Abstract
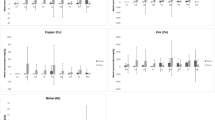
Heavy metal accumulation is recognized as a very important global pollution problem in the last decades. Plant species have been recognized as natural bioindicators of environmental pollution, especially the amount of heavy metals in soils. Moreover, only a limited number of plant species can survive in highly contaminated soils. It is also known that metal accumulation can vary greatly among different populations of the same species. This study examines the chemical composition and accumulation potential of the expansive clonal grass Calamagrostis epigejos at five localities exposed to different levels of anthropogenic pressure. Considerable differences were observed between uptake, translocation, and accumulation of total and available heavy metals, such differences corresponding to soil physico-chemical characteristics and the level of site pollution. The results indicate that Calamagrostis epigejos uptakes a significant portion of the available fraction of heavy metals in the soil and stores it in the roots, thereby exhibiting a certain potential for metal phytostabilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken, S. G., Dore, W. G., Lefkovitch, L. P., & Armstrong, K. C. (1989). Calamagrostis epigejos (Poaceae) in North America, especially Ontario. Canadian Journal of Botany, 67(11), 3205–3321. https://doi.org/10.1139/b89-400.
Alloway, B.J. (2013). Heavy Metals in Soils–Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils. London: Chapman & Hall. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1344-1.
Al-Wabel, M. I., Sallam, A. E. A. S., Usman, A. R., Ahmad, M., El-Naggar, A. H., El-Saeid, M. H., Al-Faraj, A., El-Enazi, K., & Al-Romian, F. A. (2017). Trace metal levels, sources, and ecological risk assessment in a densely agricultural area from Saudi Arabia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(6), 252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5919-1.
Antonijević, M. M., Dimitrijević, M. D., Milić, S. M., & Nujkić, M. M. (2012). Metal concentrations in the soils and native plants surrounding the old flotation tailings pond of the copper mining and smelting complex Bor (Serbia). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 14(3), 866–877. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em10803h.
Ashraf, M. A., Maah, M. J., & Yusoff, I. (2011). Heavy metals accumulation in plants growing in ex tin mining catchment. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 8(2), 401–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326227.
Baumeister, W., & Ernst, W. H. O. (1978). Mineralstoffe und Pflanzenwachstum. Stuttgart: G Fischer.
Bert, V., Lors, C., Ponge, J. F., Caron, L., Biaz, A., Dazy, M., & Masfaraud, J. F. (2012). Metal immobilization and soil amendment efficiency at a contaminated sediment landfill site: a field study focusing on plants, springtails, and bacteria. Environmental Pollution, 169, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.021.
Bloemen, M. L., Markert, B., & Lieth, H. (1995). The distribution of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in topsoils of Osnabrück in relation to land use. Science of the Total Environment, 166(1), 137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(95)04520-B.
Bose, S., & Bhattacharyya, A. K. (2008). Heavy metal accumulation in wheat plant grown in soil amended with industrial sludge. Chemosphere, 70(7), 1264–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.062.
Bryndová, I., & Kovář, P. (2004). Dynamics of the demographic parameters of the clonal plant Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth in two kinds of industrial deposits (abandoned sedimentation basins in Bukovina and Chvaletice). In P. Kovář (Ed.), Natural recovery of human-made deposits in landscape (biotic interactions and ore/ash-slag artificial ecosystems) (pp. 267–276). Prague: Academia.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., Fan, K. K., Yu, K., Wu, X., & Tian, Q. Z. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60(4), 542–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.072.
Davies, B. E. (1995). Lead. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (pp. 206–223). London: Blackie Academic. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1344-1_9.
Drakatos, P. A., Kalavrouziotis, I. K., Hortis, T. C., Varnanas, S. P., Drakatos, S. P., Bladenopoulou, S., & Fanariotou, I. N. (2002). Antagonistic action of Fe and Mn in Mediterranean-type plants irrigated with wastewater effluents following biological treatment. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 59(1), 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207230211961.
Dudka, S., & Adriano, D. C. (1997). Environmental impacts of metal ore mining and processing: a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26(3), 590–602. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600030003x.
Dukić, D. (1960). Reke Beograda i njegove okoline (the rivers of Belgrade and its surroundings). Zbornik Radova Geografskog Instituta, 17, 151–163 (In Serbian).
