Abstract
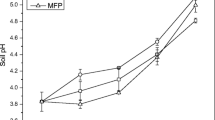
The effect of the addition of industrial by-products (gypsum and calcite) on the leaching of As and metals (Cu, Zn, Ni, Pb and Cd) in a soil contaminated by pyritic minerals was monitored over a period of 6 months at a two-pit pilot plant. The contaminated soil was placed in one pit (non-remediated soil), whereas a mixture of the contaminated soil (80% w/w) with gypsum (10% w/w) and calcite (10% w/w) was placed in the other pit (remediated soil). Soil samples and leachates of the two pits were collected at different times. Moreover, the leaching pattern of major and trace elements in the soil samples was assessed at laboratory level through the application of the pHstat leaching test. Addition of the by-products led to an increase in initial soil pH from around 2.0 to 7.5, and it also provoked that the concentration of trace elements in soil extracts obtained from the pHstat leaching test decreased to values lower than quantification limits of inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and lower than the hazardous waste threshold for soil management. The trace element concentration in the pilot-plant leachates decreased over time in the non-remediated soil, probably due to the formation of more insoluble secondary minerals containing sulphur, but especially decreased in pit of the remediated soil, in agreement with laboratory data. The pH in the remediated soil remained constant over the 6-month period, and the X-ray diffraction analyses confirmed that the phases did not vary over time, thus indicating the efficacy of the addition of the by-products. This finding suggests that soil remediation may be a feasible option for the re-use of non-hazardous industrial by-products.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashrafi, M., Mohamad, S., Yusoff, I., & Hamid, F. S. (2015). Immobilization of Pb, Cd, and Zn in a contaminated soil using eggshell and banana stem amendments: metal leachability and a sequential extraction study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 223–230.
Cappuyns, V., Swennen, R., & Verhulst, J. (2004). Assessment of acid neutralizing capacity and potential mobilisation of trace metals from land-disposed dredged sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 333, 233–247.
CEN/TS 14429. (2006b). Characterization of waste. Leaching behaviour tests. Influence of pH on leaching with initial acid/base addition. Brussels: European Committee of Standardisation.
CEN/TS 15364. (2006a). Characterization of waste. Leaching behaviour tests. Acid and base neutralization capacity test. Brussels: European Committee of Standardisation.
de Andalucía, J. (1999). Los criterios y estándares para declarar un suelo contaminado en Andalucía y la metodología y técnicas de toma de muestra y análisis para su investigación. Spain: Consejería del Medio Ambiente de la Junta de Andalucía.
Dijkstra, J. J., Van Der Sloot, H. A., & Comans, R. N. J. (2006). The leaching of major and trace elements from MSWI bottom ash as a function of pH and time. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 335–351.
Doumett, S., Lamperi, L., Checchini, L., Azzarello, E., Mugnai, S., Mancuso, S., Petruzzelli, G., & Del Bubba, M. (2008). Heavy metal distribution between contaminated soil and Paulownia tomentosa, in a pilot-scale assisted phytoremediation study: influence of different complexing agents. Chemosphere, 72, 1481–1490.
Doumett, S., Fibbi, D., Azzarello, E., Mancuso, S., Mugnai, S., Petruzzelli, G., & Del Bubba, M. (2011). Influence of the application renewal of glutamate and tartrate on Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn distribution between contaminated soil and Paulownia tomentosa in a pilot-scale assisted phytoremediation study. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13, 1–17.
European Council. (2003). Decision 2003/33/CE, establishing criteria and procedure for the acceptance of waste at landfill pursuant to Article 16 and Annex II to Directive 1999/31/CE. Official Journal of European Communities. Brussels: EU Commission.
Farrell, M., Perkins, W. T., Hobbs, P. J., Griffith, G. W., & Jones, D. L. (2010). Migration of heavy metals in soil as influenced by compost amendments. Environmental Pollution, 158, 55–64.
Garrido, F., Illera, V., Campbell, C. G., & García-González, M. T. (2006). Regulating the mobility of Cd, Cu and Pb in an acid soil with amendments of phosphogypsum, sugar foam, and phosphoric rock. European Journal of Soil Science, 57, 95–105.
González-Núñez, R., Alba, M. D., Orta, M. M., Vidal, M., & Rigol, A. (2011). Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials—part I: characterization and viability studies for the selection of non-hazardous waste materials and silicates. Chemosphere, 85, 1511–1517.
González-Núñez, R., Alba, M. D., Orta, M. M., Vidal, M., & Rigol, A. (2012). Remediation of metal-contaminated soils with the addition of materials—part II: leaching tests to evaluate the efficiency of materials in the remediation of contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 87, 829–837.
González-Núñez, R., Alba, M. D., Vidal, M., & Rigol, A. (2015). Viability of adding gypsum and calcite for remediation of metal-contaminated soil: laboratory and pilot plant scales. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12(8), 2697–2710.
Hamon, R., McLaughlin, M., & Lombi, E. (2007). Natural attenuation of trace element availability in soils. Pensa-cola, Florida: SETAC Press.
