Abstract
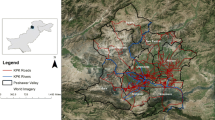
Contemporary studies demonstrate that rodent bites do not occur frequently. However, a huge number of cases were reported from Peshawar vale, Pakistan during 2016. Two species, the local black rat Rattus rattus (Linnaeus, 1758) and the invasive brown rat Rattus norvegicus (Berkenhout, 1769) might be the suspected cause. Several studies indicated the invasion of brown rats into Pakistan presumably via port city of Karachi. In this study, we modeled geospatial distribution of rodent bites for risk assessment in the region. Bite cases reported to tertiary care lady reading hospital were monitored from January 1 to August 31, 2016. Among 1747 cases, statistically informative data (n = 1295) was used for analyses. MaxEnt algorithm was employed for geospatial modeling, taking into account various environmental variables (temperature, precipitation, humidity, and elevation) and anthropogenic factors (human population density, distance from roads, distance from water channels, and land use/land cover). MaxEnt results revealed that urban slums (84.5%) are at highest risk followed by croplands (10.9%) and shrublands (2.7%). Anthropogenic factors affecting incidence of rodent bites included host density (contribution: 34.7), distance from water channels (3.2), land use/land cover (2.8), and distance from roads (2). Most of the cases occurred within a radius of 0.3 km from roads and 5 km from water channels. Rodent bite incidence is currently at its peak in Peshawar vale. Factors significantly affecting rodents’ bite activity and their distribution and dispersal include urbanization, distance from roads, and water channels. Further studies are needed to determine the impact of invasion by brown rat on bite incidence.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamian, F. M., & Goldstein, E. J. (2011). Microbiology of animal bite wound infections. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 24(2), 231–246.
Ahmad, E., Hussain, I., & Brooks, J. E. (1995). Losses of stored foods due to rats at grain markets in Pakistan. International biodeterioration & biodegradation, 36(1-2), 125–133.
Alam, S., Fatima, A., & Butt, M. S. (2007). Sustainable development in Pakistan in the context of energy consumption demand and environmental degradation. Journal of Asian Economics, 18(5), 825–837.
Aplin, K. P., Suzuki, H., Chinen, A. A., Chesser, R. T., Ten Have, J., Donnellan, S. C., et al. (2011). Multiple geographic origins of commensalism and complex dispersal history of black rats. PLoS One, 6(11), e26357.
Baker, R. H. A., Sansford, C. E., Jarvis, C. H., Cannon, R. J. C., MacLeod, A., & Walters, K. F. A. (2000). The role of climatic mapping in predicting the potential geographical distribution of non-indigenous pests under current and future climates. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 82(1), 57–71.
Banks, P. B., & Smith, H. M. (2015). The ecological impacts of commensal species: black rats, Rattus rattus, at the urban–bushland interface. Wildlife Research, 42(2), 86–97.
Bordes, F., Caron, A., Blasdell, K., Garine-Wichatitsky, M., & Morand, S. (2017). Forecasting potential emergence of zoonotic diseases in South-East Asia: network analysis identifies key rodent hosts. Journal of Applied Ecology, 54(3), 691–700.
Bregman, B., & Slavinski, S. (2012). Using emergency department data to conduct dog and animal bite surveillance in New York City, 2003–2006. Public Health Reports, 127(2), 195–201.
Buckle, A. (2013). Anticoagulant resistance in the United Kingdom and a new guideline for the management of resistant infestations of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus Berk). Pest Management Science, 69(3), 334–341.
Burke, V. D., & Johnson, K. A. (1975). U.S. Patent No. 3,906,656. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Capizzi, D., Bertolino, S., & Mortelliti, A. (2014). Rating the rat: global patterns and research priorities in impacts and management of rodent pests. Mammal Review, 44(2), 148–162.
Carnahan, D., Gove, W., & Galle, O. R. (1974). Urbanization, population density, and overcrowding: trends in the quality of life in urban America. Social Forces, 53(1), 62–72.
