Abstract
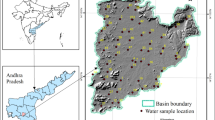
The groundwater quality assessment for the drinking and irrigation purpose is carried out in the Kandivalasa River Sub Basin covered with khondalitic suite (Garneti ferrous, Sillimanite, Gneiss) of rocks, near Cheepurupalli town of Vizianagaram district, Andhra Pradesh, India. The analysis for the groundwater quality for drinking has shown the slightly alkaline nature and high values of alkalinity in the study area. A very high concentration of total dissolved solids value is observed at one pocket where there has been contamination by many fertilizer industries located nearby the study area. The groundwater is highly affected by the nitrate. Higher fluoride values are obtained at few pockets. Most of the samples in the study area are categorized as very hard category. According to the Piper trilinear diagram, it can be observed that the carbonate hardness and secondary salinity have occupied at major part of study area. From the analysis of sodium adsorption ratio, salinity hazard, sodium percentage, residual sodium carbonate, and Kelly’s ratio, all the groundwater samples except at few locations fell under the category of good to excellent for irrigation. The prepared integrated groundwater quality maps for the drinking purpose and agricultural purposes are indicating that, by and large, the low-lying areas are having poor groundwater quality than the uplands for drinking as well as agricultural needs which means that the groundwater quality of the basin is following the topography.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary, P., Dash, C., Chandrasekharan, H., Rajput, T., Dubey, S., (2011). Evaluation of groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking using GIS and geostatistics in a peri-urban area of Delhi, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0330-7
Al-Taani, A. (2013). Seasonal variations in water quality of Al-Wehda Dam north of Jordan and water suitability for irrigation in summer. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(4), 1131–1140.
American Public Health Association (APHA). (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Baltimore: United Book Press, Inc..
Bohlke, J. K. (2002). Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination. Hydrogeology Journal, 10, 153–179.
Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), 2005). District groundwater management studies of Palghat District, Kerala, Technical Report Series Report No.25/KR/CGWB/2004–05.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS). (1993). Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Indian Standard (IS: 10500), New Delhi, India.
Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), (2013). Groundwater brochure, Vizianagaram district, Andhra Pradesh. A CGWB report, Ministry of Water Resources, New Delhi, India.
Davis, S.N. and De Wiest, R.J.M. (1967). Hydrogeology, 2nd ed. New York, London, Sydney, Wiley. p. 463.
Doneen, L. D. (1964). Notes on water quality in agriculture. Water science and engineering. Davis: University of California.
Drever, J. I. (1982). The geochemistry of natural waters. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Eaton, E. M. (1950). Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. Soil Science, 69, 12–133.
Gopal, R., & Gosh, P. K. (1985). Fluoride in drinking water—its effects and removal. Defence Science Journal, 35(1), 71–88.
Handa, B. K. (1964). Modified classification procedure for rating irrigation waters. Soil Science, 98, 264–269.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. USGS water supply paper, 2254, 117–120.
Kannan, N., & Sabu, J. P. (2009). Quality of groundwater in the shallow aquifers of a paddy dominated agricultural river basin, Kerala, India. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 52, 475–482.
Karnath, K. R. (1987). Groundwater assessment, development and management. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill.
Kelly, W.P., 1940. Alkali soils—their formation, properties and reclamation. Reinhold, New York.
Khodapanah, L., Sulaiman, W. N. A., & Khodapanah, N. (2009). Groundwater quality assessment for different purposes in Eshtehard District, Tehran, Iran. European Journal of Scientific Research, 36, 543–553.
Lenin, S. M., & Saseetharan, M. K. (2008). Groundwater quality in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu along Noyyal River. Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering, 50(3), 187–190.
Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA), 1999. Effects of Land Use on Ground Water Quality. St. Cloud Area, Minnesota. 1998 Results. St. Paul, MN 46 p.
National Academy of Science (NAS). (1974). Water quality criteria. National Academy of Sciences, 23, 105.
Nishanthiny, C. S., Thushyanthy, M., Barathithasan, T., & Saravanan, S. (2010). Irrigation water quality based on hydro chemical analysis, Jaffna, Sri Lanka. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences, 7(1), 100–102.
Nordstrom, P.L., 1987. Groundwater resource of the antlers and Travis peak formations in the outcrop area of north central Texas, Texas Water Development Board, Rep. No. 298, P 280.