Ebbs, S. D., & Kochian, L. V. (1997). Toxicity of zinc and copper to Brassica species: implications for phytoremediation. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26(3), 776–781. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600030026x.
Eisenhauer, N., Beßler, H., Engels, C., Gleixner, G., Habekost, M., Milcu, A., Partsch, S., Sabais, A. C. W., Scherber, C., Steinbeiss, S., Weigelt, A., Weisser, W. W., & Scheu, S. (2010). Plant diversity effects on soil microorganisms support the singular hypothesis. Ecology, 91(2), 485–496. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-2338.1.
Elhottová, D., Krištufek, V., Malý, S., & Frouz, J. (2009). Rhizosphere effect of colonizer plant species on the development of soil microbial community during primary succession on postmining sites. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 40(1-6), 758–770. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620802693193.
Ellenberg, H., Weber, H. E., Düll, R., Wirth, V., Werner, W., & Paulissen, D. (1991). Zeigerwerte von Pflanzen in Mitteleuropa. Scripta Geobotanica 18. Göttingen: Erich Goltze.
FAO. (1974). The Euphrates pilot irrigation project. Methods of soil analysis. Gadeb soil laboratory (a laboratory manual). Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Gajić, G., Pavlović, P., Kostić, O., Jarić, S., Đurđević, L., Pavlović, D., & Mitrović, M. (2013). Ecophysiological and biochemical traits of three herbaceous plants growing on the disposed coal combustion fly ash of different weathering stage. Archives of Biological Sciences, 65(4), 1651–1667. https://doi.org/10.2298/ABS1304651G.
Greger, M. (2004). Metal availability, uptake, transport and accumulation in plants. In M. N. Prasad & J. Hagemeyer (Eds.), Heavy metal stress in plants (pp. 1–27). Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-07743-6_1.
ISO 11047 (1998). Soil quality—determination of cadmium, chromium, cobalt, copper, lead, manganese, nickel and zinc—flame and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric methods. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO 11261 (1995). Soil quality. Determination of total nitrogen. Modified Kjeldahl method. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
ISO 11466. (1995). Soil quality-extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
Izaguirre-Mayoral, M. L., & Sinclair, T. R. (2005). Soybean genotypic difference in growth, nutrient accumulation and ultrastructure in response to manganese and iron supply in solution culture. Annals of Botany, 96(1), 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci160.
Jelenković, R., Milovanović, D., Koželj, D., & Banješević, M. (2016). The mineral resources of the Bor metallogenic zone: a review. Geologia Croatica, 69(1), 143–155. https://doi.org/10.4154/GC.2016.11.
John, M. K. (1976). Interelationships between plant cadmium and uptake of some other elements from culture solutions by oats and lettuce. Environmental Pollution, 11(2), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-9327(76)90021-5.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group.
Koronatova, N. G., & Milyaeva, E. V. (2011). Plant community succession in post-mined quarries in the northern-taiga zone of West Siberia. Contemporary Problems of Ecology, 4(5), 513–518. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995425511050109.
Kovář, P., Štěpánek, J., Kirschner, J. (2004). Clonal diversity of Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth in relation to type of industrial substrate and successional stage. In: Kovář P. (ed.): Natural Recovery of Human-Made Deposits in Landscape (Biotic Interactions and Ore/Ash-Slag Artificial Ecosystems), 285–293.
Lehmann, C. (1997). Clonal diversity of populations of Calamagrostis epigejos in relation to environmental stress and habitat heterogeneity. Ecography, 20(5), 483–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.1997.tb00416.x.
Lehmann, C., & Rebele, F. (2004a). Evaluation of heavy metal tolerance in Calamagrostis epigejos and Elymus repens revealed copper tolerance in a copper smelter population of C. epigejos. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 51(3), 199–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2003.10.002.
Lehmann, C., & Rebele, F. (2004b). Assessing the potential for cadmium phytoremediation with Calamagrostis epigejos: a pot experiment. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 6(2), 169–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/16226510490454849.
Lehmann, C., & Rebele, F. (2005). Phenotypic plasticity in Calamagrostis epigejos (Poaceae): response capacities of genotypes from different populations of contrasting habitats to a range of soil fertility. Acta Oecologica, 28(2), 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2005.03.005.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42(3), 421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x.
