Abstract
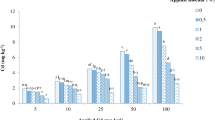
The straw from three different cadmium (Cd) hyperaccumulators (Galinsoga parviflora, Youngia erythrocarpa, and Solanum photeinocarpum) was added to Cd-contaminated soil, and its effects on plant growth and Cd accumulation in loquat seedlings were evaluated. Straw from each of G. parviflora, Y. erythrocarpa, and S. photeinocarpum was added to Cd-contaminated soil before planting seedlings of two varieties of loquat (Dawuxing and Chuanzao). Addition of straw from G. parviflora and S. photeinocarpum increased the root and shoot biomasses of both loquat varieties, compared with that in the control. Addition of straw also increased Cd uptake by loquat seedlings. The treatments could be ranked, from highest Cd contents in roots and shoots of loquat seedlings to lowest, as follows: S. photeinocarpum straw > Y. erythrocarpa straw > G. parviflora straw > control. All three types of hyperaccumulator straw increased the amount of Cd extracted by shoots of two loquat seedlings, with the maximum effect in the S. photeinocarpum straw treatment. Addition of hyperaccumulator straw also resulted in increased soil invertase, urease, and catalase activities to varying degrees. Among the three types of hyperaccumulator straw, S. photeinocarpum straw was the most effective to increase Cd accumulation in loquat seedlings. Therefore, this material has the potential to increase the phytoremediation capacity of loquat seedlings in Cd-contaminated orchards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asten, P. J. A. V., Bodegom, P. M. V., Mulder, L. M., & Kropff, M. J. (2005). Effect of straw application on rice yields and nutrient availability on an alkaline and a pH-neutral soil in a Sahelian irrigation scheme. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 72, 255–266.
Baker, A. J. M., Mcgrath, S. P., Reeves, R. D., & Smith, J. A. C. (2000). Metal hyperaccumulator plants: A review of the ecology and physiology of a biochemical resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils. In T. Norman & G. Banuelos (Eds.), Phytoremdiation of contaminated soil and water (pp. 85–107). Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Bao, S. D. (2000). Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press (in Chinese).
Blanco-Canqui, H., & Lal, R. (2007). Soil structure and organic carbon relationships following 10 years of wheat straw management in no-till. Soil and Tillage Research, 95, 240–254.
Cheema, Z. A., Farooq M, & Wahid A. (2012). Allelopathy: current trends and future applications. Springer Science & Business Media.
Chen, J. Z. (2003). Theories of fruit tree cultivation (southern version) (3rd ed.). Beijing: China Agriculture Press (in Chinese).
Dai, W., & Bai, H. Y. (1995). Correlations of soil catalase activity and it’s kinetic characteristic with some soil properties. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 17, 37–41 (in Chinese).
Han, J. L., Jin, F. S., Zhao, M., & Egashira, K. (2007). Environmental impact assessment of orchard soilds by the heavy metal concentration in Yantai City of Shandong Province, China. Journal-Faculty of Agriculture Kyushu University, 52, 123–128.
Hui, J. C. (2009). Effects of abscisic acid on the uptake of zinc and chromium by soybean (master thesis). In Sichuan agricultural University, Ya’an. Sichuan: China (in Chinese).
Inderjit, D., & S. O. (2003). Ecophysiological aspects of alleopathy. Planta, 217, 529–539.
Inderjit, Wardle, D. A., Karban, R., & Callaway, R. M. (2011). The ecosystem and evolutionary contexts of allelopathy. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 26, 655–662.
Kosterna, E. (2014). The effect of different types of straw mulches on weed-control in vegetables cultivation. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 15, 109–117.
Kretsinger, R. H., Uversky, V. N., & Permyakov, E. A. (2013). Encyclopedia of metalloproteins. New York: Springer.
Li, J. T., Qiu, J. W., Wang, X. W., Zhong, Y., Lan, C. Y., & Shu, W. S. (2006). Cadmium contamination in orchard soils and fruit trees and its potential health risk in Guangzhou, China. Environmental Pollution, 143, 159–165.
Li, X. H., Tao, J. M., Chen, J. D., Hu, F., & Li, H. X. (2010). Uptake of cadmium in grapevine with different scion-rootstock combinations and their fruit quality analysis under cadmium stress. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19, 1082–1086 (in Chinese).
Li, Y. J. (2001). Environmental problems and countermeasures of intensive agriculture. Beijing: China Agriculture Press (in Chinese).
Lin, L., Jin, Q., Liu, Y., Ning, B., Liao, M., & Luo, L. (2014a). Screening of a new cadmium hyperaccumulator, Galinsoga parviflora, from winter farmland weeds using the artificially high soil cadmium concentration method. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 33, 2422–2428.
