Abstract
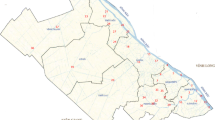
Rapid urbanization in China has been causing dramatic deterioration in the water quality of rivers and threatening aquatic ecosystem health. In this paper, multivariate techniques, such as factor analysis (FA) and cluster analysis (CA), were applied to analyze the water quality datasets for 19 rivers in Liangjiang New Area (LJNA), China, collected in April (dry season) and September (wet season) of 2014 and 2015. In most sampling rivers, total phosphorus, total nitrogen, and fecal coliform exceeded the Class V guideline (GB3838-2002), which could thereby threaten the water quality in Yangtze and Jialing Rivers. FA clearly identified the five groups of water quality variables, which explain majority of the experimental data. Nutritious pollution, seasonal changes, and construction activities were three key factors influencing rivers’ water quality in LJNA. CA grouped 19 sampling sites into two clusters, which located at sub-catchments with high- and low-level urbanization, respectively. One-way ANOVA showed the nutrients (total phosphorus, soluble reactive phosphorus, total nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, and nitrite), fecal coliform, and conductivity in cluster 1 were significantly greater than in cluster 2. Thus, catchment urbanization degraded rivers’ water quality in Liangjiang New Area. Identifying effective buffer zones at riparian scale to weaken the negative impacts of catchment urbanization was recommended.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberto, W. D., Pilar, M. D., Valeria, A. M., Fabiana, P. S., Cecilia, H. A., & Angeles, B. (2001). Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquía River basin (Córdoba-Argentina). Water Research, 35(12), 2881–2894.
Almeida, C. A., Quintar, S., González, P., & Mallea, M. A. (2007). Influence of urbanization and tourist activities on the water quality of the Potrero de los Funes River (San Luis – Argentina). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment., 133, 459–465.
Al-Murairi, N., Abahussain, A., & El-Bettay, A. (2014). Spatial and temporal characterizations of water quality in Kuwait Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin., 83, 127–131.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Publish Health association.
Chen, D. Q., Xiong, F., Wang, K., & Chang, Y. H. (2009). Status of research on Yangtze fish biology and fisheries. Environmental Biology of Fishes., 85, 337–357.
Chen, X., Zhou, W. Q., Pickett, S. T. A., Li, W. F., Han, L. J., & Ren, Y. F. (2016). Diotoms are better indicators of urban stream conditions: a case study in Beijing, China. Ecological Indicators, 60, 265–274.
Dodds, W. K., & Oakes, R. M. (2008). Headwater influences on downstream water quality. Environmental management., 41, 367–377.
Fu, F. C., Zhou, B. T., & Liang, K. X. (2012). Research of the ecosystem services value (ESV) of land use in Liangjiang New Area of Chongqing. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition)., 37(1), 68–73.
Gu, Q. W., Wang, H. Q., Zheng, Y. N., Zhu, J. W., & Li, X. K. (2015). Ecological footprint analysis for urban agglomeration sustainability in the middle stream of Yangtze River. Ecological Modelling, 318, 86–99.
Jirka, G. H., & Herlina. (2008). Reaeration. Encyclopedia of Ecology., 2975–2981.
Li, L. Y. (2015). State rescaling and national new area development in China: the case of Chongqing Liangjiang. Habitat International., 50, 80–89.
Li, Y., Li, Y. F., Qureshi, S., Kappas, M., & Hubacek, K. (2015). On the relationship between landscape ecological patterns and water quality across gradient zones of rapid urbanization in coastal China. Ecological Modelling, 318, 100–108.
Li, B. J., Chen, D. X., Wu, S. H., Zhou, S. L., Wang, T., & Chen, H. (2016). Spatio-temporal assessment of urbanization impacts on ecosystem services: case study of Nanjing City, China. Ecological Indicators, 71, 416–427.
