). Guia para la determinación de los artrópodos bentônicos sudamericanos. Tucumán: Universidad Nacional de Tucumán 282 p.
Fischer, P., & Öhl, O. (2005). Effects of water-level fluctuations on the littoral benthic fish community in lakes: a Mesocosm experiment. Behavioral Ecology, 16, 741–746.
Fontes, M. L. S., Marotta, H., MacIntyre, S., & Petrucio, M. M. (2015). Inter-and intra-annual variations of pCO2 and pO2 in a freshwater subtropical coastal lake. Inland Waters, 5, 107–116.
Freire, R.H.F., Benassi, R.F., Calijuri, M.C., Sanchez, A.A. (2015). Influence of water fluctuations on the limnological characteristics of two floodplain lagoons (Ribeira do Iguape Valley, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia, 27, 431–440.
Fuentes, E. V., & Petrucio, M. M. (2015). Water level decrease and increased water stability promotes phytoplankton growth in a mesotrophic subtropical lake. Marine and Freshwater Research, 66, 711–718.
Gasith, A., & Gafny, S. (1990). Effects of water level fluctuation on the structure and function of the littoral zone. In M. M. Tilzer & C. Serruya (Eds.), Large lakes: ecological structure and function (pp. 156–171). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Ghani, W. M. H. W. A., Rawi, C. S. M., Hamid, S. A., & Al-Shami, S. A. (2016). Efficiency of different sampling tools for aquatic macroinvertebrate collections in Malaysian streams. Tropical Life Sciences Research, 27, 115–133.
Giller, P. S., & Malmqvist, B. (1998). The biology of streams and rivers. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Graça, M. A., & Cressa, C. (2010). Leaf quality of some tropical and temperate tree species as food resource for stream shredders. Hydrobiologia, 95, 27–41.
Graça, M. A. S., Ferreira, W. R., Firmiano, K., França, J., & Callisto, C. (2015). Macroinvertebrate identity, not diversity, differed across patches differing in substrate particle size and leaf litter packs in low order tropical Atlantic forest streams. Limnetica, 34, 29–40.
Hennemann, M. C., & Petrucio, M. M. (2011). Spatial and temporal dynamic of trophic relevant parameters in a subtropical coastal lagoon in Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 181, 347–361.
Johnson, R. K., Goedkoop, W., & Sandin, L. (2004). Spatial scale and ecological relationships between the macroinvertebrate communities of stony habitats of streams and lakes. Freshwater Biology, 49, 1179–1194.
Kubosova, K., Brabec, K., Jarkovsky, J., & Syrovatka, V. (2010). Selection of indicative taxa for river habitats: a case study on benthic macroinvertebrates using indicator species analysis and the random forest methods. Hydrobiologia, 651, 101–114.
Larsen, S., Vaughan, I. P., & Ormerod, S. J. (2009). Scale-dependent effects of fine sediments on temperate headwater invertebrates. Freshwater Biology, 54, 203–219.
Leira, M., & Cantonati, M. (2008). Effects of water-level fluctuations on lakes: an annotated bibliography. Hydrobiologia, 613, 171–184.
Lemes-Silva, A. L., Pagliosa, P. P., & Petrucio, M. M. (2014). Inter-and intra-guild patterns of food resource utilization by chironomid larvae in a subtropical coastal lagoon. Limnology, 15, 1–12.
Lemes-Silva, A. L., Pires, J. R., Pagliosa, P. R., & Petrucio, M. M. (2016). Distribution of aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages in a subtropical coastal lake: response to environmental parameters. Fundamental and Applied Limnology, 188, 113–127.
Magbanua, F. S., Mendoza, N. Y. B., Uya, C. J. C., Matthaeib, D. C., & Onga, P. S. (2015). Water physicochemistry and benthic macroinvertebrate communities in a tropical reservoir: the role of water level fluctuations and water depth. Limnologica, 55, 13–20.
McEwen, D. C., & Butler, M. G. (2010). The effects of water level manipulation on the benthic invertebrates of a managed reservoir. Freshwater Biology, 55, 1086–1101.
Merritt, R. W., Cummins, K. W., & Berg, M. B. (2008). An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. Dubuque: Hunt Publishing Company.
Mormul, R. P., Thomaz, S. M., Takeda, A. M., Behrend, R. D. (2011). Structural complexity and distance from source habitat determine invertebrate abundance and diversity. Biotropica, 43, 738–745.
Mugnai, R., Nessimian, J. L., & Baptista, D. F. (2010). Manual de identificação de Macroinvertebrados aquáticos do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. Technical Books.
Neves dos Santos, A. F. G., Santos, L. N., & Araújo, F. G. (2004). Water level influences on body condition of Geophagus brasiliensis (Perciformes: Cichlidae) in a Brazilian oligotrophic reservoir. Neotropical Ichthyology, 2, 151–156.
Pardo, I., & Armitage, P. D. (1997). Species assemblages as descriptors of mesohabitats. Hydrobiologia, 344, 111–128.
