Abstract
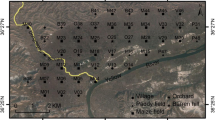
The accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils has been the subject of great concern because these metals have the potential to be transferred to soil solutions and subsequently accumulate in the food chain. To study the persistence of trace metals in crop and orchard soils, representative surface soil samples were collected from terrace farmland that had been cultivated for various numbers of years (3, 8, 12, 15, and >20 years), terrace orchard land that had been cultivated for various numbers of years (4, 7, 10, 12, 15, 18, 25, and >30 years), and slope farmland with various gradients (3°, 5°, 8°, 12°, 15°, and 25°) and analyzed for heavy metals (As, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, and Zn). These samples were collected from Nihegou catchment of Chunhua county in the southern Loess Plateau of China. The six heavy metals demonstrated different trends with time or gradient in the three land-use types. The Cu and Zn contents of the soil were higher than the referee background values of the loessal soil, and the contents of Cr and Ni, and especially those of As and Hg, were lower. Cu was the only heavy metal that just met the Grade III Environmental Quality Standard for Soils of China, while the others reached grade I. Cu and Hg were considered contaminant factors and Hg was a moderate potential ecological risk factor in the catchment. Of the sites investigated, 89.5% fell into the category with a low degree of contamination (C d ) and rest were moderate, while all three land-use types had low potential ecological risk (RI). Changes of C d and RI were consistent with the cultivated time in the terrace farmland and terrace orchard land. Values of RI increased while C d decreased with the increasing of slope gradient in the slope farmland. Evaluating the ecological risk posed by heavy metals using more soil samples in a larger study area is necessary on the Loess Plateau of China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. H., Farrar, D. B., & Zodrow, J. M. (2013). Terrestrial metals bioavailability: a comprehensive review and literature-derived decision rule for ecological risk assessment. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 19(6), 1488–1513. doi:10.1080/10807039.2012.708269.
Andreu, V., & Gimeno-García, E. (1999). Evolution of heavy metals in marsh areas under rice farming. Environmental Pollution, 104(2), 271–282. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00179-1.
Bao, S. D. (Ed.). (2000). Soil agro-chemical analysis (in Chinese) (3rd ed.pp. 370–404). Beijing: China Agriculture Press.
Baran, A., Czech, T., & Wieczorek, J. (2014). Chemical properties and toxicity of soils contaminated by mining activity. Ecotoxicology, 23(7), 1234–1244.
Cao, H. C., Luan, Z. Q., Wang, J. D., & Zhang, X. L. (2009). Potential ecological risk of cadmium, lead and arsenic in agricultural black soil in Jilin Province, China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 23, 57–64. doi:10.1007/s00477-007-0195-1.
Chen, H. M. (Ed.). (2002). The behavior and environmental quality of chemical substance in soils (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press.
Chen, H. M., Chen, N. C., & Chen, Y. X. (Eds.). (1996). Heavy metals pollution in soil-plant (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press.
Chen, X. M., Zhu, Y. C., Dong, H. P., & Luo, Y. Q. (2011a). Evaluation of the concentration of heavy metals in apple orchard soils in Tianshui area (in Chinese). Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 30(3), 132–136.
Chen, X. M., Zhu, Y. C., & Fu, X. Y. (2011b). Source and enrichment situation of heavy metals in apple orchard soils of Tianshui area, China (in Chinese). Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 30(5), 893–898.
Chinese National Environmental Monitoring Center. (1990). Background contents of elements of soils in China (in Chinese). Beijing: Chinese Environmental Science Press.
Dahms, S., Baker, N. J., & Greenfield, R. (2017). Ecological risk assessment of trace elements in sediment: a case study from Limpopo, South Africa. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 135, 106–114. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.09.036.
Fock, H. (2011). Integrating multiple pressures at different spatial and temporal scales: a concept for relative ecological risk assessment in the European marine environment. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 17(1), 187–211. doi:10.1080/10807039.2011.538634.
