Abstract
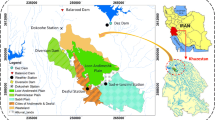
In semi-arid areas like the Kairouan region, salinization has become an increasing concern because of the constant irrigation with saline water and over use of groundwater resources, soils, and aquifers. In this study, a methodology has been developed to evaluate groundwater contamination risk based on the unsaturated zone hydraulic properties. Two soil profiles with different ranges of salinity, one located in the north of the plain and another one in the south of plain (each 30 m deep) and both characterized by direct recharge of the aquifer, were chosen. Simulations were conducted with Hydrus-1D code using measured precipitation data for the period 1998–2003 and calculated evapotranspiration for both chosen profiles. Four combinations of initial conditions of water content and salt concentration were used for the simulation process in order to find the best match between simulated and measured values. The success of the calibration of Hydrus-1D allowed the investigation of some scenarios in order to assess the contamination risk under different natural conditions. The aquifer risk contamination is related to the natural conditions where it increased while facing climate change and temperature increase and decreased in the presence of a clay layer. Hydrus-1D was a useful tool to predict the groundwater level and quality in the case of a direct recharge and in the absence of any information related to the soil layers except for the texture.














Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 October 2018
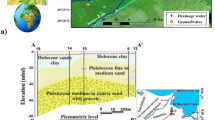
The Fig. 3 in this article has been obscured as the required permissions to reproduce it were not obtained.
References
Allen, R. G., Pereira, L. S., Raes, D., Smith, M. (1998). Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage, 300. Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, p. 6541.
Arampatzis, G., Tzimopoulos, C., Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M., & Yannopoulos, S. (2001). Estimation of unsaturated flow in layered soils with the finite control volume method. Irrigation and Drainage, 50, 349–358.
Bahri, A. (1982). Utilisation des eaux et des sols salés dans la plaine de Kairouan (156 pp). INP Toulouse: Thèse du diplôme de docteur-ingénieur.
Belkhodja, K. (1970). Origine, évolution et caractères de la salinité dans les sols de la plaine de Kairouan (Tunisie centrale): contribution à l'étude de leur mise en valeur (Doctoral dissertation).
Ben Ammar, S. (2007). Contribution to the hydrogeological, geochemical and isotopic study of Ain El Beidha and Merguellil (Kairouan plain) aquifers: Implication for the dam-aquifer relationship. INIS-TN-075.
Besbes, M. (1975). Etude hydrogéologique de la plaine de Kairouan sur modèles mathématiques. CIG–EMP/DGRE, Fontainebleau, France, Rapport scientifique, LHM/RD/75/16 (p. 121).
Besbes, M., Marsily, G. (1976). L'analyse d'un grand réservoir aquifère en vue de sa modélisation. In :Conférence AIH - L'hydrologie des grands bassins sédimentaires, Budapest.
Bouwer, H. (2000). Integrated water management: emerging issues and challenges. Agricultural Water Management, 45, 217–228.
Castany, G. (1968). Aménagement des oueds Zeroud et Merguellil. Alimentation des nappes de la plaine de Kairouan par les eaux des oueds Zeroud et Merguellil Direction de l’Hydraulique et de l’Equipement Rural. Paris: BRGM.
Chaieb, H. (1988). Contribution à la réactualisation des modèles hydrogéologiques de la plaine de Kairouan. DEA, Faculté des sciences de Tunis. 87p.
Cruesi. (1970). Recherche et Formation en matières d’irrigation avec les eaux salées : 1962-1969. Rapport Technique. Projet PNUD / UNESCO, 243:99.
Damodhara, R. M., Raghuwanshi, N. S., & Singh, R. (2006). Development of a physically based 1d-infiltration model for irrigated soils. Agricultural Water Management, 85, 165–174.
Gallali, T. (1980). Transfert sels-matière organique en zones arides méditerranéennes. Thèse, INPL Nancy, 202 pp.
Hachicha, A. A., Rodríguez, I., Capdevila, R., & Oliva, A. (2013). Heat transfer analysis and numerical simulation of a parabolic trough solar collector. Applied Energy, 111, 581–592.
Hillel, D. (1986). Negev-land, water, and life in a desert environment. Soil Environment, 141(1), 89.
Hopmans, J. W., & Stricker, J. N. M. (1989). Stochastic analysis of soil water regime in a watershed. Journal of Hydrology, 105, 57–84.
Kanzari, S., Sahraoui, H., & Hachicha, M. (2014). Laboratory method for characterization of soil/water adsorption coefficient. The Experiment Journal, 29(2), 1952–1956.
Keren, R. (2000). Salinity. In M. E. Summer (Ed.), Handbook of soil science (pp. G1–G26). Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press.
Luedeling, E., Nagiebn, M., Wichernn, F., Brandt, M., Deurer, M., & Buerkert, A. (2005). Drainage, salt leaching and physicochemical properties of irrigated man-made terrace soils in a mountain oasis of northern Oman. Geoderma, 125, 273–285.
Mansouri, R. (1995). Mobilisation des Ressources Supplémentaires à partir de la nappe de Kairouan. Direction des Études. Division Hydrogéologie centre et sud, SONEDE.
Mansouri, R. (1997). Bilan de la nappe mio-plio quaternaire de la nappe de Kairouan. Direction des Études. Division Hydrogéologie centre et sud, SONEDE.
Mualem, Y. (1976). A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resources Research, 12(3), 513–522.
Rumynin, V. G. (2011). Subsurface solute transport models and case histories. Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous, 25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1306-2.
Schaap, M. G., Leij, F. J., & van Genuchten, M. T. (2001). Rosetta: a computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions. Journal of Hydrology, 251, 163–176.
Selker, J. S., Keller, C. K., & McCord, J. T. (1999). Vadoze zone processes (339pp). New York: Lewiw Publishers.
Šimůnek, J., Šejna, M., Saito, H., Sakai, M., Van Genuchten, M. Th. (1998). HYDRUS 1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media: IGWMC—TPS70 version 2.0. Colorado School of Mines, 178 pages.
Soutter, M., & Musy, A. (1999). Global sensitivity analysis of three pesticide leaching models using a Monte-Carlo approach. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28(4), 1290–1297.
Stephens, D. B. (1996). Vadoze Zone Hydrology. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press.
Vanderborght, J., & Vereecken, H. (2007). Review of dispersivities for transport modeling in soils. Vadose Zone Journal, 6, 29–52.
Van Genuchten, M. T. (1980). A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 44(5), 892–898.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saâdi, M., Zghibi, A. & Kanzari, S. Modeling interactions between saturated and un-saturated zones by Hydrus-1D in semi-arid regions (plain of Kairouan, Central Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 190, 170 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6544-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6544-3