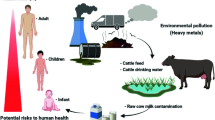
Abstract
Concentrations of essential (Cu, Mn, and Zn) and toxic (Cr, Cd, and Pb) trace metals in 30 raw cow’s milk samples were quantified using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. The samples were collected from the Nara-Awudarda, Tana-Abo, and Kosoye Amba-Rass sites in North Gondar, Ethiopia, preserved in a deep freezer (−20 °C), and then digested by Kjeldahl apparatus with HNO3/H2O2 (5:2; v/v) at 300 °C for 2.5 h. The data were subject to principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least square–discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). Overall hazard quotient (HQ) and carcinogenic risk (CR) values were also estimated to assess metal-related health risks. The mean concentrations of Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in the milk samples ranged 0.468–0.828, 1.614–2.806, 0.840–1.532, 1.208–5.267, ND–0.330, and ND–0.186 mg/kg, respectively. The lowest values were obtained for Kosoye Amba-Rass milk samples, while the highest were found for those collected from Nara-Awudarda milk samples, probably due to high mineral enrichment and metal leaching (especially Cd and Pb) from coal deposits. PCA revealed clustering of samples with respect to their geographic origin. Validation of PLS-DA model showed 100% classification efficiency using external validation samples and detected Cd and Cu as trace metal markers. The HQ and CR values were within the safe level; however, the former is close to the alert threshold level for Nara-Awudarda milk samples. Thus, further studies on common foodstuffs, constituting a higher proportion in the local diet, are required in this area to provide a complete risk assessment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla, M. O. M., Hassabo, A. A., & Elsheikh, N. A. H. (2013). Assessment of some heavy metals in waste water and milk of animals grazed around sugar cane plants in Sudan. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 25 (12).
Akele, M. L., Kelderman, P., Koning, C. W., & Irvine, K. (2016). Trace metal distributions in the sediments of the Little Akaki River, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(7). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5387-z.
Arellano, F. E., Gonçalvez, C. V. A., Carrera, A. L. P., Resio, A. N. C., & Cirelli, A. F. (2014). Presence of inorganic trace elements with an important nutritional value in ruminant S milk. Revista Senasa, 1–8.
Ataro, A., McCrindle, R. I., Botha, B. M., McCrindle, C. M. E., & Ndibewu, P. P. (2008). Quantification of trace elements in raw cows milk by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chemistry, 111(1), 243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.03.056.
Belete, T., Hussen, A., & Rao, V. M. (2014). Determination of concentrations of selected heavy metals in cows milk Borena zone, Ethiopia. Journal of Health Science, 4(5), 105–112. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.health.20140405.01.
Bilandžić, N., Dokić, M., Sedak, M., Solomun, B., Varenina, I., Knežević, Z., & Benić, M. (2011). Trace element levels in raw milk from northern and southern regions of Croatia. Food Chemistry, 127(1), 63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.12.084.
Birhanu, W. T., Chaueby, A. K., Teklemariam, T. T., Funtua, I. I., Oladipo, M. O. A., & Abubakar, N. (2014). Elemental analysis of soil around Aykle in Chilga District North Gondar, Ethiopia using the technique of instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA). International Journal of Advanced Scientific and Technical Research, 6(4), 455–468.
Brodziak, A., Litwińczuk, A., Kędzierska-Matysek, M., & Król, J. (2011). Content of selected macro- and microelements in milk of different cows breed and rennet whey. OchrOna ŚrOdOwiska i ZasObów naturalnych, 48, 467–474.
Chong, I. G., & Jun, C. H. (2005). Performance of some variable selection methods when multicollinearity is present. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 78(1), 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2004.12.011.
Codex Alimentarius Commission. (2007). Joint FAO/WHO food standards programme. Codex committee on methods of analysis and sampling, 28th session, Budapest, Hungary, 5–9 March 2007.
Daşbaşı, T., Saçmacı, Ş., Çankaya, N., & Soykan, C. (2016). Synthesis, characterization and application of a new chelating resin for solid phase extraction, preconcentration and determination of trace metals in some dairy samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 211, 68–73. daysoi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.037.
Dawd, A. G., Gezmu, T. B., & Haki, G. D. (2012). Essential and toxic metals in cow ’ s whole milk from selected sub-cities in Addis Ababa. Ethiopia, 1(1), 12–19.
Demirel, S., Tuzen, M., Saracoglu, S., & Soylak, M. (2008). Evaluation of various digestion procedures for trace element contents of some food materials. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152(3), 1020–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.077.