Padmanaban, R., Dharmendira Kumar, M., Sakthivel, P. B., & Elangovan, N. S. (2013). A case study on chemical properties of ground water in Madurai District, Tamil Nadu, India. International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, 2(4), 715–718.
Piper, A. M. (1953). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. USGS Ground Water Note, 12, 63.
Prakash, K. L., & Somashekar, R. K. (2006). Groundwater quality—assessment on Anekal Taluk, Bangalore urban district, India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 27(4), 633–637.
Prasanna, M. V., Chidambaram, S., Gireesh, T. V., & Jabir Ali, T. V. (2011). A study on hydrochemical characteristics of surface and sub-surface water in and around Perumal Lake, Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu. South India. Environ. Earth Sci., 64(5), 1419–1431.
Rajmohan, N., & Elango, L. (2005). Nutrient chemistry of groundwater in an intensively irrigated region of southern India. Journal of Environmental Geology, 47, 820–830.
Ramesh, K., (2008). Hydrochemical studies and effect of irrigation on groundwater quality Tondiar basin Tamil Nadu. Dissertation, Anna University, Chennai, Tamilnadu.
Ramesh, K., & Elango, L. (2012). Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(6), 3887–3899.
Ravikumar, P., Somashekar, R., & Angami, M. (2011). Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1), 459–487.
Richards, L.A., (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkaline soils. US Department of Agriculture hand book, US Salinity Laboratory, USA.
Robertson, W. D., Cherry, J. A., & Sudicky, E. A. (1991). Groundwater contamination from two small septic systems in sand aquifers. Groundwater, 29(1), 82–91.
Saralakumari, D., Rao, P.R., 1993. Endemic fluorosis in the village Ralla, Anantapuram in Andra Pradesh. An epidemiological study. Fluoride, 26(3), 177–180.
Satish Kumar, V., Amarender, B., Dhakate, R., Sankaran, S., & Raj Kumar, K. (2014). Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation use in shallow hard rock aquifer of Pudunagaram, Palakkad District Kerala. Applied Water Science, 6, 149–167.
Sharma V. V. J., (1982). Ground water resources of northern eastern Ghats, Procs. of the Seminar on Resources Development and Environment in the Eastern Ghats, Visakhapatnam, 69–75.
Sharma, V.V.J., Narayanaswamy, A., 1986. Regional groundwater flow investigations in Visakhapatnam Basin, Andhra Pradesh. Journal of Geological Society of India, 27, 386–391.
Simsek, C., & Gunduz, O. (2007). IWQ index: a GIS-integrated technique to assess irrigation water quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 128(1), 277–300.
Siva Prasad, Y., & Venkateswara Rao, B. (2018). Groundwater depletion and groundwater balance studies of Kandivalasa River Sub Basin, Vizianagaram District, A.P., India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 6, 71–78.
Soman, K. (1977). Geology of Kerala. Geological Society of India, 280.
Subba Rao, N., & Krishna Rao, G. (1984). Dug wells and bore wells in hard rock aquifers of Visakhapatnam District, Andhra Pradesh—a comparative study. Association of Exploration Geophysics, 4, 11–18.
Subba Rao, N., & Krishna Rao, G. (1991). Groundwater chemistry for location of wells in Visakapatnam area, Andhra Pradesh. Bhujal News, 10, 7–10.
Suryanarayana, K. (1995). Effect of groundwater quality on health hazards in parts of eastern ghats. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 15(7), 497–500.
Todd, D. K. (1959). Groundwater hydrology. New York: Wiley.
USSL (United States Salinity Laboratory) (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. United States Development Agency handbook 60. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, 147p.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Rajiv Ganthi, R., Vijayaraghavan, K., & Sarma, V. S. (2012). Characterisation and quality assessment of groundwater with a special emphasis on irrigation utility: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 5(2), 245–258.
Venateswara Rao B., 1995. Integrated studies for evaluation of groundwater potential in a typical khondalitic terrain, Dissertation, JNT University Hyderabad, India.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters. Washington: US Department of Agriculture.
World Health Organization (Ed.). (1993). Guidelines for drinking-water quality recommendations (2nd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yadav, J.P., Lata S. 2004. Fluoride levels in drinking water sources in rural areas of block Jhajjar, district Jhajjar, Haryana. Journal of Indian Water Works Association, 131–136.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for sponsoring the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, Y.S., Rao, B.V. Monitoring and assessment of groundwater quality in a khondalitic terrain, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 190, 426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6757-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6757-5