Gu, J. G., Lin, Q. Q., Hu, R., Zhuge, Y. P., & Zhou, Q. X. (2005). Heavy metals pollution in soil–plant and its research prospect (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 36(1), 128–133.
Håkanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
Hu, K. J., Wang, Y. J., Zhang, Y. D., Li, H. K., Mei, L. X., & Liang, J. (2012). Spatial distribution and cumulation evaluation of soil heavy metals in apple orchards of Weibei area, the Loess Plateau (in Chinese). Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(5), 934–941.
Huang, T., Wang, X. D., Wang, C. X., & Yue, X. J. (2009). Evaluation of orchard soil quality status on Loess Plateau (in Chinese). Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 21, 212–214,216.
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (2001). Keys to Chinese soil taxonomy (in Chinese) (3rd ed.pp. 215–223). Hefei: China Science and Technology University Press.
Jensen, J. & Pedersen, M. B. (2006). Ecological risk assessment of contaminated soil. In: G. W. Ware (Ed.), Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 186, 73–105. doi: 10.1007/0-387-32883-1_3.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2007). Soil contamination due to heavy metals from an industrial area of Surat, Gujarat, Western India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 124(124), 263–275. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9224-7.
Lago-Vila, M., Rodriguez-Sejio, A., Arenas-Lago, D., Andrade, L., & Vega, M. F. A. V. (2016). Heavy metal content and toxicity of mine and quarry soils. Journal Soils and Sediments, 17(5), 1331–1348. doi:10.1007/s11368-016-1345-0.
Li, L. X., Hao, M. D., Xue, X. H., Liu, D. B., & Wu, Q. C. (2007). Research on soil heavy metal contents of apple orchard in gully region of Loess Plateau (in Chinese). Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 21(6), 65–69.
Liang, J., Zhao, Z. Y., Wang, L. C., Zhang, L. S., Cheng, X. D., & Guo, X. J. (2004). Environmental quality evaluation of environmental friendly apple production base of Baishui county (in Chinese). Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science Edition), 32(8), 13–17.
Liang, J., Zhao, Z. Y., & Fan, M. T. (2008). Spatial distribution and pollution of mercury and cadmium in Weibei apple orchard soils of Shaanxi Province (in Chinese). Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 24(3), 209–213.
Liu, Y. X., Pang, J. L., Ding, M., & Chu, Y. B. (2009a). Evaluation of heavy metal contents of apple orchard soil in Changwu county (in Chinese). Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 37(5), 87–91.
Liu, Z. L., Zhao, Z. Y., Zhang, C. H., Liang, J., & Gao, H. (2009b). Evaluation of heavy metal contents of apple orchard soil in the major production area of Shaanxi (in Chinese). Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 27(1), 21–25.
Liu, Y. X., Pang, J. L., Ding, M., & Chu, Y. B. (2010). Distribution and evaluation of heavy metal in the long-term orchard soil in Loess Plateau (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 31(1), 32–36.
Liu, M. X., Yang, Y. Y., Yun, X. Y., Zhang, M. M., & Wang, J. (2015). Concentrations, distribution, sources, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural topsoil of the Three Gorges Dam region, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(3), 147. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4360-6.
Luo, Y. Q., Chen, Y. P., Tao, L., Li, Y. Q., & Wang, X. M. (2011). Investigation and evaluation on heavy metals pollution in farmland soil in Lanzhou city (in Chinese). Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 46(1), 98–104.
Mackie, K. A., Müller, T., & Kandeler, E. (2012). Remediation of copper in vineyards—a mini review. Environmental Pollution, 167, 16–26. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.03.023.
Makokha, V. A., Qi, Y., Shen, Y., & Wang, J. (2016). Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China. Exposure and Health, 8(1), 31–34. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0180-8.
Margin, M., Rossier, D., Crettaz, P., & Jolliet, O. (2002). Life cycle impact assessment of pesticides on human health and ecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 93(1–3), 379–392. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00336-X.
