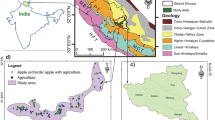
Abstract
Soil quality assessment provides a tool for evaluating the sustainability of soils under different crop cafeterias. Our objective was to develop the soil quality index for evaluating the soil quality indicators under different cropping systems in northwest Himalaya-India. Composite soil samples were taken from the study area from different cropping systems which include T1 (forest soil control), T2 (rice-oilseed, lower belts), T3 (rice-oilseed, higher belts), T4 (rice-oats), T5 (rice-fallow), T6 (maize-oats), T7 (maize-peas), T8 (apple), T9 (apple-beans), and T10 (apple-maize). Physical, chemical, and biological soil indicators were determined, and it was found that soil enzyme activities involved in nutrient cycling were significantly higher in forest soils, which were reflected in higher levels of available pool of nutrients. Carbon stocks were found significantly higher in forest soil which was translated in improved soil physical condition. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to reduce multidimensionality of data followed by scoring by homothetic transformation of the selected indicators. Pearson’s interclass correlation was performed to avoid redundancy, and highly correlated variables were not retained. Inclusion of legumes in the apple orchard floor recorded highest soil quality rating across the treatments. Cereal-based cropping systems were found in lower soil quality rating; however, the incorporation of peas in the system improved soil health.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afyuni, M., & Wagger, M. G. (2006). Soil physical properties and bromide movement in relation to tillage system. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 37, 541–556.
Alvarez, R., & Lavado, R. S. (1998). Climate, organic matter and clay content relationship in the Pampa and Chaco soils, Argentina. Geoderma, 83, 127–141.
Andrew, S. S., Mitchell, J. P., Mancinelli, R., Larlen, D. L., Hartz, T. K., Horwarth, W. R., Pettygroove, G. S., Scow, K. M., & Munk, D. S. (2002). On farm assessment of soil quality in California’s central valley. Agronomy Journal, 94, 12–23.
Berg, B., & Mcclaugherty, C. (2008). Plant litter decomposition, humus formation, and carbon sequestration (2nd ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Blair, G. B., Lefroy, R. D. B., Singh, B. P., & Till, A. R. (1997). Development and use of a carbon management index to monitor changes in soil C pool size and turnover rate. In G. Cadisch & K. E. Giller (Eds.), Driven by nature: plant litter quality and decomposition (pp. 273–281). Wallingford: CAB International.
Blake, G. R., & Hartge, K. H. (1986). Bulk density. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part I. Physical and mineralogical methods: Agronomy Monograph No. 9 (2nd ed., pp. 363–375). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Brejda, J. J., Moorman, T. B., Karlen, D. L., & Dao, T. H. (2000). Identification of regional soil quality factors and indicators I. Central and Southern High Plains. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 64, 2115–2124.
Bremner, J. M. .(1965). Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In C. A. Black, D. D. Evans, J. L. White, E. Ensminger & F. E. Clark (Eds.), Methods of soils analysis. Part 2. Agronomy No. 9 (pp. 1179–1237). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Camberdella, C. A., & Elliott, E. T. (1992). Particulate soil organic matter across grassland cultivation sequence. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56, 777–783.
Carof, M., Detourdonnet, S., Coquet, Y., Hallaire, V., & Roger-Estrade, J. (2007). Hydraulic conductivity and porosity under conventional and no-tillage and the effect of three species of cover crop in northern France. Soil Use and Management, 23, 230–237.
Crews, T. E., & Peoples, M. B. (2004). Legume versus fertilizer sources of nitrogen: ecological trade-offs and human needs. Agriculture Ecosystem and Environment, 102, 279–297.
Davidson, E. A., & Ackerman, I. L. (1993). Changes in soil carbon inventories following cultivation of previously untilled soils. Biogeochemistry, 20, 161–193.
Don, A., Schumacher, J., & Freibauer, A. (2011). Impact of tropical land-use change on soil organic carbon stocks—a meta-analysis. Global Change Biology, 17, 1658–1670.
Edwards, C. A., & Lofty, J. R. (1982). Nitrogenous fertilizers and earthworm populations in agricultural soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 14, 515–521.
