Abstract
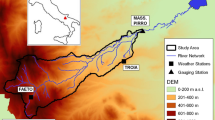
The temporal variability of phosphorus (P) transport and the relationships between discharge, suspended sediment concentration and particulate (PP), and soluble (SP) phosphorus were examined. The study was conducted at the event scale in seven tributaries of the Zarivar Lake watershed in Kurdistan Province (Iran) from March 2011 to April 2012. Based on eight runoff events, 82% of the total P was the PP carried out by suspended sediment. Results showed a high variability of P transport during different runoff events. It was found that soil erosion was the source of the high P load. For all tributaries, PP was linearly related to both discharge and suspended sediment concentration. However, the relationships of SP and PP with discharge and suspended sediment concentration showed different hysteresis patterns. The relationship between PP and discharge was generally characterized by a clockwise pattern (i.e., lower part contribution of the sub-watersheds) but the patterns between SP and discharge were mainly anticlockwise (i.e., upper part contribution of the sub-watersheds or perhaps due to a subsurface flow contribution).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell, J. M. (2013). Variability in nutrient loading to lake ecosystems and associated impacts on water quality. PhD Thesis. University of Waikato. New Zealand. 216 p.
Abell, J. M., Hamilton, D. P., & Rutherford, J. C. (2013). Quantifying spatial and temporal variations in sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus transport to a large eutrophic lake. Environ Science: Processes and Impacts, 15, 1137–1152.
Ai, L., Shi, Z. H., Yin, W., & Huang, X. (2015). Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: linkage with landscape characteristics. Journal of Hydrology, 523, 398–408.
Ballantine, D., Walling, D. E., & Leeks, G. J. L. (2009). Mobilisation and transport of sediment-associated phosphorus by surface runoff. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 196, 311–320.
Blanco, A. C., Nadaoka, K., Yamamoto, T., & Kinjo, K. (2010). Dynamic evolution of nutrient discharge under stormflow and baseflow conditions in a coastal agricultural watershed in Ishigaki Island, Okinawa, Japan. Hydrological Processes, 24, 2601–2616.
Borah, D. K., Bera, M., & Shaw, S. (2003). Water, sediment, nutrient, and pesticide measurements in an agricultural watershed in Illinois during storm events. Transaction of the Society of Agricultural Engineers, 46(3), 657–674.
Bowes, M. J., House, W. A., Hodgkinson, R. A., & Leach, D. V. (2005). Phosphorus discharge hysteresis during storm events along a river catchment: the River Swale, UK. Water Research, 39, 751–762.
Bowes, M. J., Smith, J. T., & Neal, C. (2009). The value of high-resolution nutrient monitoring: a case study of the River Frome, Dorset, UK. Journal of Hydrology, 378, 82–96.
Buendia, C., Vericat, D., Batalla, R. J., & Gibbins, C. N. (2016). Temporal dynamics of sediment transport and transient in-channel storage in a highly erodible catchment. Land Degradation & Development, 27(4), 1045–1063.
Butturini, A., Alvarez, M., Bernal, S., Vazquez, E., & Sabater, F. (2008). Diversity and temporal sequences of forms of DOC and NO3-discharge responses in an intermittent stream: predictable or random succession? Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, G03016.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8(3), 559–568.
Davis, J. R., & Koop, K. (2006). Eutrophication in Australian rivers, reservoirs and estuaries—a Southern Hemisphere perspective on the science and its implications. Hydrobiologia, 559(1), 23–76.
Davudirad, A. A., Sadeghi, S. H. R., & Sadoddin, A. (2016). The impact of development plans on hydrological changes in the Shazand Watershed, Iran. Land Degradation & Development, 27(4), 1236–1244.
Ebrahimi Mohammadi, S. H., Sadeghi, S. H. R., & Chapi, K. (2012). Analysis of runoff, suspended sediment and nutrient yield from different tributaries to the Zarivar Lake in event and base flows. Journal of Water and Soil Resources Conservation, 2(1), 61–76 (In Persian).
Eghball, B., & Gilley, J. E. (1999). Phosphorus and nitrogen in runoff following beef cattle manure or compost application. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28(4), 1201–1210.
EPA (1972). Role of Phosphorus in Eutrophication. Ecological Research Series, EPA-R3–72-001, 49 p.
Firdous, S., Begum, S., & Yasmin, A. (2016). Assessment of soil quality parameters using multivariate analysis in the Rawal Lake watershed. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 533. doi:10.1007/s10661-016-5527-5.
Foster, I. D. L., Chapman, A. S., Hodgkinson, R. M., Jones, A. R., Lees, J. A., Turner, S. E., & Scott, M. (2003). Changing suspended sediment and particulate phosphorus loads and pathways in underdrained lowland agricultural catchments; Herefordshire and Worcestershire, U.K. Development ofb Biohydrology, 169, 119–126.
Gelbrecht, J., Lengsfeld, H., Pöthig, R., & Opitz, D. (2005). Temporal and spatial variation of phosphorus input, retention and loss in a small catchment of NE Germany. Journal of Hydrology, 304, 151–165.
