Abstract
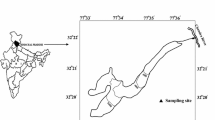
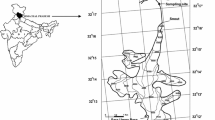
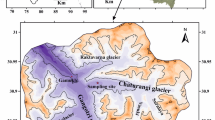
The hydrochemistry of meltwater from the Sutri Dhaka Glacier, Western Himalaya, has been studied to understand the influence of the factors controlling the weathering processes of the glaciers during the peak ablation period. The high solar irradiance prompted intense melting, which has raised the stream flow of the glacier. The meltwater has been observed as slightly alkaline (mean pH 8.2) and contains the major anions (HCO3 − > SO4 2− > NO3 − > Cl−) and cations (Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ > Na+ > NH4 +) with Ca2+ (78.5%) and HCO3 − (74.5%) as the dominant species. The piper diagram indicates the category of stream meltwater as Ca2+-HCO3 − type. In addition, it is evident from the Gibbs diagram that the interaction between the meltwater and bedrock controls the ionic concentrations of the glacial meltwater. The high ratio value (~ 0.75) of HCO3 −/(HCO3 − + SO4 2−) indicates that the carbonate weathering is dominant. Fe and Al followed by Mn, Sr, and Ti are the most dominant trace elements present in the meltwater. The significant negative correlation exhibited by the major ions and Sr with the discharge is recommended for the enrichment of these solutes during the lean discharge periods. However, the insignificant correlation of Fe, Al, Mn, and Ti with discharge suggests their physicochemical control. The principal component analysis (PCA) carried has highlighted three dominant composites, i.e., the water-rock interaction, atmospheric dust inputs, and physicochemical changes in the meltwater. Hence, the present study elucidates the export of geochemical solutes from Sutri Dhaka Glacier and factors governing the water chemistry, which helps in the better understanding of hydrochemical processes of the Himalayan glaciers and substantial improvement of our understanding about the glacio-hydrological environments and their response in the scenario of global warming.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, S., Hasnain, S. I. (2000). Meltwater characteristics of Garhwal Himalayan glaciers. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 56, 431–439.
Anshumali, & Ramanathan, A. L. (2007). Seasonal variation in the major ion chemistry of Pandoh Lake, Mandi District, Himachal Pradesh, India. Applied Geochemistry, 22(8), 1736–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.03.045.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21st Edition. Washington DC: American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation.
Bolch, T., Kulkarni, A., Kaab, A., Huggel, C., Paul, F., Cogley, J. G., et al. (2012). The state and fate of Himalayan glaciers. Science, 336, 310–314. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215828.
Bowman, R. S. (1997). Aqueous environmental geochemistry. Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 78(50), 586. https://doi.org/10.1029/97EO00355.
Brown, G. H. (2002). Glacier meltwater hydrochemistry. Applied Geochemistry, 17(7), 855–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00123-8.
Brown, G. H., & Fuge, R. O. N. (1998). Trace element chemistry of glacial meltwaters in an alpine headwater catchment, 2(248), 435–442.
Gaillardet, J., Dupre, B., Louvat, P., & Allegre, C. J. (1999). Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chemical Geology, 159(1–4), 3–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5.
Gaillardet, J., Viers, J., & Dupre, B. (2003). Trace elements in river waters. Treatise on Geochemistry, 5, 225–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043751-6/05165-3.
Garrels, R. M., & Fred, T. M. (1972). A quantitative model for the sedimentary rock cycle. Marine Chemistry, 1(1), 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(72)90004-7.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170(3962), 1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088.
Hasnain, S. I., & Thayyen, R. J. (1999). Discharge and suspended-sediment concentration of meltwaters, draining from the Dokriani glacier, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Journal of Hydrology, 218(3-4), 191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00033-5.
Huang, X., Sillanpää, M., Gjessing, E. T., & Vogt, R. D. (2009). Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Science of the Total Environment, 407(24), 6242–6254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.09.001.
Hubbard, B., & Nienow, P. (1997). Alpine subglacial hydrology. Quaternary Science Reviews, 16(9), 939–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(97) 00031-0.
Immerzeel, W. W., Kraaijenbrink, P. D. A., Shea, J. M., Shrestha, A. B., Pellicciotti, F., Bierkens, M. F. P., & De Jong, S. M. (2014). High-resolution monitoring of Himalayan glacier dynamics using unmanned aerial vehicles. Remote Sensing of Environment, 150, 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.04.025.
Immerzeel, W. W., van Beek, L. P. H., & Bierkens, M. F. P. (2010). Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science (New York, N.Y.), 328(5984), 1382–1385. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1183188.
Meybeck, M. (1987). Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. American Journal of Science, 287, 401–428. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.287.5.401.
Mitchell, A. C., & Brown, G. H. (2007). Diurnal hydrological—physicochemical controls and sampling methods for minor and trace elements in an Alpine glacial hydrological system. Journal of Hydrology, 332(1–2), 123–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.06.026.
Mitchell, A. C., Brown, G. H., & Fuge, R. (2005). Are minor and trace elements useful indicators of chemical weathering processes and flow-routing in subglacial hydrological systems. 62nd Eastern Snow Conference Waterloo, ON, Canada, 49–67.
Moeller, C. A., Mickelson, D. M., Anderson, M. P., & Winguth, C. (2007). Groundwater flow beneath Late Weichselian glacier ice in Nordfjord, Norway. Journal of Glaciology, 53(180), 84–90. https://doi.org/10.3189/172756507781833811.