Illera, V., Garrido, F., Serrano, S., & García-González, M. T. (2004). Immobilization of the heavy metals Cd, Cu and Pb in an acid soil amended with gypsum- and lime-rich industrial by-products. European Journal of Soil Science, 55, 135–145.
Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I; Dumat, C. (2016). A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration Available online
Ko, I., Lee, C.-H., Lee, K.-P., Lee, S.-W., & Kim, K.-W. (2006). Remediation of soil contaminated with arsenic, zinc, and nickel by pilot-scale soil washing. Environmental Progress, 25, 39–48.
Kosson, D. S., Van Der Sloot, H. A., Sanchez, F., & Garrabrants, A. C. (2002). An integrated framework for evaluating leaching in waste management and utilization of secondary materials. Environmental Engineering Science, 19(3), 159–204.
Lee, M., Sung, I., Kim, I., Kang, H., & Lee, S. (2007). Remediation of heavy metal contaminated groundwater originated from abandoned mine using lime and calcium carbonate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 144, 208–214.
Lin, Z., & Herbert, R. B. (1997). Heavy metal retention in secondary precipitates from a mine rock dump and underlying soil, Dalarna, Sweden. Environmental Geology, 33, 1–12.
Madejón, P., Pérez-de-Mora, A., Burgos, P., Cabrera, F., Lepp, N. W., & Madejón, E. (2010). Do amended, polluted soils require re-treatment for sustainable risk reduction?—evidence from field experiments. Geoderma, 159, 174–181.
Mahar, A., Wang, P., Li, R., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Immobilization of lead and cadmium in contaminated soil using amendments: a review. Pedosphere, 25, 555–568.
Oliva, J. (2011). Avaluació i caracterització d’una apatita biogènica pel tractament in situ d’aigües subterrànies i sòls contaminats per activitats mineres. PhD Thesis, Barcelona
Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Moreno, N., Alvarez-Ayuso, E., García-Sánchez, A., Cama, J., Ayora, C., & Simón, M. (2006). Immobilization of heavy metals in polluted soils by the addition of zeolitic material synthesized from coal fly ash. Chemosphere, 62, 171–180.
Raicevic, S., Kaludjerovic-Radoicic, T., & Zouboulis, A. I. (2005). In situ stabilization of toxic metals in polluted soils using phosphates: theoretical prediction and experimental verification. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B117, 41–53.
Rigol, A., Mateu, J., González-Núñez, R., Rauret, G., & Vidal, M. (2009). pHstat vs. single extraction tests to evaluate heavy metals and arsenic leachability in environmental samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 632, 69–79.
Sarria, M. (2013). Evaluación del comportamiento de arsénico, cobre, plomo y zinc en suelos afectados por el vertido de la mina de Aznalcóllar (Sevilla, España). PhD Thesis, Colombia
Sastre, J., Hernández, E., Rodríguez, R., Alcobe, X., Vidal, M., & Rauret, G. (2004). Use of sorption and extraction tests to predict the dynamics of the interaction of trace elements in agricultural soils contaminated by a mine tailing accident. Science of the Total Environment, 329, 261–281.
Scholz, R., & Schanabel, U. (2006). Decision making under uncertainty in case of soil remediation. Journal of Environmental Management, 80, 132–147.
Simón, M., Martín, F., Ortiz, I., García, I., Fernández, J., Fernández, E., Dorronsoro, C., & Aguilar, J. (2001). Soil pollution by oxidation of tailings from toxic spill of a pyrite mine. Science of the Total Environment, 279, 63–74.
Vareda, J. P., Valente, A. J. M., & Duraes, L. (2016). Heavy metals in Iberian soils: removal by current adsorbents/amendments and prospective for aerogels. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 237, 28–42.
Webster, J. G., Swedlund, P. J., & Webster, K. S. (1998). Trace metal adsorption onto an acid mine drainage iron (III) oxy hydroxy sulfate. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 1361–1368.
Westland, R.E. (2012). New phases in the hydous ferric sulfate system, a supporting argument that the mineral lausenite is of formula Fe2(SO4)3·5H2O and the crystal structure refinement and hydrogen bonding scheme of the minerals quenstedtite and romerite. PhD Thesis, Canada
Wuana, R. A., & Okieimen, F. E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecology, 2011(4), 1–20.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Spain’s Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (Project CTM2011-27211), the Secretaría General para la Prevención de la Contaminación y el Cambio Climático (Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, contract 300/PC/08/3-01.1) and the Generalitat de Catalunya (AGAUR 2014SGR1277). ICP-OES analyses were conducted at the CCiT of the University of Barcelona. XRF measurements were conducted at the CITIUS of the University of Seville. The authors would like to thank EDP Energía for supplying the materials and Befesa Gestión de Residuos Industriales for supplying the contaminated soils and for permitting access to the pilot plant for the 300/PC/08/3-01.1 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 762 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Núñez, R., Rigol, A. & Vidal, M. Assessing the efficacy over time of the addition of industrial by-products to remediate contaminated soils at a pilot-plant scale. Environ Monit Assess 189, 155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5864-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5864-z