Gouze, E., Raimbault, P., & Garcia, N. (2008). Nutrient and suspended matter discharge by tributaries into the Berre Lagoon (France): the contribution of flood events to the matter budget. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 340, 233–244.
Heathwaite, A. L. (2003). Making process-based knowledge useable at the operational level: a framework for modeling diffuse pollution from agricultural land. Environmental Modelling and Software, 18(8–9), 753–760.
House, W. A., & Warwick, M. S. (1998). Hysteresis of the solute concentration/discharge relationship in rivers during storms. Water Research, 32, 2279–2290.
Kato, T., Kuroda, H., & Nakasone, H. (2009). Runoff characteristics of nutrients from an agricultural watershed with intensive livestock production. Journal of Hydrology, 368, 79–87.
Kreiling, R. M., & Houser, J. N. (2016). Long-term decreases in phosphorus and suspended solids, but not nitrogen, in six upper Mississippi River tributaries, 1991–2014. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 454. doi:10.1007/s10661-016-5464-3.
Kronvang, B., Vagstad, N., Behrent, H., Bøgestrand, J., & Larsen, S. E. (2007). Phosphorus losses at the catchment scale within Europe: an overview. Soil Use Management, 23, 104–116.
Kurdistan Ministry of Interior (2008). Study of environmental, limnological and ecological balance conservation the Zarivar Lake-Marivan. Final Limnological Report. 146 P.
Lee, J. H., & Bang, K. W. (2000). Characterization of urban stormwater runoff. Water Research, 34(6), 1772–1780.
Lundberg, C. J., Lane, R. R., & Day, J. W. (2014). Spatial and temporal variations in nutrients and water-quality parameters in the Mississippi River-influenced Breton Sound Estuary. Journal of Coastal Research, 294(2), 328–336.
Macrae, M. L., English, M. C., Schiff, S. L., & Stone, M. (2007). Capturing temporal variability for estimates of annual hydrochemical export from a first-order agricultural catchment in southern Ontario, Canada. Hydrological Processes, 21, 1651–1663.
McDiffett, W. F., Beidler, A. W., Dominick, T. F., & McCrea, K. D. (1989). Nutrient concentration-stream discharge relationships during storm events in a first-order stream. Hydrobiologia, 179, 97–102.
National Research Council. (2000). Clean coastal waters: understanding and reducing the effects of nutrient pollution (405 p). Washington: National Academy Press.
Nazari, F. (2010). Effect of fire severity on dynamic of forest soil nutrient under laboratory conditions. MSc. Thesis, Kurdistan University. Iran. 86 p. (In Persian).
Patnaik, P. (2010). Handbook of environmental analysis, chemical pollutants in air, water, soil and solid wastes (2nd ed.p. 730). USA: Taylor and Francis Group.
Pierzynski, G. M. (2000). Methods for phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters. Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin No., 396, 110.
Pommel, B., & Dorioz, J. M. (1997). Movement of phosphorus from agricultural soil to water. In H. Tunney, O. H. Carton, P. C. Brookes, & A. E. Johnston (Eds.), Phosphorus loss from soil to water (pp. 243–251). Wallingford: CAB International Publishing.
Pote, D. H., Daniel, T. C., Sharpley, A. N., Moore, P. A., Edwards, J. D. R., & Nichols, D. J. (1996). Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 855–859.
Ramos, T. B., Gonçalves, M. C., Branco, M. A., Brito, D., Rodrigues, S., Sánchez-Pérez, J. M., Prazeres, A., Martins, J. C., Fernandes, M. L., & Pires, F. P. (2015). Sediment and nutrient dynamics during storm events in the Enxoé temporary river, southern Portugal. Catena, 127, 177–190.
Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., & Taboada-Castro, M. T. (2013). Phosphorus transport into a stream draining from a mixed land use catchment in Galicia (NW Spain): significance of runoff events. Journal of Hydrology, 481, 12–21.
Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., & Taboada-Castro, M. T. (2010a). Factors controlling hydro-sedimentary response during runoff events in a rural catchment in the humid Spanish zone. Catena, 82, 206–217.
Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., & Taboada-Castro, M. T. (2010b). Sediment and phosphorus loss in runoff from an agroforestry catchment, NW Spain. Land Degradation & Development, 21(2), 161–170.
Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., Taboada-Castro, M. T., & Oropeza-Mota, J. L. (2009). Nutrient dynamics during storm events in an agroforestry catchment. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 40, 889–900.
Römkens, M. J. M., & Nelson, D. W. (1974). Phosphorus relationships in runoff from fertilized soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 3(1), 10–13.
Russell, M. A., Walling, D. E., Webb, B. W., & Bearne, R. (1998). The composition of nutrient fluxes from contrasting UK river basins. Hydrological Processes, 12, 1461–1482.