McLaughlin, M. J., Parker, D. R., & Clarke, J. M. (1999). Metals and micronutrients-food safety issues. Field Crops Research, 60(1–2), 143–163. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00137-3.
Ministry of Environmental Protection and Ministry of Land and Resources. (2014). Report on national general survey on soil contamination. Available at: http://english.sepa.gov.cn/News_service/news_release/201404/t20140428_271088.shtml. Accessed in 28 Aug 2016.
Pansu, M., & Gautheyrou, J. (Eds.). (2006). Handbook of soil analysis—mineralogical, organic and inorganic methods (pp. 895–974). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-31211-6.
Perrodin, Y., Boillot, C., Angerville, R., Donguy, G., & Emmanuel, E. (2011). Ecological risk assessment of urban and industrial systems: a review. Sceince of the Total Environment, 409(24), 5162–5176. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.08.053.
Ren, H. L., Cui, B. S., Bai, J. H., Dong, S. K., Hu, B., & Zhao, H. (2008). Distribution of heavy metal in paddy soil of Hani Terrace core zone and assessment on its potential ecological risk (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(4), 1625–1634.
Song, W., Chen, B. M., & Liu, L. (2013). Soil heavy metal pollution of cultivated land in China (in Chinese). Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 20(2), 293–298.
State Environmental Protection Administration and State Bureau of Technical Supervision of China. (1995). Environmental quality standard for soils of China (no. GB 15618-1995) (in Chinese).
Tannenbaum, L. V. (2005). A critical assessment of the ecological risk assessment process: a review of misapplied concepts. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 1(1), 66–72. doi:10.1897/IEAM_2004a-008.1.
Wang, H. (2000). Pollution ecology (in Chinese) (pp. 188–213). Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Wang, Y. Y., Wen, A. B., Guo, J., Shi, Z. L., & Yan, D. C. (2017). Spatial distribution, sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Shenjia River watershed of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Journal of Mountain Science, 14(2), 325–335. doi:10.1007/s11629-016-3838-1.
Wong, S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., Qi, S. H., & Min, Y. S. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119(1), 33–44. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(01)00325-6.
Xia, J. Q. (1996). Detailed annotation environmental quality standard for soils (in Chinese) (pp. 24–25). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press.
Xia, Z. L., Cai, S. Y., Xu, J. L., & Zhang, X. X. (1992). Soil environmental capacity in China (in Chinese). Beijing: Seismological Press.
Xu, Z. Q., Ni, S. J., Tuo, X. G., & Zhang, C. J. (2008). Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index (in Chinese). Environmental Science & Technology, 31(2), 112–115.
Zhang, Z. H. (2005). Land eco-economic evaluation in the Nihegou valley (in Chinese). Yangling, Shaanxi: Master Degree Thesis. Northwest A & F University.
Zhang, L. S., Liang, J., Wu, C. L., Duan, M., Wang, X. L., Zhao, Z. Y., & Zhao, S. L. (2004). Evaluation and concentration of soil heavy metals in apple orchards of Shaanxi province (in Chinese). Journal of Fruit Science, 21(2), 103–105.
Zheng, G. Z., & Yue, L. P. (2008). Investigation and assessment on heavy metals pollution of soil in Luochuan apple orchard (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 39(2), 401–405.
Zhu, G. W., & Chen, X. Y. (2001). A review of geochemical behaviors and environmental effects of organic matter in sediments (in Chinese). Journal of Lake Sciences, 13(3), 272–279.
Zhu, M. L., Pang, J. L., Zhang, W. Q., Li, X. G., Chang, M. R., & Zhang, C. Y. (2009). Investigation and assessment of heavy metals of agricultural soil and apple orchard soil in Luochuan (in Chinese). System Science and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 25(2), 142–146.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2016YFD0300301-03) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41203049). The two anonymous reviewers and the Editor are acknowledged for their comments, which significantly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wu, F., Zhang, X. et al. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in three land-use types on the southern Loess Plateau, China. Environ Monit Assess 189, 470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6140-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6140-y