Abstract
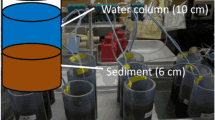
The effect of bentonite and sand, as natural capping agents, on the fluxes of nutrients and trace metals across the sediment-water interface was studied through sediment incubation, and the ecotoxicological impact was assessed by using Daphnia magna. Bentonite and sand were layered on the sediment at 15, 75, and 225 mg cm−2, and the concentration of cations, nutrients, and trace metals was measured. Sediment incubation showed that bentonite reduced the N flux but increased the P flux as a result of dissolution of non-crystalline P from bentonite, while sand slightly decreased the N fluxes but not the P flux. The concentration of Na increased in the overlying water with increasing application rates of bentonite, while that of Ca decreased. However, regardless of the rate of sand application, concentrations of all cation species remained unchanged. The concentration of As and Cr increased with bentonite application rate but decreased with sand. Both capping materials suppressed fluxes of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn compared to control, and the extent of suppression was different depending on the trace metal species and capping agents used. During sediment incubation, the survival rate of D. magna significantly decreased in bentonite suspension but began to decrease at the end in sand suspension. Sediment capping of mildly polluted sediments by using bentonite and sand lowered the level of nutrients and trace metals. However, unexpected or undesirable side effects, such as influxes of P and As from bentonite to the overlying water and a possibility of toxic impacts to aquatic ecosystems, were observed, suggesting that capping agents with an adequate assessment of their side effects and toxicity should be predetermined for site-specific sediment management strategies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou, M. I., Al-sabagh, A. M., & Dardir, M. M. (2013). Evaluation of Egyptian bentonite and nano-bentonite as drilling mud. Egyptian Journal of Petroleum, 22(1), 53–59. doi:10.1016/j.ejpe.2012.07.002.
Akcay, H., Oguz, A., & Karapire, C. (2003). Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments. Water Research, 37(4), 813–822. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00392-5.
Akcil, A., Erust, C., Ozdemiroglu, S., Fonti, V., & Beolchini, F. (2015). A review of approaches and techniques used in aquatic contaminated sediments: metal removal and stabilization by chemical and biotechnological processes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 86, 24–36. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.009.
Arega, F., & Hayter, E. (2008). Coupled consolidation and contaminant transport model for simulating migration of contaminants through the sediment and a cap. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 32(11), 2413–2428. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2007.09.024.
Aşçi, Y., Nurbaş, M., & Saǧ Açikel, Y. (2008). A comparative study for the sorption of Cd(II) by K-feldspar and sepiolite as soil components, and the recovery of Cd(II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Journal of Environmental Management, 88(3), 383–392. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.03.006.
ASTM. (2005). Standard test method for measutring the toxicity of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates. EI706-05. ASTM Standards on Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Evaluation. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials
Baker, L. A. (1992). Introduction to nonpoint source pollution in the United States and prospects for wetland use. Ecological Engineering, 1(1–2), 1–26. doi:10.1016/0925-8574(92)90023-U.
Brechbühl, Y., & Christl, I. (2012). Competitive sorption of carbonate and arsenic to hematite: combined ATR-FTIR and batch experiments. Journal of colloid and …, 377, 313–321. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.025.
Carabante, I., Grahn, M., Holmgren, A., & Hedlund, J. (2010). In situ ATR-FTIR studies on the competition adsorption of arsenate and phosphate on ferrihydrite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 351, 523–531.
D’elia, C. F., Steudler, P. A., & Corwin, N. (1977). Determination of total nitrogen in aqueous samples using persulfate digestion. Limnology and Oceanography. doi:10.4319/lo.1977.22.4.0760.
Downs, R., & Hall-Wallace, M. (2003). The American mineralogist crystal structure database. American Mineralogist, 88, 247–250.
Elzinga, E. J., Huang, J.-H., Chorover, J., & Kretzschmar, R. (2012). ATR-FTIR spectroscopy study of the influence of pH and contact time on the adhesion of Shewanella putrefaciens bacterial cells to the surface of hematite. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(23), 12848–12855. doi:10.1021/es303318y.
Fink, D. H., Nakayama, F. S., & McNeal, B. L. (1971). Demixing of exchangeable cations in free-swelling bentonite clay. Soil Science Society of America Procedings, 35, 552–555.