Lin, L., Liao, M., Mei, L., Liu, J., Cheng, J., Luo, L., & Liu, Y. (2014b). Two ecotypes of hyperaccumulators and accumulators affect cadmium accumulation in cherry seedlings by intercropping. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 33, 1251–1257.
Lin, L., Liao, M., Ren, Y., Luo, L., Zhang, X., Yang, D., & He, J. (2014c). Effects of mulching tolerant plant straw on soil surface on growth and cadmium accumulation of Galinsoga parviflora. PloS One, 9, e114957.
Lin, L., Ning, B., Liao, M., Ren, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Cheng, J., & Luo, L. (2015a). Youngia erythrocarpa, a newly discovered cadmium hyperaccumulator plant. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 4205.
Lin, L., Yang, D., Tang, F., Luo, L., Liao, M., & Yuan, L. (2015b). Effects of applying accumulator straw in soil on cadmium accumulation of Capsella bursa-pastoris. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 46, 483–488 (in Chinese).
Lukačová Kuliková, Z., & Lux, A. (2010). Silicon influence on maize, Zea mays L., hybrids exposed to cadmium treatment. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85, 243–250.
Masciandaro, G., Ceccanti, B., Benedicto, S., Lee, H. C., & Cook, H. F. (2004). Enzyme activity and C and N pools in soil following application of mulches. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 84(1), 19–30.
Sampietro, D. A., Sgarigliaj, M. A., Soberon, R., & Vattuone, M. A. (2007). Effects of sugarcane straw allelochemicals on growth and physiology of crops and weeds. Allelopathy Journal, 19, 351–360.
Shan, Y. H., Li, C. G., Chen, C., Wang, X. Z., & Feng, K. (2008). Effects of straw incorporation on the solubility of cadmium and copper in flooded soil. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27, 1362–1366 (in Chinese).
Shi, J., Hu, R. P., Chu, X. D., Li, C. C., Zhang, J., & Lin, L. J. (2015). Cadmium accumulation characteristics of loquat seedlings from seeds. Shanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 62(1–5), 52 (in Chinese).
Takahashi, S., Uenosono, S., & Ono, S. (2003). Short- and long-term effects of rice straw application on nitrogen uptake by crops and nitrogen mineralization under flooded and upland conditions. Plant and Soil, 251, 291–301.
Tang, F. Y., Lin, L. J., Liao, J. Q., Liao, M. A., He, J., Yang, D. Y., & Zhang, X. (2015). Effects of applying accumulator straw in soil on growth and cadmium accumulation of Galinsoga parviflora. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 30, 213–218 (in Chinese).
Tang, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, D., Liu, W., & Yu, J. (2011). Pollution investigation and assessment of heavy metals in orchard soil—a case study in golden orchard of Chongqing. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 27, 244–249.
Tessier, A., Compbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51, 844–850.
Wang, J., Liu, C., Zhang, X., Lin, L., Liao, M., Lv, X., Xia, H., & Liang, D. (2016). Effects of applying hyperaccumulator straw in soil on growth and cadmium accumulation of Galinsoga parviflora. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 35, 618–623.
Yang, Y. Y., Jung, J. Y., Song, W. Y., Suh, H. S., & Lee, Y. (2000). Identification of rice varieties with high tolerance or sensitivity to lead, and characterization of the mechanism of tolerance. Plant Physiology, 124, 1019–1026.
Zhang, X. F., Xia, H. P., Li, Z. A., Zhuang, P., & Gao, B. (2011). Identification of a new potential Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum by soil seed bank-metal concentration gradient method. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189, 414–419.
Zhang, X. F., Xia, H. P., Li, Z. A., Zhuang, P., & Gao, B. (2010). Potential of four forage grasses in remediation of cd and Zn contaminated soils. Bioresource Technology, 101, 2063–2066.
Zhao, S., Li, K., Zhou, W., Qiu, S., Huang, S., & He, P. (2016). Changes in soil microbial community, enzyme activities and organic matter fractions under long-term straw return in north-central China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 216, 82–88.
Zhou, L. K. (1987). Soil enzymology. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
Zhu, H. H., Wu, J. S., Huang, D. Y., Zhu, Q. H., Liu, S. L., Su, Y. R., Wei, W. X., Keith Syers, J., & Li, Y. (2010). Improving fertility and productivity of a highly-weathered upland soil in subtropical China by in corporating rice straw. Plant and Soil, 331, 427–437.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Liao, M., Lv, X. et al. Addition of straw from hyperaccumulator plants to cadmium-contaminated soil increases cadmium uptake by loquat seedlings. Environ Monit Assess 189, 217 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5941-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5941-3