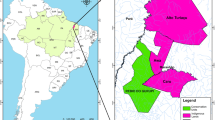
Abstract
Classification of land cover dynamics via satellite imagery has played indispensible services in developing effective management strategies for evaluation and management of water resources. The present study employed geospatial techniques, i.e., integrated GIS and remote sensing for effectual land change study. Hybrid classification approach was applied using ERDAS Imagine 11 to detect changes in land cover dynamics using satellite imagery of Landsat 4, 5 TM, Landsat 7 ETM, and Landsat 8 OLI for the years of 1992, 2002, and 2015, respectively. The study area was classified into four categories, i.e., vegetation, water body, barren, and urban area. Resultant maps, overlay maps, and post classification comparison maps were produced using ArcGIS 10.2 indicated remarkable shrinkage of water body up to 58.81%, reduction in vegetation area 53.24%, and increase in urban and barren area to 49.04 and 137.32%, respectively. The significant changes in land cover dynamics of Soan River are posing threats to its survival. Therefore, proper management, policies, and development of land use inventory are needs of the hour for saving Soan River.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdeji, A., & Ajibade, L. T. (2008). The change detection of major dams in Osun State, Nigeria using remote sensing (RS) and GIS techniques. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 1(6), 110–115.
Ahmad, F. (2012). Detection of change in vegetation cover using multi-spectral and multi-temporal information for District Sargodha, Pakistan. Sociedade Natureza, 24, 557–572.
Ahmad, I., Ahmad, Z., & Ahmad, S. A. (2012). Flood frequencies in Soan Valley. Pakistan Journal of Science, 64(1), 1–5.
Ali, M., Khan, S. J., Aslam, I., & Khan, Z. (2008). Simulation of the impacts of land-use change on surface runoff of Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Landscape Urban Planning, 102, 271–279.
Appiah, D. O., Schröder, D., Forkuo, E. K., & Bugri, J. T. (2015). Application of geo-information techniques in land use and land cover change analysis in a peri-urban district of Ghana. ISPRS International Journal of Geographic Information, 4, 1265–1289.
Ashraf, A. (2013). Changing hydrology of the Himalayan watershed. Current perspectives in contaminant hydrology and water resources sustainability. Islamabad: Intech.
Ashraf, M., Kahlown, M. A., & Ashfaq, A. (2007). Impact of small dams on agriculture and groundwater development: a case study from Pakistan. Agricultural Water Management, 92, 90–98.
Bailly, H. (2007). Environmental baseline study of Margala and Margala north blocks. Islamabad: MOL Pakistan Oil and Gas Company BV.
Bazgeera, S., Sharma, P. K., Maheya, R. K., Hundala, S. S., & Sood, A. (2008). Assessment of land use changes using remote sensing and GIS and their implications on climatic variability for Balachaur watershed in Punjab, India. Desert, 12, 139–147.
Butt, A., Shabbir, R., Ahmad, S. S., & Aziz, N. (2015). Land use change mapping and analysis using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Simly watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18, 251–259.
Campbell, J. B., & Wynne, R. H. (2011). Introduction to remote sensing. Fifth ed: Guilford Press.
Caruso, G., Rounsevell, M. D. A., & Cojacarus, G. (2005). Exploring a spatiodynamic neighborhood-based model of residential behavior in the Brussels peri-urban area. International Journal of Geographic Information Science, 19, 103–123.
Chilar, J. (2000). Land cover mapping of large areas from satellites: status and research priorities. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(67), 1093–1114.
Coppin, P., Jonckheere, I., Nackaerts, K., Muys, B., & Lambin, E. (2004). Digital change detection methods in ecosystem monitoring: a review. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(9), 1565–1596.
Dietzel, C., Herold, M., Hemphill, J. J., & Clarke, K. C. (2005). Spatial-temporal dynamics in California’s central valley: empirical links to urban theory. International Journal of Geographic Information Science, 19, 175–195.
FAO. (1995). Planning for sustainable use of land resources; towards a new approah. Accessed April 2nd, 2014. http://www.fao.org/docrep/v8047e/v8047e00.htm
Fareed, N., Ghaffar, A., & Malik, T. S. (2016). Spatio-temporal extension and spatial analyses of dengue from Rawalpindi, Islamabad and Swat during 2010–2014. Climate, 4(23), 1–18.