Gates, W. P., Bouazza, A., & Churchman, G. J. (2009). Bentonite clay keeps pollutants at bay. Elements, 5(2), 105–110. doi:10.2113/gselements.5.2.105.
Gimsing, A. L., & Borggaard, O. K. (2007). Phosphate and glyphosate adsorption by hematite and ferrihydrite and comparison with other variable-charge minerals. Clays and Clay Minerals, 55(1), 108–114. doi:10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550109.
Go, J., Lampert, D. J., Stegemann, J. A., & Reible, D. D. (2009). Predicting contaminant fate and transport in sediment caps: mathematical modelling approaches. Applied Geochemistry, 24(7), 1347–1353. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.04.025.
Hanawalt, J. D., Rinn, H. W., & Frevel, L. K. (1938). Chemical analysis by X-ray diffraction. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, Analytical Edition, 10(9), 457–512. doi:10.1021/ac50125a001.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25(1), 101–110. doi:10.1023/A:1008119611481.
Helfferich, F. G. (1962). Ion exchange. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hyun, S., Jafvert, C. T., Lee, L. S., & Rao, P. S. C. (2006). Laboratory studies to characterize the efficacy of sand capping a coal tar-contaminated sediment. Chemosphere, 63(10), 1621–1631. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.025.
Jia, Y., & Demopoulos, G. P. (2008). Coprecipitation of arsenate with iron(III) in aqueous sulfate media: effect of time, lime as base and co-ions on arsenic retention. Water Research, 42(3), 661–668. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.08.017.
Keeney, D. R., & Nelson, D. W. (1982). Nitrogen in organic forms. In A. L. Page et al. (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis, part 2 (pp. 643–698). Madison: American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America.
Kiipli, T., Orlova, K., Kiipli, E., & Kallaste, T. (2008). Use of immobile trace elements for the correlation of Telychian bentonites on Saaremaa Island, Estonia, and mapping of volcanic ash clouds. Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(1), 39. doi:10.3176/earth.2008.1.04.
Kim, K. S., Park, M., Choi, C. L., Lee, D. H., Seo, Y. J., Kim, C. Y., et al. (2011). Suppression of NH3 and N2O emissions by massive urea intercalation in montmorillonite. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(3), 416–422. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0326-z.
Kuo, S. (1996). Phosphorus. In D. L. Sparks et al. (Eds.), Mehtods of soil analysis, part 3 (pp. 869–919). Madison: American Society of Agronomy and Society of Soil Science of America.
Li, Y., Wang, X., & Wang, J. (2011). Cation exchange, interlayer spacing, and thermal analysis of Na/Ca-montmorillonite modified with alkaline and alkaline earth metal ions. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 110(3), 1199–1206. doi:10.1007/s10973-011-2109-1.
Lin, J., Zhan, Y., & Zhu, Z. (2011). Evaluation of sediment capping with active barrier systems (ABS) using calcite/zeolite mixtures to simultaneously manage phosphorus and ammonium release. The Science of the Total Environment, 409(3), 638–646. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.10.031.
Lu, P., & Zhu, C. (2010). Arsenic eh–pH diagrams at 25 °C and 1 bar. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(8), 1673–1683. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0652-x.
Lutterotti, L., Matthies, S., Wenk, H.-R., Schultz, A. S., & Richardson, J. W. (1997). Combined texture and structure analysis of deformed limestone from time-of-flight neutron diffraction spectra. Journal of Applied Physics, 81(2), 594. doi:10.1063/1.364220.
Masue, Y., Loeppert, R. H., & Kramer, T. A. (2007). Arsenate and arsenite adsorption and desorption behavior on coprecipitated aluminum:iron hydroxides. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(3), 837–842.
McBride, M. B. (1994). Environmental chemistry of soils. New York: Oxford University Press.
McKenzie, R. (1980). The adsorption of lead and other heavy metals on oxides of manganese and iron. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 18(1), 61. doi:10.1071/SR9800061.
Meis, S., Spears, B. M., Maberly, S. C., & Perkins, R. G. (2013). Assessing the mode of action of Phoslock® in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (loch Flemington, UK). Water Research, 47(13), 4460–4473. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.017.