Seeger, M., Errea, M. P., Begueria, S., Arnaez, J., Marti, C., & Garcia-Ruiz, J. M. (2004). Catchment soil moisture and rainfall characteristics as determinant factors for discharge/suspended sediment hysteresis loops in a small headwater catchment in the Spanish Pyrenees. Journal of Hydrology, 288, 299–311.
Sharpley, A. N. (1985). The selective erosion of plant nutrients in runoff. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 49, 1527–1534.
Sharma, A., Tiwari, K. N., & Bhadoria, P. B. S. (2011). Effect of land use land cover change on soil erosion potential in an agricultural watershed. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1), 789–801.
Sharpley, A. N., Chapra, S. C., Wedepohl, R., Sims, J. T., Daniel, T. C., & Reddy, K. R. (1994). Managing agricultural phosphorus for protection of surface waters: issues and options. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23(3), 437–451.
Sharpley, A. N., Kleinman, P. J., Heathwaite, A. L., Gburek, W. J., Folmar, G. J., & Schmidt, J. P. (2008). Phosphorus loss from an agricultural watershed as a function of storm size. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 362–368.
Sharpley, A. N., & Rekolainen, S. (1997). Phosphorus in agriculture and its environmental implications. In H. Tunney, O. T. Brookes, & A. E. Johnston (Eds.), Phosphorus loss from soil to water (pp. 1–53). New York: Center for Agriculture and Biosciences International.
Smith, V. H. (1998). Cultural eutrophication of inland, estuarine, and coastal waters. In M. L. Pace & P. M. Groffman (Eds.), Successes, limitations, and frontiers in ecosystem science (pp. 7–49). New York, NY: Springer-Verlag.
Stutter, M. I., Langan, S. J., & Cooper, R. J. (2008). Spatial contributions of diffuse inputs and within-channel processes to the form of stream water phosphorus over storm events. Journal of Hydrology, 350, 203–214.
Tian, P., Zhai, J., Zhao, G., & Mu, X. (2016). Dynamics of runoff and suspended sediment transport in a highly erodible catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degradation & Development, 27(3), 839–850.
U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation. (2001). Water Measurement Manual. 317 p Available from: http://www.usbr.gov/pmts/hydraulics_lab/pubs/manuals/WMM_3rd_2001.pdf.
Udawatta, R. P., Motavalli, P. P., & Garrett, H. E. (2004). Phosphorus loss and runoff characteristics in three adjacent agricultural watersheds with claypan soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 1709–1719.
Udeigwe, T. K. (2005). Relating suspended solids and phosphorus in surface water runoff from agricultural soils to soil salinity measurements (80 p). MSc. Thesis: Louisiana State University Available from: http://etd.lsu.edu/docs/available/etd-07132005-210635/.
Uusitalo, R., Turtola, E., Kauppila, T., & Lilja, T. (2001). Particulate phosphorus and sediment in surface runoff and drainflow from clayey soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(2), 589–595.
Valk, H., Sebek, L. B. J., & Beynen, A. C. (2002). Influence of phosphorus intake on phosphorus excretion and phosphorus concentrations of blood plasma and saliva in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Research, 10, 2642–2649.
Wall, G. J., Bos, A. W., & Marshall, A. H. (1996). The relationship between phosphorus and suspended sediment loads in Ontario watersheds. Journal of Soiland Water Conservation, 51, 504–507.
Walling, D. E., Webb, B. W., & Russell, M. A. (1997). Sediment-associated nutrient transport in UK rivers. In B. Webb (Ed.), Freshwater contamination, IAHS Publication. No (Vol. 243, pp. 69–81).
Yeshaneh, E., Salinas, J. L., & Blöschl, G. (2015). Decadal trends of soil loss and runoff in the Koga catchment, Northwestern Ethiopia. Land Degradation & Development. doi:10.1002/ldr.2375.
Zhang, Z., Tao, F., Shi, P., Xu, W., Sun, Y., Fukushima, T., & Onda, Y. (2010). Characterizing the flush of stream chemical runoff from forested watersheds. Hydrological Processes, 24(20), 2960–2970.
Acknowledgments
The present paper has been written during the sabbatical leave of the first author facilitated by Tarbiat Modares University in Iran and Texas A&M University in USA whose valuable supports are acknowledged. The fieldwork data collection in this study has been also acquired in collaboration with the University of Kurdistan and NGO members in the study area. All physicochemical analyses of water and sediment samples have been done by the authors at the University of Kurdistan Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
• We determined the spatiotemporal variations of phosphorous to a eutrophicating inland lake in Iran.
• Some 82% of the total phosphorous was carried out by suspended sediment.
• The lower part of the sub-watersheds contributed more in transporting particulate phosphorous.
• Hysteresis patterns of solute phosphorous and discharge was mainly anticlockwise.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeghi, S.H., Ebrahimi Mohammadi, S., Singh, V.P. et al. Non-point source contribution and dynamics of soluble and particulate phosphorus from main tributaries of the Zarivar Lake watershed, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 189, 238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5937-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5937-z