Abstract
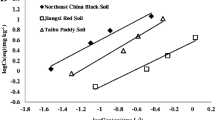
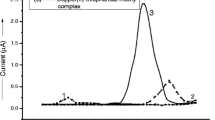
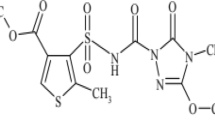
Pyraoxystrobin, (E)-2-(2-((3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-5-yloxy)methyl)phenyl)-3-methoxyacrylate, is a newly developed strobilurin fungicide with high antifungal efficiency. It has high potential to enter soil environments that might subsequently impact surface and groundwater. Therefore, 14C-labeled pyraoxystrobin was used as a tracer to study the adsorption/desorption and migration behavior of this compound under laboratory conditions in three typical agricultural soils. The adsorption isotherms conformed with the Freundlich equation. Single factor analysis showed that organic matter content was the most important factor influencing the adsorption. The highest adsorption level was measured in soil with low pH and high organic carbon content. Once adsorbed, only 2.54 to 6.41% of the adsorbed compound could be desorbed. In addition, the mobility results from thin-layer chromatography and column leaching studies showed that it might be safe to use pyraoxystrobin as a fungicide without causing groundwater pollution from both runoff and leaching, which might be attributed to its strong hydrophobicity. High organic matter content enhanced pyraoxystrobin adsorption and desorption because of the rule of similarity (lipid solubility). In the column leaching study, 95.02% (minimum value) of the applied 14C remained within the upper 4.0-cm layer after 60 days.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur, J. D., Mark, N. W., Taylor, S., Simunek, J., Brusseau, M. L., & Dontsova, K. M. (2017). Batch soil adsorption and column transport studies of 2,4-dinitroanisole (DNAN) in soils. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 199, 14–23.
Boivin, A., Cherrier, R., Perrin-Ganier, C., & Schiavon, M. (2004). Time effect on bentazone sorption and degradation in soil. Pest Management Science, 60(8), 809–814. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.889.
Boivin, A., Cherrier, R., & Schiavon, M. (2005a). A comparison of five pesticides adsorption and desorption processes in thirteen contrasting field soils. Chemosphere, 61(5), 668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.024.
Boivin, A., Amellal, S., Schiavon, M., & Van Genuchten, M. T. (2005b). 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) sorption and degradation dynamics in three agricultural soils. Environmtal Pollution, 138(1), 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.02.016.
Carrizosa, M. J., Calderon, M. J., Hermosin, M. C., & Cornejo, J. (2000). Organosmectites as sorbent and carrier of the herbicide bentazone. Science of the Total Environment, 247(2-3), 285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00498-2.
Chen, K. L., Liu, L. C., & Chen, W. R. (2017). Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics in high organic content soils. Environmental Pollution, 231(Pt 1), 1163–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.011.
Clausen, L., & Fabricius, I. (2002). Atrazine, isoproturon, mecoprop, 2, 4-D, and bentazone adsorption onto iron oxides. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 858–869.
Cox, L., Hermosín, M. C., Celis, R., & Cornejo, J. (1997). Sorption of two polar herbicides in soils and soil clays suspensions. Water Research, 31(6), 1309–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00337-5.
Ding, G. W., Novak, J. M., Herbert, S., & Xing, B. S. (2002). Long-term tillage effects on soil metolachlor sorption and desorption behavior. Chemosphere, 48(9), 897–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00188-1.
Dubus, I. G., Barriuso, E., & Calvet, R. (2001). Sorption of weak organic acids in soils: clofencet, 2,4-D and salicylic acid. Chemosphere, 45(6-7), 767–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00108-4.
Dur, J. C., Gouy, V., Calvet, R., Belamie, R., & Chaplain, V. (1998). Influence of adsorption-desorption phenomena on pesticide runoff measured under controlled conditions. Comptes Rendus de 1’Academie des Sciences-Series IIA-Earth Planetary Science, 327, 405–411.
Gao, J. P., Maguhn, J., Spitzauer, P., & Kettrup, A. (1998). Sorption of pesticides in the sediment of the Teufelsweiher pond (southern Germany).: equilibrium assessments, effect of organic carbon content and pH. Water Research, 32(5), 1662–1672. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00377-1.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle size analysis klute a methods of soil analysis part 1 physical and mineralogical methods (pp. 383–412). Madison, WI: Soil Science Society Soil of America.