Nijampurkar, V. N., & Rao, D. K. (1992). Accumulation and flow rates of ice on Chhota Shigri glacier, central Himalaya, using radio active and stable isotopes. Journal of Glaciology, 38(128), 43–50. https://doi.org/10.3198/1992JoG38-128-43-50.
Owen, L. A. (1998). Timing and style of glaciation in the Himalayas. Himalayan Geology., 19(2), 39–47.
Owen, L. A., & England, J. (1998). Observations on rock glaciers in the Himalayas and Karakoram Mountains of northern Pakistan and India. Geomorphology, 26(1–3), 199–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(98)00059-2.
Palmer, C. D., & Cherry, J. A. (1984). Geochemical evolution of groundwater in sequences of sedimentary rocks. Journal of Hydrology, 75(1–4), 27–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(84)90045-3.
Pandey, S., & Parcha, S. K. (2013). Systematics, Biometry of the species Opsidiscus from the Middle Cambrian succession of the Spiti Basin, India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 82(4), 330–338.
Parkhurst, D. L. (1995). User’s guide to PHREEQE—a computer program for speciation, reaction-path, advective transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey Water Resources graphical user interface for the geochemical computer program Investigations Report.
Patel, L. K., Sharma, P., Thamban, M., Singh, A., & Ravindra, R. (2016). Debris control on glacier thinning—a case study of the Batal glacier, Chandra basin, Western Himalaya. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(4), 309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2362-5.
Paudyal, K., Baral, H., Burkhard, B., Bhandari, S. P., & Keenan, R. J. (2014). Participatory assessment and mapping of ecosystem services in a data-poor region: case study of community-managed forests in central Nepal. Ecosystem Services, 13, 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2015.01.007.
Paudyal, R., Kang, S., Sharma, C. M., Tripathee, L., Huang, J., Rupakheti, D., & Sillanpää, M. (2016). Major ions and trace elements of two selected rivers near Everest region, southern Himalayas, Nepal. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(1), 1–11.
Pedretti, D., Russian, A., Sanchez-Villa, X., & Dentz, M. (2016). Scale dependence of the hydraulic properties of a fractured aquifer estimated using transfer functions. Water Resour. Res., 52, 5008–5024. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR018660.
Plummer, L. N., Parkhurst, D. L., & Thorstenson, D. C. (1983). Development of reaction models for ground-water systems. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 47(4), 665–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016/0016.
Raina, V. K., & Srivastava, D. (2008). Glacier Atlas of India. Banglore: Geological Society of India.
Sharma, P., Patel, L. K., Ravindra, R., Singh, A., Mahalinganathan, K., & Thamban, M. (2016). Role of debris cover to control specific ablation of adjoining Batal and Sutri Dhaka glaciers in Chandra Basin (Himachal Pradesh) during peak ablation season. Journal of Earth System Science, 125, 459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0681-2.
Sharma, P., Ramanathan, A. L., & Pottakkal, J. (2013). Study of solute sources and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes of the Chhota Shigri Glacier meltwaters, Himachal Himalaya, India. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 58(5), 1128–1143. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.802092.
Shiller, A. M. (1997). Dissolved trace elements in the Mississippi River: seasonal, interannual, and decadal variability. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(20), 4321–4330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00245-7.
Singh, O. P., Hatwar, H. R., & Prasad.O. (2007). Surface and upper air meteorological features during onset phase of 2003 monsoon. Journal of Earth System Science, 116(4), 305–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0027-1.
Singh, V. B., Ramanathan, A. L., Pottakkal, J. G., & Kumar, M. (2014). Seasonal variation of the solute and suspended sediment load in Gangotri glacier meltwater, central Himalaya, India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79(PA), 224–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.010.
Singh, V. B., Ramanathan, A., Sharma, P., & Pottakkal, J. G. (2013). Dissolved ion chemistry and suspended sediment characteristics of meltwater draining from Chhota Shigri Glacier, western Himalaya, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(1), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1176-y.
Srivastava, D., Kumar, A., Verma, A., & Swaroop, S. (2014). Characterization of suspended sediment in Meltwater from Glaciers of Garhwal Himalaya. Hydrological Processes, 28(3), 969–979. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9631.
Tranter, M., Sharp, M. J., Lamb, H. R., Brown, G. H., Hubbard, B. P., & Willis, I. C. (2002). Geochemical weathering at the bed of Haut glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland—a new model. Hydrological Processes, 16(5), 959–993. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.309.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Director of National Centre for Antarctic and Ocean Research and Dr. Rasik Ravindra for their encouragement and the Ministry of Earth Science for providing financial support. The authors also wish to thank BL Redkar, Ashish Painginkar, and Lathika N. Padmanabhan for assistance with the laboratory analysis. The first author would like to thank Dr. Roseline Thakur, Dr. Kanthanathan Mahalinganathan, Dr. Runa Antony, Racheal Chacko, Rupesh Kumar Sinha, Vinay Kumar Gaddam, Dr. Bhanu Pratap, and Sunil Oulkar for their valuable comments. We acknowledge Dr. Andrew Mitchell for his assistance with the PHEERIQC software. We would like to thank the editor and an anonymous reviewer for careful reading and constructive suggestions, which helped us to improve our manuscript. This is NCAOR contribution number 33/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.T., Laluraj, C.M., Sharma, P. et al. Export fluxes of geochemical solutes in the meltwater stream of Sutri Dhaka Glacier, Chandra basin, Western Himalaya. Environ Monit Assess 189, 555 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6268-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6268-9