Abstract
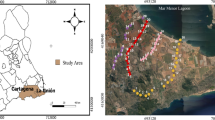
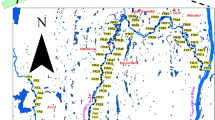
An extensive spatial survey was conducted on trace metal content in stream sediments from Oued El Maadene basin, northern Tunisia. Our objectives were to evaluate the level of trace metal pollution and associated ecological risk and identify the major sources of metal pollution. A total of 116 stream sediment samples were collected and analysed for total As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, V, Zn, and Zr concentrations. The results showed that concentrations of Cr, Ni, V, and Zr were close to natural levels. In contrast, As, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn had elevated concentrations and enrichment factors compared to other contaminated regions in northern Tunisia. Ecological risk to aquatic ecosystems was highlighted in most areas. Principal component analysis showed that Cr, Ni, V, and Zr mainly derived from local soil and bedrock weathering, whilst As, Cd, Pb, and Zn originated from mining wastes. Trace metals could be dispersed downstream of tailings, possibly due to surface runoff during the short rainy season. Surprisingly, Cu, and to a lesser extent As, originated from agricultural activities, related to application of Cu-based fungicides in former vineyards and orchards. This study showed that, despite the complete cessation of mining activities several decades ago, metal pollution still impacts the local environment. This large pollution, however, did not mask other additional sources, such as local agricultural applications of fungicides.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidi, R. (2010). Mineralogy and fluid inclusion study of the carbonate-hosted Mississippi valley-type Ain Allega Pb-Zn-Sr-Ba ore deposit, Northern Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 57, 262–272. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.08.006.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils. London: Blackie Academic and Professional.
Anju, M., & Banerjee, D. K. (2012). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in soils of a Pb–Zn mining area, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 4191–4206. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2255-8.
Barbieri, M., Sappa, G., Vitale, S., Parisse, B., & Battistel, M. (2014). Soil control of trace metals concentrations in landfills: a case study of the largest landfill in Europe, Malagrotta, Rome. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 143, 146–154. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.04.001.
Berg, T., & Steinnes, E. (1997). Recent trends in atmospheric deposition of trace elements in Norway as evident from the 1995 moss survey. Science of the Total Environment, 208, 197–206. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00253-2.
Bourennane, H., Douay, F., Sterckeman, T., Villanneau, E., Ciesielski, H., King, D., & Baize, D. (2010). Mapping of anthropogenic trace elements inputs in agricultural topsoil from Northern France using enrichment factors. Geoderma, 157, 165–174. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.04.009.
Boussen, S., Soubrand, M., Bril, H., Ouerfelli, K., & Abdeljaouad, S. (2013). Transfer of lead, zinc and cadmium from mine tailings to wheat (Triticum aestivum) in carbonated Mediterranean (Northern Tunisia) soils. Geoderma, 192, 227–236. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.08.029.
Candeias, C., Ferreira da Silva, E., Salgueiro, A. R., Pereira, H. G., Reis, A. P., Patinha, C., Matos, J. X., & Avila, P. H. (2011). The use of multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data for assessing the spatial distribution of soil contamination by potentially toxic elements in the Aljustrel mining area (Iberian Pyrite Belt, Portugal). Environment and Earth Science, 62, 1461–1479. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0631-2.
Daldoul, G., Souissi, R., Souissi, F., Jemmali, N., & Chakroun, H. K. (2015). Assessment and mobility of heavy metals in carbonated soils contaminated by old mine tailings in North Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 110, 150–159. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.06.004.
Decreé, S., de Putter, T., Yans, J., Moussi, B., Recourt, P., Jamoussi, F., Bruyère, D., & Dupuis, C. (2008). Iron mineralisation in Mio-Pliocene sediments of the Tamra iron mine (Nefza mining district, Tunisia): mixed influence of pedogenesis and hydrothermal alteration. Ore Geology Reviews, 33, 397–410. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.02.001.
Decrée, S., Marignac, C., Liégeois, J. P., Yans, J., Ben Abdallah, R., & Demaiffe, D. (2014). Miocenemagmatic evolution in the Nefza district (Northern Tunisia) and its relationship with the genesis of polymetallic mineralizations. Lithos, 192–195, 240–258. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.02.001.