Minh, N. H., Minh, T. B., Kajiwara, N., Kunisue, T., Iwata, H., Viet, P. H., et al. (2007). Pollution sources and occurrences of selected persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in sediments of the Mekong River delta, South Vietnam. Chemosphere, 67(9), 1794–1801. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.144.
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27(C), 31–36. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5.
Paytan, A., & McLaughlin, K. (2007). The oceanic phosphorus cycle. Chemical Reviews, 107(2), 563–576. doi:10.1021/cr0503613.
Pellegrini, D. (1999). Characterisation of harbour and coastal sediments: specific destinations of dredged material. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management, 2(4), 455–464. doi:10.1016/S1463-4988(99)00044-5.
Peng, J.-F., Song, Y.-H., Yuan, P., Cui, X.-Y., & Qiu, G.-L. (2009). The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 633–640. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.061.
Pils, J. R. V., Laird, D. A., & Evangelou, V. P. (2007). Role of cation demixing and quasicrystal formation and brekup on the stability of smectite colloids. Applied Clay Science, 35, 201–211.
Pinto, E., Sigaud-kutner, T. C. S., Leitao, M. A. S., Okamoto, O. K., Morse, D., & Colepicolo, P. (2003). Heavy metal-induced oxidative stress in algae. Journal of Phycology, 39(6), 1008–1018. doi:10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.02-193.x.
van Reeuwijk, L. P. (1992). Procedures for soil analysis (third ed.). Wageningen, The Netherlands: International Soil Reference and Information Centre.
Robinson, S. E., Capper, N. A., & Klaine, S. J. (2010). The effects of continuous and pulsed exposures of suspended clay on the survival, growth, and reproduction of Daphnia magna. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29(1), 168–175. doi:10.1002/etc.4.
Schaanning, M., Breyholtz, B., & Skei, J. (2006). Experimental results on effects of capping on fluxes of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) from historically contaminated sediments. Marine Chemistry, 102(1–2), 46–59. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2005.10.027.
Smith, V. H., & Schindler, D. W. (2009). Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 24(4), 201–207. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.11.009.
Stachowicz, M., Hiemstra, T., & van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2008). Multi-competitive interaction of as(III) and as(V) oxyanions with Ca2+, Mg2+, PO3-4, and CO2-3 ions on goethite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 320(2), 400–414. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2008.01.007.
Tarabara, V. V., & Wiesner, M. R. (2005). Physical and transport properties of bentonite-cement composites: a new material for in situ capping of contaminated underwater sediments. Environmental Engineering Science, 22(5), 578–590. doi:10.1089/ees.2005.22.578.
Tombácz, E., & Szekeres, M. (2006). Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite. Applied Clay Science, 34(1–4), 105–124. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2006.05.009.
Viana, P. Z., Yin, K., & Rockne, K. J. (2008). Modeling active capping efficacy. 1. Metal and Organometal contaminated sediment remediation. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(23), 8922–8929. doi:10.1021/es800942t.
Wang, S., Jin, X., Bu, Q., Jiao, L., & Wu, F. (2008). Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 316(1–3), 245–252. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.09.007.
Zamparas, M., Deligiannakis, Y., & Zacharias, I. (2013). Phosphate adsorption from natural waters and evaluation of sediment capping using modified clays. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(13–15), 2895–2902. doi:10.1080/19443994.2012.748139.
Zamparas, M., Drosos, M., Deligiannakis, Y., & Zacharias, I. (2014). Eutrophication control using a novel bentonite humic-acid composite material Bephos™. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2014.12.013.
Zhang, H., & Selim, H. M. (2008). Reaction and transport of arsenic in soils: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Advances in Agronomy, 98, 45–115.
Zoumis, T., Schmidt, A., Grigorova, L., & Calmano, W. (2001). Contaminants in sediments: remobilisation and demobilisation. The Science of the Total Environment, 266(1–3), 195–202. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00740-3.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported not only by the Basic Science Research Program (NRF-2014R1A1A2059196) and Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program (NRF-2015H1A2A1034068) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea, but also by the Brain Korea 21 Plus Program funded by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Ro, HM., Cho, K.H. et al. Fluxes of nutrients and trace metals across the sediment-water interface controlled by sediment-capping agents: bentonite and sand. Environ Monit Assess 188, 566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5583-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5583-x