Chaisiri, K., Siribat, P., Ribas, A., & Morand, S. (2015). Potentially zoonotic helminthiases of murid rodents from the Indo-Chinese peninsula: impact of habitat and the risk of human infection. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 15(1), 73–85.
Chambers, L., Singleton, G., & Wensveen, V. M. (1996). Spatial heterogeneity in wild populations of house mice on the Darling Downs, Southeastern Queensland. Wildlife Research, 23, 23–38.
Chhabra, S., Chhabra, N., & Gaba, S. (2015). Maxillofacial injuries due to animal bites. Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery, 14(2), 142–153.
Childs, J. E., McLafferty, S. L., Sadek, R., Miller, G. L., Khan, A. S., DuPree, E. R., & Glass, G. E. (1998). Epidemz rats (Rattus norvegicus and Rattus rattus). Urban Ecosystems, 17(1), 149–162.
Colvin, B. A., & Jackson, W. B. (1999). Urban rodent control programs for the 21st century.
Costa, F., Ribeiro, G. S., Felzemburgh, R. D., Santos, N., Reis, R. B., Santos, A. C., & Reis, M. G. (2014). Influence of household rat infestation on Leptospira transmission in the urban slum environment. PLoS neglected tropical diseases, 8(12), e3338.
Craig, T. (2016, April 5). As giant rats menace Pakistan, conspiracy theories swirl. The Washington Post.
Dendle, C., & Looke, D. (2008). Animal bites: an update for management with a focus on infections. Emergency Medicine Australasia, 20(6), 458–467.
Dickman, C. R., & Doncaster, C. P. (1987). The ecology of small mammals in urban habitats. I. Populations in a patchy environment. The Journal of Animal Ecology, 56, 629–640.
Feng, A. Y., & Himsworth, C. G. (2014). The secret life of the city rat: a review of the ecology of urban Norway and black rats (Rattus norvegicus and Rattus rattus). Urban Ecosystems, 17(1), 149–162.
Fourcade, Y., Engler, J. O., Rödder, D., & Secondi, J. (2014). Mapping species distributions with MAXENT using a geographically biased sample of presence data: a performance assessment of methods for correcting sampling bias. PLoS One, 9(5), e97122.
Gaughan, A. E., Stevens, F. R., Linard, C., Jia, P., & Tatem, A. J. (2013). High resolution population distribution maps for Southeast Asia in 2010 and 2015. PLoS One, 8(2), e55882.
Ghalib, S. A., Jabbar, A. B. D. U. L., Khan, A. R., & Zehra, A. (2007). Current status of the mammals of Balochistan. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 39(2), 117.
Gilchrist, G. W. (1995). Specialists and generalists in changing environments. I. Fitness landscapes of thermal sensitivity. The American Naturalist, 146(2), 252–270.
Gill, N., Khan, M. M., & Memon, M. S. (2003). Changes in blood parameters due to bladder worm (Cestoda) infection in liver of Rattus norvegicus. In Proceedings of the Pakistan Congress of Zoology, 23, 141–149.
Gratz, N. G. (1999). Urbanization, arthropod and rodent pests and human health. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Urban Pests (pp. 19–22). Czech University of Agriculture, Prague, Czech Republic.
Han, B. A., Schmidt, J. P., Bowden, S. E., & Drake, J. M. (2015). Rodent reservoirs of future zoonotic diseases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(22), 7039–7044.
Hijmans, R. J., Cameron, S. E., Parra, J. L., Jones, P. G., & Jarvis, A. (2005). Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25(15), 1965–1978.
Hussain, I. (1998). Susceptibility to anticoagulants and the development of physiological resistance in Rattus norvegicus and Bandicota bengalensis. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Animal and Microbial Sciences, University of Reading, Reading Berkshire, U.K.
Hussain, I., & Iqbal, M. A. (2002). Sampled from ration shops, Rawalpindi. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 34(3), 239–242.