Erick, E. D., & Reynolds, W. D. (1992). Method for analyzing constant-head well permeameter data. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56, 320–323.
Francis, C. A., & Clegg, M. D. (1990). Crop rotation in sustainable production systems. In C. A. Edwards, R. Lar, P. Madden, R. H. Miller & G. House (Eds.), Sustainable agricultural systems (pp. 107–122). Ankeny: Soil and Water Conservation Society.
Giller, K. E. (2001). Nitrogen fixation in tropical cropping systems (2nd ed.). Wallingford: CAB International.
Goh, K. M., & Ridgen, G. E. (1997). Comparison of understory biological nitrogen fixation and biomass production in grassed-down conventional and organic apple orchards in Canterbury, New Zealand. Communication in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 28, 1103–1116.
Green, V. S., Stott, D. E., & Diack, M. (2006). Assay for fluorescein diacetate hydrolytic activity: optimization for soil samples. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38, 693–701.
Harinikumar, K. M., & Bagyaraj, D. J. (1988). Effect of crop rotation on native vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal propagules in soil. Plant and Soil, 110, 77–80.
Haynes, R. J., & Goh, K. M. (1980). Some effects of orchard soil management on sward composition, levels of nutrients in the soil, and leaf nutrient content of mature ‘Golden Delicious’ apple tree. Scientia Horticulturae, 13, 15–25.
Haynes, R. J., & Naidu, R. (1998). Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical condition: a review. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystem, 51, 123–137.
Heviaa, G. G., Buschiazzoa, D. E., & Heppera, E. N. (2003). Organic matter in size fractions of soils of the semiarid Argentina. Effects of climate, soil texture and management. Geoderma, 116, 265–277.
Homann, P. S., Sollins, P., Chappell, H. N., & Stangenberger, A. G. (1995). Soil organic carbon in a mountainous, forested region: relation to site characteristics. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59, 1468–1475.
Houghton, R. A. (2003). Why are estimates of the terrestrial carbon balance so different? Global Change Biology, 9, 500–509.
IPCC. Climate change. (2007). The physical science basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Islam, K. R., & Weil, R. R. (2000). Land use effects on soil quality in a tropical forest ecosystem of Bangladesh. Agriculture, Ecosystem and Environment, 79, 9–16.
Jackson, M.L. (1973) Soil chemical analysis Prentice Hall of India. Pvt Ltd, New Delhi.
Jenkinson, D. S., & Powlson, D. S. (1976). The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil—V: a method for measuring soil biomass. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 8, 209–213.
Jokela, W. E., Grabber, J. H., Karlen, D. L., Balser, T. C., & Palmquist, D. E. (2009). Cover crop and liquid manure effects on soil quality indicators in a corn silage system. Agronomy Journal, 101, 727–737.
Justin, G. K., Singh, R. D., Patra, A. K., & Arunkumar, K. (2013). Soil carbon pools and carbon management index under different land use systems in the Central Himalayan Region. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica Section B Soil and Plant Science, 63, 200–2205.
Kang, H., & Freeman, C. (1999). Phosphatase and arylsulphatase activities in wetland soils: annual variation and controlling factors. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 31, 449–454.
Karamanos, A. J., Bilalia, D., & Sidiras, N. (2004). Effects of reduced tillage and fertilization practices on soil characteristics, plant water status, growth and yield of upland cotton. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 190, 262–276.
Karen, B., Jens, L., Erika, H., & Jurg, F. (2010). Alpine pasture soils accumulate a large fraction of labile carbon due to combined effect of low temperature, low pH, and poor litter quality on decomposition. Geophysical Research, 13, 40–54.
Karlen, D. L., Mausbach, M. J., Doran, J. W., Cline, R. G., Harris, R. F., & Schuman, G. E. (1997). Soil quality: a concept, definition, and framework for evaluation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 4–10.
Keen, B., & Raczkowski, H. J. (1921). Relationship between clay and certain physical properties of soils. Journal of Agricultural Science, 11, 441–449.