Guo, J. F., Zhu, G. N., & Shi, J. J. (2003). Adsorption, desorption and mobility of fomesafen in Chinese soils. Water Air Soil Pollution, 148(1/4), 77–85. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025484213539.
He, L. W., Shi, L. L., Kong, D. Y., Shan, Z. J., & Zong, L. G. (2006). Leaching of carbofuran and atrazine in soil columns and its affecting factors. Journal of Ecology Rural Environment, 22, 71–74.
Huang, W. L., Yu, H., & Weber Jr., W. J. (1998). Hystersis in the sorption and desorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants by soils and sediments: I. A comparative analysis of experimental protocols. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 31(1–2), 129–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(97)00056-9.
Laabs, V., Amelung, W., Pinto, A., Altstaedt, A., & Zech, W. (2000). Leaching and degradation of corn and soybean pesticides in an Oxisol of Brazilian Cerrados. Chemosphere, 41(9), 1441–1449. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00546-9.
Li, M., Liu, C. L., Yang, J. C., Zhang, J. B., Li, Z. N., Zhang, H., & Li, Z. M. (2010). Synthesis and biological activity of new (E)-α- (methoxyimino)benzeneacetate derivatives containing a substituted pyrazole ring. Journal of Agriculture Food Chemistry, 58(5), 2664–2667. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9026348.
Linn, D. M., Carski, T. H., Brusseau, M. L., & Chang, F. H. (1993). Sorption and degradation of pesticides and organic chemicals in soil (p. 260). Madison, WI: Soil Science Society of America.
Liu, X. Y., Ye, Q. F., Kan, D. L., Zhang, Z., & Ding, X. C. (2011). Synthesis of carbon-14 labeled pyraoxystrobin, a novel fungicide. Journal of Labelled Compounds and Pharmaceuticals, 54(13), 780–782. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlcr.1929.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In A. M. Page (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 2, chemical and microbiological properties (pp. 539–579). Wisconsin, Madison: American Society of Agronomy: Roeth FW. Enhanced herbicide.
OECD. (2000). Guideline for the testing of chemicals (106): Adsorption–desorption using a batch equilibrium method. Paris, France.
Ravanel, P., Liégeois, M. H., Chevallier, D., & Tissult, M. (1999). Soil thin-layer chromatography and pesticide mobility through soil microstructures. New technical approach. Journal of Chromatography A, 864(1), 145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(99)01007-9.
Redoudo, M. J., Ruiz, M. J., & Boluda, R. (1997). Dissipation and distribution of atrazine, simazine, chlorpyrifos, and tetradifon residues in citrus orchard soil. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 32(4), 346–352.
Ren, W. J., Wang, M. E., & Zhou, Q. X. (2011). Effect of soil pH and organic matter on desorption hysteresis of chlorimuron-ethyl in two typical Chinese soils. Journal of Soils Sediment, 11(4), 552–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0337-4.
Sánchez-Camazano, M., Sánchez-Martín, M. J., & Delgado-Pascual, R. (2000). Adsorption and mobility of linuron in soils as influenced by soil properities, organic amendments, and surfactants. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48(7), 3018–3026. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf990812i.
Spark, K. M., & Swift, R. S. (2002). Effect of soil composition and dissolved organic matter on pesticide sorption. Science of Total Environment, 298(1-3), 147–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00213-9.
Wang, L., Li, B. J., Xiang, W. S., Shi, Y. X., & Liu, C. L. (2008). Control effects of pyraoxystrobin on cucumber powdery mildew. Agrochemistry. (in Chinese), 47(5), 378–380.
Weber, J.(1986). Herbicide mobility in soil leaching columns. In Research Methods in weed science; Camper, N.D., Ed.; Southern Weed Science Society, Champaign.
Worrall, F., Fernandez-Perez, M., Johnson, A. S., Flores Cesperedes, F., & Gonzalez-Pradas, E. (2001). Limitations on the role of incorporated organic matter in reducing pesticide leaching. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 49(3-4), 241–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00197-2.
Yue, L., Ge, C. H., Feng, D., Yu, H. M., Deng, H., & Fu, B. M. (2017). Adsorption-desorption behavior of atrazine on agricultural soils in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 57, 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.11.002.
Acknowledgements
We thank Catherine Dandie, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Research Development Fund of Zhejiang A&F University (2015FR013) and Program of Innovative Entrepreneurship Training for Undergraduate of China (201610341008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wu, H., Hu, T. et al. Adsorption and leaching of novel fungicide pyraoxystrobin on soils by 14C tracing method. Environ Monit Assess 190, 86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6458-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6458-5