Foody, G. M. (2010). Assessing the accuracy of land cover change with imperfect ground reference data. Remote Sensing Environment, 114, 2271–2285.
Fortin, M. J., Boots, B., Csillag, F., & Remmel, T. K. (2003). On the role of spatial stochastic models in understanding landscape indices in ecology. Oikos, 102, 203–212.
Gajbhiye, S., & Sharma, S. K. (2012). Land use and land cover change detection of Indra river watershed through remote sensing using multi-temporal satellite data. International Journal of Geomatics and Geosciences, 3, 89–96.
Gwet, K. (2002). Kappa statistics is not satisfactory for assessing the extent of agreement between raters. Statistical Method for Inter-Rater Reliability Assessment, 76, 378–383.
Harris, P. M., & Ventura, S. J. (1995). The integration of geographic data with remotely sensed imagery to improve classification in an urban area. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 61(8), 993–998.
Hu, H. B., Liu, H. Y., Hao, J. F., & An, J. (2012). Analysis of land use change characteristics based on remote sensing and GIS in the Jiuxiang river watershed. International Journal on Smart Sensing and Intelligent System, 5, 811–823.
Hussain, F., Khaliq, A., Ashraf, M. I., & Khan, I. A. (2014). Morphological and hydrological responses of Soan and Khad rivers to impervious land use in district Murree, Pakistan. Journal of Agricultural Research, 52(2), 269–282.
International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). (2005). Rapid environmental appraisal of developments in and around Murree hills. Retrieved May 5, 2016 from http://www.iucn.pk
Iqbal, F., Ali, M., Salam, A., Khan, B. A., Ahmad, S., Qamar, M., & Umer, K. (2004). Seasonal variations of physico-chemical characteristics of River Soan Water at Dhoak Pathan Bridge (Chakwal), Pakistan. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 6(1), 89–92.
Jehanzeb. (2004). Evaluation of flooding hazards of Soan river in Rawalpindi area [M.Sc. Thesis]. CEWRE, University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore. pp. 32–56
Jensen, J. R. (1996). Introductory digital image processing: a remote sensing perspective. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Jensen, J. R. (2007). Remote sensing of the environment: an earth resource perspective. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Jensen, J. R., & Im, J. (2007). Remote sensing change detection in urban environments. In R. R. Jensen, J. D. Gatrell, & D. McLean (Eds.), Geo-spatial technologies in urban environments: policy, practice and pixels (second ed., pp. 7–30). Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Kachhwala, T. S. (1985). Temporal monitoring of forest land for change detection and forest cover mapping through satellite remote sensing. In Proceedings of the 6th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing (pp. 77–83). Hyderabad: National Remote Sensing Agency.
Kearns, F. R., Kelly, N. M., Carter, J. L., & Resh, V. H. (2005). A method for the use of landscape metrics in freshwater research and management. Landscape Ecology, 20, 113–125.
Keller, A., Sakthivadivel, R., & Seckler, D. (2000). Water scarcity and the role of storage in development. International Water Management Institute, 39, 1–20.
Lachowski, H. (1996). Guidelines for the use of digital. Collingdale: DIANE Publishing.
Lea, C., and Curtis, A.C. (2010). Thematic accuracy assessment procedures: National Park Service Vegetation Inventory, version 2.0. Natural Resource Report NPS/2010/NRR––2010/204, National Park Service, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA.
Liu, J. G., & Mason, P. (2009). Essential image processing and GIS for remote sensing. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons.
Lu, Q., & Weng, D. (2005). Urban classification using full spectral information of Landsat ETM+ imagery in Marion County, Indiana. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 71(11), 1275–1284.
Lu, D., Mausel, P., Brondıˋzio, E., & Moran, E. (2004). Change detection techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25, 2365–2407.
Martellozzo, F., Ramankutty, N., Hall, R. J., Price, D. T., Purdy, B., & Friedl, M. (2014). Urbanization and the loss of prime farmland: a case study in the Calgary-Edmonton corridor of Alberta. Regional Environmental Change, 15, 881–893.
Mather, A. S., & Needle, C. L. (2000). The relationships of population and forest trends. Geography Journal, 166(1), 2–13.