Klein, D. A., Loh, T. C., & Goulding, R. L. (1971). A rapid procedure to evaluate dehydrogenase activity of soils low in organic matter. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 3, 385–387.
Lindsay, W. L. & Norvell, W. A. (1978). Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Mahboubi, A. A., Lal, R., & Fausey, N. R. (1993). Twenty-eight years of tillage effect on two soils in Ohio. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 57, 506–512.
Mandiringana, O. T., Mnkeni, P. N. S., Mkile, Z., van Averbeke, W., Van Ranst, E., & Verplancke, H. (2005). Mineralogy and fertility status of selected soils of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Communication in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 36, 2431–2446.
Mann, L. K. (1986). Changes in soil carbon after cultivation. Soil Science, 142, 279–288.
Massimo, T., Giustino, T., Francesca, S., Ana, Q., Simone, P., Giulia, M., Paola, G., & Andrea, M. (2007). Nutrient recycling during the decomposition of apple leaves (Malus domestica Borkh.) and mowed grasses in an orchard. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 118, 191–200.
Masto, R. E., Chhonkar, P. K., Singh, D., & Patra, A. K. (2007). Soil quality response to long-term nutrient and crop management on a semi-arid Inceptisol. Agriculture Ecosystem & Environment, 118, 130–142.
Masto, R. E., Chhonkar, P. K., Singh, D., & Patra, A. K. (2008). Alternative soil quality indices for evaluating the effect of intensive cropping, fertilisation and manuring for 31 years in the semi-arid soils of India. Environment Monitoring & Assessment, 136, 419–435.
Mitchell, C. C., Arriaga, F. J., Entry, J. A., Goodman, W. R., Novak, J. L., Reeves, D. W., et al. (1996). 100 years of sustainable cropping research (p. 26). Alabama: Anburn University. Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull.
Mushtaq, A. W., & Rajkumar. (2005). Potassium release from soil separates of Kashmir. Clay Research, 24, 87–95.
Nguyen, M. L., & Goh, K. M. (1990). Accumulation of soil sulphur fractions in grazed pastures receiving long-term superphosphate applications. New Zealand Journal of Agriculture Research, 32, 245–262.
Olsen, S. R., Cole, C. V., Watanable, F. S., & Dean, L. A. (1954). Estimation of available phosphorus in soil by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Washington, DC: US Department of Agriculture. Circular No 939.
Pagliai, M., Rousseva, S., Vignozzi, M., Piovanelli, C., Pelegrini, S., & Miclaus, N. (1998). Tillage impact on soil quality. 1: soil porosity and related physical properties. Italian Journal of Agronomy, 2, 11–20.
Pagliai, M., Vignozzi, M., Pelegrini, S., Ceccon, P., Giovanardi, R., & Cioutti, S. (2000). Impact of different cropping systems on soil porosity and structure. Italian Journal of Agronomy, 4, 43–51.
Patrick, J. B., Peter, M. G., Charles, T. D., Timothy, J. F., & Thomas, G. S. (2001). Plant soil microbial interactions in a northern hardwood forest. Ecology, 5, 965–978.
Peoples, M. B., & Crasswell, E. T. (1992). Biological nitrogen fixation: investment, expectations and actual contributions to agriculture. Plant and Soil, 141, 13–39.
Peoples, M. B., Herridge, D. F., & Ladha, J. K. (1995). Biological nitrogen fixation: an efficient source of nitrogen for sustainable agricultural production. Plant and Soil, 174, 3–28.
Quideau, S. A., Chadwick, O. A., Graham, R. C., & Wood, H. B. (1996). Base cation biogeochemistry and weathering under oak and pine: a controlled long-term experiment. Biogeochemistry, 35, 377–398.
Quideau, S. A., Chadwick, Q. A., Benesi, A., Graham, R. C., & Anderson, M. A. (2001). A direct link between forest vegetation type and soil organic matter composition. Geoderma, 104, 41–60.
Reynolds, W. D. (1993). Saturated hydraulic conductivity: field measurement. In M. R. Carter (Ed.), Soil sampling and method of analysis (pp. 599–613). Boca: Lewis Publisher.