Fernandez-Caliani, J. C., Barba-Brioso, C., Gonzalez, I., & Galan, E. (2009). Heavy metal pollution in soils around the abandoned mine sites of the Iberian pyrite belt (Southwest Spain). Water Air Soil Pollution, 200, 211–226. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9905-7.
Ghorbel, M., Munoz, M., Courjault-Radé, P., Destrigneville, C., de Parseval, P., Souissi, R., Souissi, F., Ben Mammou, A., & Abdeljaouad, S. (2010). Health risk assessment for human exposure by direct ingestion of Pb, Cd, Zn bearing dust in the former miner’s village of Jebel Ressas, NE Tunisia. European Journal of Mineralogy, 22(5), 639–649. doi:10.1127/0935-1221/2010/0022-2037.
González-Corrochano, B., Esbrí, J. M., Alonso-Azcárate, J., Martínez-Coronado, A., Jurado, V., & Higueras, P. (2014). Environmental geochemistry of a highly polluted area: the La Union Pb–Zn mine (Castilla-La Mancha region, Spain). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144, 345–354. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.02.014.
Hakanson, L. (1980). Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(80)/90143-8.
Henke, K. R., & Atwood, D. A. (2009). Arsenic in human history and modern societies. In K. R. Henke (Ed.), Arsenic: environmental chemistry, health threats and waste treatment (pp. 277–302). Chichester: Wiley.
Jallouli, C., Mickus, K., Turki, M. M., & Rihane, C. (2003). Gravity and aeromagnetic constraints on the extent of Cenozoic rocks within the Nefza–Tabarka region, northwestern Tunisia. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 122, 51–68. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00469-9.
Jdid, E. A., Blazy, P., Kamoun, S., Guedria, A., Marouf, B., & Kitane, S. (1999). Environmental impact of mining activity on the pollution of the Medjerda River, north-west Tunisia. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 57, 273–280. doi:10.1007/s100640050045.
Khalil, A., Hanich, L., Bannari, A., Zouhri, L., Pourret, O., & Hakkou, R. (2013). Assessment of soil contamination around an abandoned mine in a semi-arid environment using geochemistry and geostatistics: pre-work of geochemical process modeling with numerical models. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 125, 117–129. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.11.018.
Klassen, R. A., Douma, S., & Rencz, A. N. (2010). Environmental and human health risk assessment for essential trace elements: considering the role for geoscience. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A, 73, 242–252. doi:10.1080/15287390903340906.
Lui, G., Tao, L., Lui, X., Hou, J., Wang, A., & Li, R. (2013). Heavy metal speciation and pollution of agricultural soils along Jishui River in non-ferrous metal mine area in Jiangxi Province, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 132, 156–163. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.017.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31. doi:10.1002/etc.5620190524.
Matschullat, J., Ottenstein, R., & Reimann, C. (2000). Geochemical background—can we calculate it? Environmental Geology, 39, 990–1000. doi:10.1007/s002549900084.
Mlayah, A., Ferrera da Silva, E., Rocha, F., Ben Hamza, C. H., Charef, A., & Noronha, F. (2009). The Oued Mellègue: mining activity, stream sediments and dispersion of base metals in natural environments, North-western Tunisia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 102, 27–36. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.11.016.
Mlayah, A., Ferrera da Silva, E., Hatira, N., Jallali, S., Lachaal, F., Charef, A., Noronha, F., & Ben Hamza, C. H. (2011). Bassin d’oued Serrat : Terrils et rejets domestiques, reconnaissance des métaux lourds et polluants, impact sur les eaux souterraines (nord-ouest de la Tunisia). Revue des Sciences de l’Eau, 24(2), 159–175. doi:10.7202/1006109ar.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geology Journal, 2, 109–118.
Navarro, M. C., Pérez-Sirvent, C., Martínez-Sánchez, M. J., Vidal, J., Tovar, P. J., & Bech, J. (2008). Abandoned mine sites as a source of contamination by heavy metals: a case study in a semi-arid zone. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 96, 183–193. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2007.04.011.