Jarvis, A., Reuter, H. I., Nelson, A., & Guevara, E. (2008). Hole-filled seamless SRTM data V4. International Centre for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT).
Kajdacsi, B., Costa, F., Hyseni, C., Porter, F., Brown, J., Rodrigues, G., & Caccone, A. (2013). Urban population genetics of slum-dwelling rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Salvador, Brazil. Molecular Ecology, 22(20), 5056–5070.
Khan, H. (2016). Rat bite cases continue to spike in Peshawar. Pakistan: The Express Tribune.
Kosoy, O. I., Lambert, A. J., Hawkinson, D. J., Pastula, D. M., Goldsmith, C. S., Hunt, D. C., & Staples, J. E. (2015). Novel thogoto virus associated with febrile illness and death, United States, 2014. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 21(5), 760–764.
Kriticos, D. J., Webber, B. L., Leriche, A., Ota, N., Macadam, I., Bathols, J., & Scott, J. K. (2012). CliMond: global high resolution historical and future scenario climate surfaces for bioclimatic modelling. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 3, 53–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2011.00134.x.
Lack, J. B., Hamilton, M. J., Braun, J. K., Mares, M. A., & Van Den Bussche, R. A. (2013). Comparative phylogeography of invasive Rattus rattus and Rattus norvegicus in the US reveals distinct colonization histories and dispersal. Biological Invasions, 15(5), 1067–1087.
Lambert, M. S., Quy, R. J., Smith, R. H., & Cowan, D. P. (2008). The effect of habitat management on home-range size and survival of rural Norway rat populations. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45(6), 1753–1761.
Lima, M., Marquet, P. A., & Jaksic, F. M. (1999). El Nino events, precipitation patterns, and rodent outbreaks are statistically associated in semiarid Chile. Ecography, 22(2), 213–218.
Madsen, T., & Shine, R. (1999). Rainfall and rats: climatically driven dynamics of a tropical rodent population. Austral Ecology, 24(1), 80–89.
Marsh R. E., (1994) Roof rats. The handbook: prevention and control of wildlife damage. Paper 6.
Meehan, A. P. (1984). Rats and mice. Their biology and control. Rentokil Ltd..
Meerburg, B. G., Singleton, G. R., & Kijlstra, A. (2009). Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 35(3), 221–270.
Morand, S., Bordes, F., CHEN, H. W., Claude, J., COSSON, J. F., Galan, M., & Ribas, A. (2015). Global parasite and Rattus rodent invasions: the consequences for rodent-borne diseases. Integrative Zoology, 10(5), 409–423.
Mushtaq, M., Kayani, A. R., Nadeem, M. S., & Beg, M. A. (2014). Distribution Pattern of commensal rodents in shops of urban Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 46(6), 1585–1589.
Ordog, G. J., Balasubramanium, S., & Wasserberger, J. (1985). Rat bites: fifty cases. Annals of Emergency Medicine, 14(2), 126–130.
Patz, J. A., Campbell-Lendrum, D., Holloway, T., & Foley, J. A. (2005). Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature, 438(7066), 310–317.
Pedersen, P. O. (2001). Freight transport under globalisation and its impact on Africa. Journal of Transport Geography, 9(2), 85–99.
Phillips, S. J., Anderson, R. P., & Schapire, R. E. (2006). Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190(3), 231–259.
Rafique, A., Rana, S. A., Khan, H. A., & Sohail, A. (2009). Prevalence of some helminths in rodents captured from different city structures including poultry farms and human population of Faisalabad. Pakistan. Pakistan Vet. J, 29(3), 141–144.
Roberts, T. J. (1997). The mammals of Pakistan. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Rothe, K., Tsokos, M., & Handrick, W. (2015). Animal and human bite wounds. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 112(25), 433–42; quiz 443.
Roy, D. P., Wulder, M. A., Loveland, T. R., Woodcock, C. E., Allen, R. G., Anderson, M. C., & Scambos, T. A. (2014). Landsat-8: science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sensing of Environment, 145, 154–172.