Lux, A., Martinka, M., Vaculík, M., & White, P. J. (2010). Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. Journal of Experimental Botany, 62(1), 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq281.
Malcová, R., Albrechtová, J., & Vosátka, M. (2001). The role of the extraradical mycelium network of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the establishment and growth of Calamagrostis epigejos in industrial waste substrates. Applied Soil Ecology, 18(2), 129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(01)00156-1.
Mattina, M. I., Lannucci-Berger, W., Musante, C., & White, J. C. (2003). Concurrent plant uptake of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from soil. Environmental Pollution, 124(3), 375–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00060-5.
McDonald, R. C., Isbell, R. F., Speight, J. G., Walker, J., & Hopkins, M. S. (1998). Australian soil and land survey field handbook. Canberra: Australian Collaborative Land Evaluation Program.
McKeague, J. A. (1978). Manual on soil sampling and methods of analysis. Ottawa: Canadian Society of Soil Science.
Mitrović, M., Pavlović, P., Lakušić, D., Djurdjević, L., Stevanović, B., Kostić, O., & Gajić, G. (2008). The potential of Festuca rubra and Calamagrostis epigejos for the revegetation of fly ash deposits. Science of the Total Environment, 407(1), 338–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.09.001.
Muchuweti, M., Birkett, J. W., Chinyanga, E., Zvauya, R., Scrimshaw, M. D., & Lester, J. N. (2006). Heavy metal content of vegetables irrigated with mixtures of wastewater and sewage sludge in Zimbabwe: implications for human health. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 112(1), 41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2005.04.028.
Mudrinić, Č. (1975). Primary dispersion aureoles of the antimony deposit stolice (Western Serbia) [in Serbian]. Belgrade: Transactions of the Faculty of Mining and Geology, University of Belgrade.
Nádaská, G., Lesny, J., & Michalik, I. (2010). Environmental aspect of manganese chemistry. Health and Environment Journal, 100702-A, 1–16.
Nagajyoti, P. C., Lee, K. D., & Sreekanth, T. V. M. (2010). Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8(3), 199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-010-0297-8.
Navarrete, I. A., Gabiana, C. C., Dumo, J. R. E., Salmo, S. G., Guzman, M. A. L. G., Valera, N. S., & Espiritu, E. Q. (2017). Heavy metal concentrations in soils and vegetation in urban areas of Quezon City, Philippines. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(4), 145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5849-y.
Orwin, K. H., Buckland, S. M., Johnson, D., Turner, B. L., Smart, S., Oakley, S., & Bardgett, R. D. (2010). Linkages of plant traits to soil properties and the functioning of temperate grassland. Journal of Ecology, 98(5), 1074–1083. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2010.01679.x.
Peplow, D. (1999). Environmental impacts of mining in Eastern Washington. Washington DC: Center for Water and Watershed studies fact sheet, University of Washington.
Prach, K., & Pyšek, P. (2001). Using spontaneous succession for restoration of human-disturbed habitats: experience from Central Europe. Ecological Engineering, 17(1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(00)00132-4.
Radosavljević, A. S., Stojanović, N. J., Radosavljević-Mihajlović, S. A., & Kašić, V. (2013). Polymetallic mineralization of the Boranja Orefield, Podrinje Metallogenic District, Serbia: zonality, mineral associations and genetic features. Periodico di Mineralogia, 82(1), 61–87.
Ranđelović, D., Jovanović, S., Mihailović, N., Šajn, R. (2015). The content of manganese in soils and plants of Bor mine overburden site (Serbia, SE Europe). Proceedings of XXIII International Conference ‘Ecological Truth’, 17–20 June 2015, Kopaonik, Serbia, 186–192.
Rebele, F. (2000). Competition and coexistence of rhizomatous perennial plants along a nutrient gradient. Plant Ecology, 147(1), 77–94. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009808810378.
Rebele, F., & Lehmann, C. (2001). Biological flora of central Europe: Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth. Flora, 196(5), 325–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0367-2530(17)30069-5.
Rutkowski, L. (2008). A key to identification of vascular plants of lowland Poland. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN.