Newton, D. E. (2010). Chemical elements (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills: Gale.
Nriagu, J. O. (1989). A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature, 338, 47–49. doi:10.1038/338047a0.
Othmani, M. A., Souissi, F., Benzaazoua, M., Bouzahzah, H., Bussiere, B., & Mansouri, A. (2013). The geochemical behaviour of mine tailings from the Touiref Pb–Zn district in Tunisia in weathering cells leaching tests. Mine Water and the Environment, 32, 28–41. doi:10.1007/s10230-012-0210-8.
Oyarzun, R., Lillo, J., Lopez-Garcia, J. A., Esbri, J. M., Cubas, P., Llanos, W., & Higueras, P. (2011). The Mazarron Pb-(Ag)-Zn mining district (SE Spain) as a source of heavy metal contamination in a semiarid realm: geochemical data from mine wastes, soils, and stream sediments. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 109, 113–124. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.04.009.
Pacyna, J. M. (1986). Atmospheric trace elements from natural and anthropogenic sources. In J. O. Nriagu & C. L. Davidson (Eds.), Toxic metals in the atmosphere (pp. 33–52). New York: Wiley.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 5084–5091. doi:10.1021/es001339o.
Rodriguez, L., Ruiz, E., Alonso-Azcarate, J., & Rincon, J. (2009). Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb–Zn mine in Spain. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1106–1116. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.04.007.
Rouvier, H. (1977). Géologie de l’extrême Nord-Tunisien : tectoniques et paléogéographie superposées à l’extrémité orientale de la chaîne Nord-Maghrébine (Thèse Doctorat és Science). Paris, France: Université de Pierre et Marie Curie.
Rowlatt, S. M., & Lovell, D. R. (1994). Lead, zinc and chromium in sediments around England and Wales. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28, 324–329. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)90159-7.
Sainfeld, P. (1952). Les gîtes plombo-zincifères de Tunisie. Annales des Mines et de la Géologie, Tunis, Tunisie, 9, 1–285.
Skordas, K., & Kelepertsis, A. (2005). Soil contamination by toxic metals in the cultivated region of Agia, Thessaly, Greece. Identification of sources of contamination. Environmental Geology, 48, 615–624. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-1319-x.
Souissi, R., Souissi, F., Chakroun, H. K., & Bouchardon, J. L. (2013). Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of mine tailings and Pb, Zn, and Cd mobility in a carbonate setting (Northern Tunisia). Mine Water and the Environment, 32, 16–27. doi:10.1007/s10230-012-0208-2.
Sun, Y. B., Zhou, Q. X., Xie, X. K., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 455–462. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.074.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627. doi:10.1007/s002540050473.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Oxford: Blackwell.
Wang, S., Zhimin, C., Dongzhao, L., Zhichang, Z., & Li, G. (2008). Concentration distribution and assessment of several heavy metals in sediments of west-four Pearl River Estuary. Environmental Geology, 55(1), 963–975. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1046-6.
Webster, J., & Ridgway, I. (1994). The application of the equilibrium partitioning approach for establishing sediment quality criteria at two UK Sea disposal and outfall sites. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28, 653–661. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)90300-X.
Yuan, G. L., Sun, T. H., Han, P., Li, J., & Lang, X. X. (2014). Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: Typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 136, 40–47. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.002.
Zhang, X. Y., Lin, F. F., Wong Mike, T. F., Feng, X. L., & Wang, K. (2009). Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154, 439–449. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0410-7.
Zhang, J., Li, Z. H., Chen, J., Wang, M., Tao, R., & Lui, D. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72, 1279–1288. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3047-6.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Office of Mines (Tunisia). The authors thank Mohamed Arfaoui for his constructive and helpful comments. Thanks to one anonymous reviewer for his relevant comment which improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayari, J., Agnan, Y. & Charef, A. Spatial assessment and source identification of trace metal pollution in stream sediments of Oued El Maadene basin, northern Tunisia. Environ Monit Assess 188, 397 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5402-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5402-4