Shih, W. J. (2002). Problems in dealing with missing data and informative censoring in clinical trials. Current Controlled Trials in Cardiovascular Medicine, 3(1), 4.
Stenseth, N. C., Leirs, H., Skonhoft, A., Davis, S. A., Pech, R. P., Andreassen, H. P., & Zhang, Z. (2003). Mice, rats, and people: the bio-economics of agricultural rodent pests. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 1(7), 367–375.
Stojcevic, D., Mihaljevic, Z., & Marinculic, A. (2004). Parasitological survey of rats in rural regions of Croatia. Veterinary Medicine Czech, 49, 70–74.
Tamayo-Uria, I., Mateu, J., Escobar, F., & Mughini-Gras, L. (2014). Risk factors and spatial distribution of urban rat infestations. Journal of Pest Science, 87(1), 107–115.
Timilsina, G. R., & Shrestha, A. (2009). Transport sector CO2 emissions growth in Asia: underlying factors and policy options. Energy Policy, 37(11), 4523–4539.
Traweger, D., & Slotta-Bachmayr, L. (2005). Introducing GIS-modelling into the management of a brown rat (Rattus norvegicus Berk.) (Mamm. Rodentia Muridae) population in an urban habitat. Journal of Pest Science, 78, 17–24.
Traweger, D., Travnitzky, R., Moser, C., Walzer, C., & Bernatzky, G. (2006). Habitat preferences and distribution of the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus Berk.) in the city of Salzburg (Austria): implications for an urban rat management. Journal of Pest Science, 79(3), 113–125.
Ullah, Z., Khan, H., Waseem, A., Mahmood, Q., & Farooq, U. (2013). Water quality assessment of the River Kabul at Peshawar, Pakistan: industrial and urban wastewater impacts. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 35(4), 170–176.
Venette, R. C. (Ed.). (2015). Pest risk modelling and mapping for invasive alien species (vol. 7). CABI.
White, J., Horskins, K., & Wilson, J. (1998). The control of rodent damage in Australian macadamia orchards by manipulation of adjacent non-crop habitats. Crop Protection, 17(4), 353–357.
Wykes, W. N. (1989). Rat bite injury to the eyelids in a 3-month-old child. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 73(3), 202–204.
Yan, X., Zhenyu, L., Gregg, W. P., & Dianmo, L. (2001). Invasive species in China—an overview. Biodiversity & Conservation, 10(8), 1317–1341.
Young, N., Carter, L., & Evangelista, P. (2011). A MaxEnt model v3. 3.3 e tutorial (ArcGIS v10). Colorado: Fort Collins.
Zaidi, F., Fatima, S. H., Khisroon, M., & Gul, A. (2016). Distribution modeling of three screwworm species in the ecologically diverse landscape of North West Pakistan. Acta Tropica, 162, 56–65.
Zareef, S., Nasim, S., Kalsoom, S., Jabeen, F., Javed, Z., Nadeem, M. S., & Beg, M. A. (2009). Occurrence of the Norway rat, Rattus norvegicus, in Rawalpindi and Islamabad. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 41(5), 415–416.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to two BS students of Zoology Department University of Peshawar, Miss Seemab and Miss Sumaira, for data collection from Lady Reading Hospital of Peshawar. We are also thankful to Mr. Shahryar, photographer APP, for providing photographs of Peshawar City after a rainstorm.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHF formulated methodology, carried out data analysis using GIS tools, and prepared the manuscript. FZ designed the study and prepared the manuscript. MA contributed in data acquisition. AA extended helped during the geospatial analysis. QJ collected and identified rat specimens. MK worked out the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Availability of data and materials
Our data is available on Mendeley Data online repository.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatima, S.H., Zaidi, F., Adnan, M. et al. Rat-bites of an epidemic proportion in Peshawar vale; a GIS based approach in risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 190, 233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6605-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6605-7