Dobrzański, Z., Kołacz, R., Górecka, H., Chojnacka, K., & Bartkowiak, A. (2005). The content of microelements and trace elements in raw milk from cows in the Silesian region. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 14(5), 685–689.
Elatrash, S., & Atoweir, N. (2014). Determination of lead and cadmium in biological material by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry method. International Journal of Chemical Sciences, 12(1), 92–100.
Enb, A., Donia, M. A., Abd-Rabou, N. S., Abou-Arab, A. A. K., & El-Senaity, M. H. (2009). Chemical composition of raw milk and heavy metals behavior during processing of milk products. Global Veterinaria, 3(3), 268–275.
Haiyan, W., & Stuanes, A. O. (2003). Heavy metal pollution in air-water-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 147(1–4), 79–107. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024522111341.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Masunaga, S. (2014). Trace metals in soil and vegetables and associated health risk assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(12), 8727–8739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4040-y.
Iwegbue, C. M. A., Nwozo, S. O., Ossai, E. K., & Nwajei, G. E. (2008). Heavy metal composition of some imported canned fruit drinks in Nigeria. American Journal of Food Technology, 3(3), 220–223.
Iyaka, Y. A. (2007). Concentration of Cu and Zn in some fruits and vegetables commonly available in north-central zone of Nigeria. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 6(6), 2150–2154.
Kędzierska-Matysek, M., Barłowska, J., Litwińczuk, Z., & Koperska, N. (2015). Content of macroand microelements in goat milk in relation to the lactation stage and region of production. Journal of Elementology, 20(1), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2013.18.4.549.
Kumar, A., Sharma, I. K., Sharma, A., Varshney, S., & Verma, P. S. (2009). Heavy metals contamination of vegetable foodstuffs in Jaipur (India). Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 8(2), 96–101.
LeDoux, M. (2011). Analytical methods applied to the determination of pesticide residues in foods of animal origin. A review of the past two decades. Journal of Chromatography A, 1218(8), 1021–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.12.097.
Li, Y., McCrory, D. F., Powell, J. M., Saam, H., & Jackson-Smith, D. (2005). A survey of selected heavy metal concentrations in Wisconsin dairy feeds. Journal of Dairy Science, 88, 2911–2922. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72972-6.
Licata, P., Trombetta, D., Cristani, M., Giofrè, F., Martino, D., Calò, M., & Naccari, F. (2004). Levels of “toxic” and “essential” metals in samples of bovine milk from various dairy farms in Calabria, Italy. Environment International, 30(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00139-9.
Lijalem, T., Jeevan, A., Bekele, T., & Berhe, A. (2015). Determination of some essential and toxic metals in low grade coal and drinking water in Chilga, Amhara region. Ethiopia, 17(2), 412–422.
Liu, Z. P. (2003). Lead poisoning combined with cadmium in sheep and horses in the vicinity of non-ferrous metal smelters. Science of the Total Environment, 309(1–3), 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00011-1.
Llobet, J. M., Falcó, G., Casas, C., Teixidó, A., & Domingo, J. L. (2003). Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead in common foods and estimated daily intake by children, adolescents, adults, and seniors of Catalonia, Spain. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51(3), 838–842. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020734q.
Lopez, A., Collins, W. F., & Williams, H. L. (1985). Essential elements, cadmium, and lead in raw and pasteurized cow and goat milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 68(8), 1878–1886. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(85)81044-4.
Martino, F. A. R., Sánchez, M. L. F., & Sanz-Medel, A. (2001). The potential of double focusing-ICP-MS for studying elemental distribution patterns in whole milk, skimmed milk and milk whey of different milks. Analytica Chimica Acta, 442(2), 191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)01170-9.
Matlock, M. M., Henke, K. R., & Atwood, D. a. (2002). Effectiveness of commercial reagents for heavy metal removal from water with new insights for future chelate designs. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 92(2), 129–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00389-2.
Muhib, M. I., Chowdhury, M. A. Z., Easha, N. J., Rahman, M. M., Shammi, M., Fardous, Z., et al. (2016). Investigation of heavy metal contents in cow milk samples from area of Dhaka, Bangladesh. International Journal of Food Contamination, 3(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40550-016-0039-1.
Muluken, M. (2014). Heavy metals concentration in effluents of textile industry, Tikur Wuha River and milk of cows watering on this water source, Hawassa, southern Ethiopia. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 8(8), 422–434. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjes.2014.422.434.