Rhoades, C. C. (1997). Single-tree influences on soil properties in agroforestry: lessons from natural forest and savanna ecosystems. Agroforestry Systems, 35, 71–94.
Rovira, A. D., Elliot, L. F., & Cook, R. J. (1990). The impact of cropping systems on rhizophere organisms affecting plant health. In J. M. Lynch (Ed.), The rhizosphere (pp. 389–436). New York: Wiley.
Saito, M., & Kawaguchi, K. (1971). Flocculating tendency of paddy soils (part 4). Soil structure of paddy plow-layers. Journal of the Science of Soil and Manure, 42, 95–96.
Scandellari, F., Ventura, M., Malaguti, D., Ceccon, C., Menarbin, G., & Tagliavini, M. (2010). Net primary productivity and partitioning of absorbed nutrients in field-grown apple trees. Acta Horticulturae, 868, 132–137.
Schlecht, E., Buerkert, A., Tielkes, E., & Bationo, A. (2006). A critical analysis of challenges and opportunities for soil fertility restoration in Sudano-Sahelian West Africa. Nutrient Cycling in Agro Ecosystems, 76, 109–136.
Singh, K. B., Gajri, P. R., & Arora, V. K. (2001). Modeling the effects of soil and water management practices on the water balance and performance of rice. Agricultural Water Management, 49, 77–95.
Smith, M. W., Shiferaw, A., & Rice, N. R. (1996). Legume cover crops as a nitrogen source for pecan. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 19, 1117–1130.
Snyder, D. J., & Trofymow, J. A. (1984). Rapid accurate wet oxidation diffusion procedure for determining organic and inorganic carbon in plant and soil samples. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 15, 1587–1597.
Sparling, G. P. (1985). The soil biomass. In D. Vaughn & R. E. Malcolm (Eds.), Soil organic matter and biological activity (pp. 223–262). The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
Srivastava, S. C., & Singh, J. C. (1989). Effect of cultivation on microbial carbon and nitrogen in dry tropical forest soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 8, 343–348.
Tabatabai, M. A., & Bremmer, J. A. (1969). Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1, 301–307.
Tabatabai, M. A., & Bremner, J. M. (1970). Arylsulphatase activity in soils. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 34, 225–229.
Tan, K. H. (1986). Degradation of soil minerals by organic acid. In P. M. Huang & M. Schnitzer (Eds.), Interactions of soil minerals with natural organics and microbes (pp. 1–2). Madison: Soil Science Society of America. SSSA Spec. Publ. 17.
Tateno, R., Fukushima, K., Fujimaki, R., Shimamura, T., Ohgi, S., Arai, H., Ohte, N., Tokachi, N., & Yosshioka, T. (2009). Biomass allocation and nitrogen limitation in Cryptomeria japonica plantation chronosequence. Journal of Forest Research, 14, 276–285.
Tiejun, Z., Yunwen, W., Xianguo, q., & Jianguo, H. (2009). Organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in reed meadow soils converted to alfalfa fields. Soil and Tillage Research, 105, 143–148.
Walkley, A. J., & Black, C. A. (1934). An estimation of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38.
Wander, M. M., & Bollero, G. A. (1999). Soil quality assessment of tillage impacts on Illinois. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63, 961–971.
Wardle, D. A., Yeates, G. W., Bonner, K. I., Nicholson, K. S., & Watson, R. N. (2001). Impact of ground water vegetation management strategies in a kiwifruit orchard on the composition and functioning of the soil biota. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 893–905.
Weil, R. R., & Magdoff, F. R. (2004). Significance of soil organic matter to soil quality and health. In F. R. Magdoff & R. R. Weil (Eds.), Soil organic matter in sustainable agriculture (pp. 1–43). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Williams, C. H., & Steinbergs, A. (1959). Soil sulphur fractions as chemical indices of available sulphur in some Australian soils. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 10, 340–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofi, J.A., Bhat, A.G., Kirmai, N.A. et al. Soil quality index as affected by different cropping systems in northwestern Himalayas. Environ Monit Assess 188, 161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5154-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5154-1