Pech, D., Ardisson, P. L., & Hernandéz-Guevara, N. A. (2007). Benthic community response to habitat variation: a case of study from a natural protected area, the Celestum coastal lagoon. Continental Shelf Research, 272, 523–533.
Peiró, D. F., Amaral, G. F., & Saulino, H. H. L. (2015). Structure community of aquatic insects associated with different macrophytes in ornamental lakes in a savanna region, Southeastern Brazil. Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences, 10, 273–282.
Pope, R. J., Gordon, A. M., & Kaushik, N. K. (1999). Leaf litter colonization by invertebrates in the littoral zone of a small oligotrophic lake. Hydrobiologia, 392, 99–112.
R Core Team. (2017). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Rabeni, C. F., Doisy, K. E., & Galat, D. L. (2002). Testing the biological basis of a stream habitat classification using benthic invertebrates. Ecological Applications, 12, 782–796.
Roberto, M.C., Santana, N.F., Thomaz, S.M. (2009). Limnology in the Upper Paraná River floodplain: large-scale spatial and temporal patterns, and the influence of reservoirs. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 69, 717–725.
Rosenberg, D. M., & Resh, V. H. (1993). Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. New York: Chapman & Hall.
Spitale, D., Angeli, N., Lencioni, V., Tolotti, M.,Cantonati, M. (2015). Comparison between natural and impacted Alpine lakes six years after hydropower exploitation has ceased. Biologia, 70, 1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0185.
St. Pierre, J. I., & Kovalenko, K. E. (2014). Effect of habitat complexity attributes on species richness. Ecosphere, 5, 22.
Sutela, T., Aroviita, J., & Keto, A. (2013). Assessing ecological status of regulated lakes with littoral macrophyte, macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages. Ecological Indicators, 24, 185–192.
Tadeusz, P., Miroslawa, P., & Bijok, P. (1999). Diversity of invertebrate fauna in littoral of shallow Myczkowce dam reservoir in comparison with a deep Solina dam reservoir. Hydrobiologia, 408, 203–210.
Thomaz, S. M., Dibble, E. D., Evangelista, L. R., Higuti, J., & Bini, L. M. (2008). Influence of aquatic macrophyte habitat complexity on invertebrate abundance and richness in tropical lagoons. Freshwater Biology, 53, 358–367.
Tonetta, D., Staehr, P. A., Schmitt, R., & Petrucio, M. M. (2016). Physical conditions driving the spatial and temporal variability in aquatic metabolism of a subtropical coastal lake. Limnologica, 58, 30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2016.01.006.
Tonetta, D., Staehr, P. A., & Petrucio, M. M. (2017). Changes in CO2 dynamics related to rainfall and water level variations in a subtropical lake. Hydrobiologia, 794, 109–123.
Valdovinos, C., Moya, C., Olmos, V., Parra, O., Karrasch, B., & Buettner, O. (2007). The importance of water-level fluctuation for the conservation of shallow water benthic macroinvertebrates: an example in the Andean zone of Chile. Biological Conservation, 16, 3095–3109.
Van Geest, G. J., Wolters, H., Roozen, F. C. J. M., Coops, H., Roijackers, R. M. M., Buijse, A. D., & Scheffe, M. (2005). Water-level fluctuations affect macrophyte richness in floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia, 539, 239–248.
Vera, C., Higgins, W., Amador, J., Ambrizzi, T., Garreaud, R., Gochis, D., Gutzler, D., Lettenmaier, D., Marengo, J., Mechoso, C. R., Nogues-Paegle, J., Silva Dias, P. L., & Zhang, C. (2006). Toward a unified view of the American Monsoon Systems. Journal of Climate, 19, 4977–5000.
Wang, M. Z., Liu, Z. Y., Luo, F. L., Lei, G. C., & Li, H. L. (2016). Do amplitudes of water level fluctuations affect the growth and community structure of submerged macrophytes? PLoS One, 11, e0146528. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146528.
White, M. S., Xenopoulos, M. A., Hogsden, K., Metcalfe, R. A., & Dillon, P. J. (2008). Natural lake level fluctuation and associated concordance with water quality and aquatic communities within small lakes of the Laurentian Great Lakes region. Hydrobiologia, 613, 21–31.
Zerlin, R. A., & Henry, R. (2014). Does water level affect benthic macro-invertebrates of a marginal lake in a tropical river-reservoir transition zone? Brazilian Journal of Biology, 74, 408–419.
Zohary, T., & Ostrovsky, L. (2011). Ecological impacts of excessive water level fluctuations in stratified freshwater lakes. Inland Waters, 1, 47–59.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to staff from Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology from Federal University of Santa Catarina (www.limnos.ufsc.br) for collaborative efforts related to the samplings. We thank the ICEA (Instituto de Controle do Espaco Aéreo) and CASAN (Companhia Catarinense de Água e Esgoto) for providing rainfall and water level data, respectively.
Funding
This study was funded by CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) and the first author was supported by CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lemes da Silva, A.L., Petrucio, M.M. Relationships between aquatic invertebrate communities, water-level fluctuations and different habitats in a subtropical lake. Environ Monit Assess 190, 548 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6929-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6929-3