Salminen, R., Batista, M. J., Bidovec, M., Demetriades, A., De Vivo, B., De Vos, W., Duris, M., Gilucis, A., Gregorauskiene, V., Halamic, J., Heitzmann, P., Lima, A., Jordan, G., Klaver, G., Klein, P., Lis, J., Locutura, J., Marsina, K., Mazreku, A., O'Connor, P. J., Olsson, S. A., Ottesen, R.-T., Petersell, V., Plant, J. A., Reeder, S., Salpeteur, I., Sandström, H., Siewers, U., Steenfelt, A., & Tarvainen, T. (2005). Geochemical atlas of Europe. Part 1: background information, methodology and maps. Espoo: Geological Survey of Finland.
Šerbula, S. M., Radojevic, A. A., Kalinovic, J. V., & Kalinovic, T. S. (2014). Indication of airborne pollution by birch and spruce in the vicinity of copper smelter. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(19), 11510–11520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3120-4.
Sharma, R. K., & Agrawal, M. (2005). Biological effects of heavy metals: an overview. Journal of Environmental Biology, 26(2), 301–313.
Shenker, M., & Chen, Y. (2005). Increasing iron availability to crops: fertilizers, organo-fertilizers, and biological approaches. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 51(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2005.tb00001.x.
Siedlecka, A. (1995). Some aspects of interactions between heavy metals and plant mineral nutrients. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 64(3), 265–272.
Somodi, I., Virágh, K., & Podani, J. (2008). The effect of the expansion of the clonal grass Calamagrostis epigejos on the species turnover of a semi-arid grassland. Applied Vegetation Science, 11(2), 187–192. https://doi.org/10.3170/2008-7-18354.
StatSoft. (2007). Statistica for Windows, version 8.0. Tulsa: StatSoft Inc..
Stefanowicz, A. M., Kapusta, P., Błońska, A., Kompała-Bąba, A., & Woźniak, G. (2015). Effects of Calamagrostis epigejos, Chamaenerion palustre and Tussilago farfara on nutrient availability and microbial activity in the surface layer of spoil heaps after hard coal mining. Ecological Engineering, 83, 328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.06.034.
Süss, K., Storm, C., Zehm, A., & Schwabe, A. (2004). Succession in inland sand ecosystems: which factors determine the occurrence of the tall grass species Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth and Stipa capillata L.? Plant Biology, 6(04), 465–476.
Thornton, I. (1991). Metal contamination of soils in urban areas. In P. Bullock, & P. J. Gregory (Eds.), Soils in the urban environment (pp. 47–75). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd., https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444310603.ch4
Tůma, I., Holub, P., & Fiala, K. (2009). Soil nutrient heterogeneity and competitive ability of three grass species (Festuca ovina, Arrhenatherum elatius and Calamagrostis epigejos) in experimental conditions. Biologia, 64(4), 694–704.
Viard, B., Pihan, F., Promeyrat, S., & Pihan, J. C. (2004). Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, cd) highway pollution: bioaccumulation in soil, Graminaceae and land snails. Chemosphere, 55(10), 1349–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.003.
Warden, B. T., & Reisenauer, H. M. (1991). Manganese-iron interactions in the plant-soil system. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 14(1), 7–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169109364180.
Wohltmann, F. (1903). Chilisalpeter oder Ammoniak? Berlin: Parey.
Zemanová, V., Pavlík, M., Pavlíková, D., Hnilicka, F., & Vondrackova, S. (2016). Responses to Cd stress in two Noccaea species (Noccaea praecox and Noccaea caerulescens) originating from two contaminated sites in Mezica, Slovenia and Redlschlag, Austria. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 70(3), 464–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0198-8.
Zhang, X. Y., Lin, F. F., Wong, M. T., Feng, X. L., & Wang, K. (2009). Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154(1), 439–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0410-7.
Zimdahl, R. L., Arvik, J. H., & Hammond, P. B. (1973). Lead in soils and plants: a literature review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 3(1–4), 213–224.
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Mr. Raymond Dooley for the linguistic editing.
Funding
The Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia supported this research through Projects number 176016 and 173030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranđelović, D., Jakovljević, K., Mihailović, N. et al. Metal accumulation in populations of Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth from diverse anthropogenically degraded sites (SE Europe, Serbia). Environ Monit Assess 190, 183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6514-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6514-9