Melesse, A. M., & Jordan, J. D. (2002). A comparison of fuzzy vs. augmented-ISODATA classification algorithms for cloud-shadow discrimination from Landsat images. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 68, 905–912.
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). (2005). Ecosystems and human well-being: biodiversity synthesis. Washington DC: World Resource Institute.
Parker, D., & Meretsky, V. (2004). Measuring pattern outcomes in an agent-based model of edge-effect externalities using spatial metrics. Agriculture, Ecosystem and Environment, 101, 233–250.
Prakasam, C. (2010). Land use and land cover change detection through remote sensing approach: a case study of Kodaikanal Taluk, Tamil Nadu. International Journal of Remote Sensing and Geosciences, 1(2), 150–158.
Purkis, S. J., & Klemas, V. V. (2011). Remote sensing and global environmental change. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons.
Rawat, J. S., Biswas, V., & Kumar, M. (2013). Changes in land use/cover using geospatial techniques: a case study of Ramnagar town area, district Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 16, 111–117.
Rees, G. (1999). The remote sensing data book. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Seif, A., & Mokarram, M. (2012). Change detection of Gil Playa in the northeast of Fars Province, Iran. American Journal of Scientific Research, 86, 122–130.
Singh, P., Gupta, A., & Singh, M. (2014). Hydrological inferences from watershed analysis for water resource management using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 17, 111–121.
Star, J. L., Estes, J. E., & McGwire, K. C. (1997). Integration of geographic information systems and remote sensing. University Press. New York: Cambridge.
Stewart, T. J., Janssen, R., & van Herwijnen, M. (2004). A genetic algorithm approach to multi-objective land use planning. Computers and Operations Research, 31, 2293–2313.
Story, M., & Congalton, R. (1986). Accuracy assessment—a user’s perspective. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 52, 397–399.
Tanvir, A., Shahbaz, B., & Suleri, A. (2006). Analysis of myths and realities of deforestation in northwest Pakistan: implications for forestry extension. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 8, 107–110.
Tardie, P. S., & Congalton, R. G. (2007). A change detection analysis: Using remotely sensed data to assess the progression of development in Essex County, Massachusetts from 1990 to 2001. Retrieved from University of New Hampshire Durham. URL: http://www.unh.edu/natural-resources/pdf/tardie-paper1.pdf.
Torahi, A. A., & Rai, S. C. (2011). Land cover classification and forest change analysis. Using Satellite Imagery- A case study in Dehdez Area of Zagros Mountain in Iran, Journal of Geographic Information systems, 3, 1–11.
Turner, M. G., Gardner, R. H., & O’Neill, R. V. (2001). Landscape ecology in theory and practice pattern and process. New York: Springer-Verlag.
USGS. (2016). LANDSAT Products. Retrieved April 10, 2016 from http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/?page_id=2
Verburg, P. H., Van Eck, J. R., de Hijs, T. C., Dijst, M. J., & Schot, P. (2004). Determination of land use change patterns in the Netherlands. Environment and Planning B: Planningand Design, 31, 125–150.
Vierra, A. J., & Garrett, J. M. (2005). Understanding inter observatory agreement: the kappa statistics. Family Medicine, 37, 360–363.
Wang, X., Yu, S., & Huang, G. H. (2004). Land allocation based on integrated GIS-optimization modeling at a watershed level. Landscape Urban Planning, 66, 61–74.
Wani, S. P., Sreedevi, T. K., Reddy, T. S. V., Venkateswarlu, B., & Prasad, C. S. (2008). Community watersheds for improved livelihoods through consortium approach in drought prone rain-fed areas. Journal of Hydrological Research and Development, 23, 55–77.
WWF. (1994). Ucchali complex (Khushab): a report on the planning the conservation of the water bodies based on the indigenous population
Yuan, F., Sawaya, K. E., Loeffelholz, B. C., & Bauer, M. E. (2005). Land cover classification and change analysis of the Twin Cities (Minnesota) Metropolitan Area by multitemporal Landsat remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 98(2–3), 317–328.
Zoran, M. E. (2006). The use of multi-temporal and multispectral satellite data for change detection analysis of Romanian Black Sea coastal zone. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, 8, 252–256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, H., Ahmad, S.S. Exploring geospatial techniques for spatiotemporal change detection in land cover dynamics along Soan River, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 189, 222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5935-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5935-1