Long, H. L., Liu, Y. Q., Hou, X. G., Li, T. T., & Li, Y. R. (2014). Effects of land use transitions due to rapid urbanization on ecosystem services: implications for urban planning in the new developing area of China. Habitat International., 44, 536–544.
Minaya, V., McClain, M. E., Moog, O., Omengo, F., & Singer, G. A. (2013). Scale-dependent effects of rural activities on benthic macroinvertebrates and physic-chemical characteristics in headwater streams of the Mara River. Kenya. Ecological Indicators., 32, 116–122.
Mo, D. D. (2015). Study on the healthy hydrosocial cycle—case of Liangjiang New Area, Chongqing. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
Ouyang, Y., Kizza, P. N., Wu, Q. T., Shinde, D., & Huang, C. H. (2006). Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Research, 40, 3800–3810.
Pinto, U., & Maheshwari, B. L. (2011). River health assessment in peri-urban landscapes: an application of multivariate analysis to identify the key variables. Water Research, 45, 3915–3924.
Randall, W. G., McCarthy, J., Layton, A., McKay, L. D., Williams, D., Koirala, S. R., & Sayler, G. S. (2006). Escherichia coli loading at or near base flow in a mixed-use watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality., 35, 2244–2249.
Razmkhah, H., Abrishmchi, A., & Torkian, A. (2010). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality by pattern recognition techniques: a case study on Jajrood River (Tehran, Iran). Journal of Environmental Management., 91, 852–860.
Robert, E., Grippa, M., Kergoat, L., Pinet, S., Gal, L., Cochonneau, G., & Martinez, J. M. (2016). Monitoring water turbidity and surface sediment concentration of the Bagre reservoir (Burkina Faso) using MODIS and field reflectance data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation., 52, 243–251.
Roy, A. H., Rosemond, A. D., Paul, M. J., Leigh, D. S., & Wallace, J. B. (2003). Stream macroinvertebrate response to catchment urbanisation. Freshwater Biology., 48, 329–346.
Shi, D. M., Wang, W. L., Jiang, G. Y., Peng, X. D., Yu, Y. L., Li, Y. X., & Ding, W. B. (2016). Effects of disturbed landforms on the soil water retention function during urbanization process in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Catena, 144, 84–93.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22, 464–475.
Simeonov, V., et al. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Singh, K. P., Malik, A., Mohan, D., & Sinha, S. (2004). Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—a case study. Water Research, 38, 3980–3992.
Standard. (2002). Standard methods for the analysis of water and wastewater (fourth ed.). Beijing: Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China.
Sun, Y. W., Guo, Q. H., Liu, J., & Wang, R. (2014). Scale effects on spatially varying relationships between urban landscape patterns and water quality. Environmental Management., 54, 272–287.
Tran, C. P., Bode, R. W., Smith, A. J., & Kleppel, G. S. (2010). Land-use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York State (USA). Ecological Indicators, 10, 727–733.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Şen, B. (2012). Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin. Turkey. Catena., 92, 11–21.
Wang, B. X., Liu, D. X., Liu, S. R., Zhang, Y., Lu, D. Q., & Wang, L. Z. (2012). Impacts of urbanization on stream habitats and macroinvertebrate communities in the tributaries of Qiangtang River, China. Hydrobiologia, 680, 39–51.
Wang, Y., Wang, P., Bai, Y. J., Tian, Z. X., Li, J. W., Shao, X., Mastavich, L. F., & Li, B. L. (2013). Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. Journal of Hydro- environment Research, 7, 30–40.
Zhou, X. W. (2014). Non-point source pollution research based on land use change in Liangjiang New Area. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Major National Project for Water Pollution Control (2012ZX07307-001). The authors are grateful to the Chongqing Geographic Information Center for providing land use map of the Liangjiang New Area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Hu, X., He, Q. et al. Using multivariate techniques to assess the effects of urbanization on surface water quality: a case study in the Liangjiang New Area, China. Environ Monit Assess 189, 174 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5884-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5884-8