Nicholson, F. A., Smith, S. R., Alloway, B. J., Carlton-Smith, C., & Chambers, B. J. (2003). An inventory of heavy metals inputs to agricultural soils in England and Wales. Science of the Total Environment, 311(1–3), 205–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00139-6.
Ogabiela, E. E., Udiba, U. U., Adesina, O. B., Hammuel, C., Yebpella, G. G., Mmereole, U. J., & Abdullahi, M. (2011). Assessment of metal levels in fresh milk from cows grazed around Challawa industrial Estate of Kano. Nigeria, 1(7), 533–538.
Patra, R. C., Swarup, D., Kumar, P., Nandi, D., Naresh, R., & Ali, S. L. (2008). Milk trace elements in lactating cows environmentally exposed to higher level of lead and cadmium around different industrial units. Science of the Total Environment, 404(1), 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.06.010.
Pérez-Carrera, A. L., Arellano, F. E., & Fernández-Cirelli, A. (2016). Concentration of trace elements in raw milk from cows in the southeast of Cordoba province, Argentina. Dairy Science & Technology, 96(5), 591–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-016-0290-5.
Pilarczyk, R., Wójcik, J., Czerniak, P., Sablik, P., Pilarczyk, B., & Tomza-Marciniak, A. (2013). Concentrations of toxic heavy metals and trace elements in raw milk of Simmental and Holstein Friesian cows from organic farm. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(10), 8383–8392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3180-9.
Puls, R. (1994). Mineral levels in animal health: diagnostic data. Samakhusi: Sherpa International.
Qin, L.-Q., Wang, X.-P., Li, W., Tong, X., & Tong, W.-J. (2009). The minerals and heavy metals in cows milk from China and Japan. Journal of Health Science, 55(2), 300–305. https://doi.org/10.1248/jhs.55.300.
Rodriguez, E. M. R., Alaejos, M. S., & Romero, C. D. (2001). Mineral concentrations in cows milk from the Canary Island. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 14(4), 419–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/jfca.2000.0986.
Sikirić, M., Brajenović, N., Pavlović, I., Havranek, J. L., & Plavljanić, N. (2003, 2003). Determination of metals in cow’s milk by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. sss, (11), 481–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/.j1.626.8098s.
Simsek, O., Gültekin, R., Öksüz, O., & Kurultay, S. (2000). The effect of environmental pollution on the heavy metal content of raw milk. Nahrung/Food, 44(5), 360–363.
Smith, R. M., Leach, R. M., Muller, L. D., Griel, L. C., & Baker, D. E. (1991). Effects of long-term dietary cadmium chloride on tissue, milk, and urine mineral concentrations of lactating dairy cows. R M Smith, R M Leach, L D Muller, L C Griel, Jr and D E Baker. Journal of Animal Science, 69, 4088–4096 The online version of this art, 4088–4096.
Sola-Larrañaga, C., & Navarro-Blasco, I. (2009). Chemometric analysis of minerals and trace elements in raw cow milk from the community of Navarra, Spain. Food Chemistry, 112(1), 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.05.062.
Tajkarimi, M., Ahmadi Faghih, M., Poursoltani, H., Salah Nejad, A., Motallebi, A. A., & Mahdavi, H. (2008). Lead residue levels in raw milk from different regions of Iran. Food Control, 19(5), 495–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2007.05.015.
Tripathi, R., Raghunath, R., Sastry, V., & Krishnamoorthy, T. (1999). Daily intake of heavy metals by infants through milk and milk products. Science of the Total Environment, 227(2), 229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00018-2.
William, N. G., Godfrey, M., & Savino, B. (2011). Assessment of heavy metals in milk from selected dairy farms and shops in Wakiso District, Uganda. Suza Journal of Naturaal and Social Science, 1(1), 36–52.
Wise, B. M., Gallagher, N. B., Bro, R., Shaver, J. M., Windig, W., & Koch, R. S. (2006). PLS_Toolbox Version 4.0 for use with MATLAB TM.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Nibret Belay, Mr. Mulat Tiruneh, and Mr. Yabibal Nega for their invaluable laboratory assistance and Mr. Atsbha Berhane and Ms. Laura Pont for their assistance with GIS and PCA, respectively. Special thanks go to Mr. Solomon Abraha, former Administrative Vice President, University of Gondar, Ethiopia, for his support during the field work. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akele, M.L., Abebe, D.Z., Alemu, A.K. et al. Analysis of trace metal concentrations in raw cow’s milk from three dairy farms in North Gondar, Ethiopia: chemometric approach. Environ Monit Assess 189, 499 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6203-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6203-0