Abstract
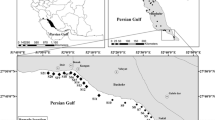
This paper reports the bioavailability of the metals (cadmium, copper, zinc, lead, and nickel) in sediment samples collected in seven stations from the São Paulo Estuary, Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil. The bioavailability was determined by employing the technique “acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metal (SEM)”. The elements cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc were determined using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV), while nickel was quantified utilizing electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry (ET AAS). The accuracy of these methods was confirmed using a certified reference material of estuarine sediment (NIST 1646). The sulfide was quantified using potentiometry with selective electrode and the organic matter determination employing an indirect volumetric method using potassium dichromate and iron(II) sulfate solutions. The bioavailability of the metals was estimated by relationship between the concentration of AVS and the sum of the concentrations of the simultaneously extracted metals (ΣSEM), considering a significant toxicity when (ΣSEM)/(AVS) is higher than 1. The bioavailability values in the seven stations studied varied from 0.93 to 1.31 (June, 2014) and from 0.34 to 0.58 (September, 2014). These results demonstrated a critical condition of toxicity (bioavailability >1) in six of the seven sediment samples collected during the rainy season (June, 2014). In the other period (September, 2014), the bioavailability was always lower than 1 for all sediment samples collected in the seven stations. The individual values of the concentrations of the five metals were compared with the parameters PEL (probable effects level) and TEL (threshold effects level), which are commonly employed for characterization of ecological risk in environmental systems. This comparison revealed that all metals have concentrations lower than the PEL and only zinc and lead in some stations have contents higher than the TEL. The bioavailability evaluation and the concentrations achieved for the five elements in the sediments samples analyzed demonstrated that the ecosystem studied does not present an environmental risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bu, H. M., Wang, W. B., Song, X. F., & Zhang, Q. F. (2015). Characteristics and source identification of dissolved trace elements in the Jinshui River of the South Qinling Mts., China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 14248–14257.
Burin, V. M., Gomes, T. M., Caliari, V., Rosier, J. P., & Luiz, M. T. B. (2015). Establishment of influence the nitrogen content in musts and volatile profile of white wines associated to chemometric tools. Microchemical Journal, 122, 20–28.
Calmano, W., Hong, J., & Förstner, U. (1993). Binding and mobilization of heavy metals in contaminated sediments affected by pH and redox potential. Wat Sci Tech, 28, 223–235.
Cardoso-Silva, S., Da Silva, D. C. V. R., Lage, F., de Paiva, T. C. B., Moschini-Carlos, V., Rosa, A. H., & Pompeo, M. (2016). Metals in sediments: bioavailability and toxicity in a tropical reservoir used for public water supply. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 310.
Di Toro, D. M., Mahony, J. D., & Hansen, D. J. (1990). Toxicity of cadmium sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide. Environ Toxic and Chem, 9, 1487–1502.
Di Toro, D. M., McGrath, J. A., Hansen, D. J., Berry, W. J., Paquin, P. R., Mathew, R., Wu, K. B., & Santore, R. C. (2005). Predicting sediment metal toxicity using a sediment biotic ligand model: methodology and initial application. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 2410–2427.
Di Toro, D. M., Zarba, C. S., Hansen, D. J., Berry, W. J., Swartz, R. C., Cowan, R. E., Pavlou, S. P., Allen, H. E., Thomas, N. A., & Paquin, P. R. (1991). Technical basis for establishing sediment quality criteria for nonionic organic chemical using equilibrium partitioning. Environ Toxic and Chem, 10, 1541–1583.
Fathollahzadeh, H., Kaczala, F., Bhatnagar, A., & Hogland, W. (2014). Speciation of metals in contaminated sediments from Oskarshamn Harbor, Oskarshamn, Sweden. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 2455–2464.
Guo, W., Huo, S. L., Xi, B. D., Zhang, J. T., & Wu, F. C. (2015). Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: distribution, bioavailability and risk. Ecolog Eng, 81, 243–255.
He, Y., Meng, W., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., Liu, S. S., & Guo, C. S. (2015). Spatial distribution and toxicity assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Liaohe River, Northeast China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 14960–14970.
Huang, G. X., Chen, Z. Y., Sun, J. C., Liu, F., Wang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2015). Effect of sample pretreatment on the fractionation of arsenic in anoxic soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 8367–8374.
Li, F., Zeng, X. Y., Yu, Y. J., Wu, C. H., Mai, G., Song, W. W., Wen, Y. M., Duan, Z. P., & Yang, J. Y. (2014). A field study of the relationship between sulfide-bound metals and bioaccumulation by Limnodrilus sp in a heavily polluted river. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 4935–4946.
Massone, G. G., Wagener, A. L. R., Abreu, H. M., & Gioda, A. (2015). Hydrocarbon concentration and source appraisal in atmospheric particulate matter (PM2.5) of an urban tropical area. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 14767–14780.
Mendil, D., Unal, O. F., Tuzen, M., & Soylak, M. (2010). Determination of trace metals in different fish species and sediments from the river Yesilirmak in Tokat, Turkey. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48, 1383–1392.
Menezes, H. C., Paulo, B. P., Paiva, M. J. N., de Barcelos, S. M. R., Macedo, D. F. D., & Cardeal, Z. L. (2015). Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in artisanal cachaca by DI-CF-SPME-GC/MS. Microchemical Journal, 118, 272–277.
Sungur, A., Soylak, M., Yilmaz, S., & Ozcan, H. (2014). Determination of heavy metals in sediments of the Ergene River by BCR sequential extraction method. Environ. Earth Science, 72, 3293–3305.
Teng, Y. G., Feng, D., Wu, J., Zuo, R., Song, L. T., & Wang, J. S. (2015). Distribution, bioavailability, and potential ecological risk of Cu, Pb, and Zn in soil in a potential groundwater source area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187 .article 293
Tuzen, M. (2003). Determination of trace metals in the river Yesilirmak sediments in Tokat, Turkey using sequential extraction procedure. Microchemical Journal, 74, 105–110.
Vasconcelos, F. M., Almeida, D. F., Santos, L., & Moreira, T. T. (2010). Caracterização do potencial de biodisponibilidade de metais (Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu e Ni) em sedimentos de corrente do Rio São Francisco. Geonomos, 18, 28–32.
Wang, J., Liu, G., Lu, I., & Liu, H. (2016). Metal distribution and bioavailability in surface sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188 .article 3
Yalcin, M. G., Narin, I., & Soylak, M. (2008). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contents of sediments from Gumusler creek, Nigde, Turkey. Environmental Geology, 54, 1155–1163.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB), the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for providing grants, fellowships, and other financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, J.B., Nascimento, R.A..., de Oliva, S.T. et al. Bioavailability assessment of toxic metals using the technique “acid-volatile sulfide (AVS)-simultaneously extracted metals (SEM)” in marine sediments collected in Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 188, 554 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5562-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5562-2