Abstract
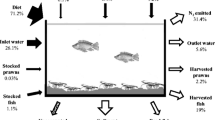
The effects of cage aquaculture on freshwater ecosystems are determined by multiple farming and environmental variables, and thus, the assessment of a wide range of abiotic and biotic variables enables better understanding of the impacts generated by this nutrient source. This study was carried out at Castanhão reservoir located in the State of Ceará, which is the largest Brazilian producer of Nile tilapia in cage systems, wherein about 8000 reservoirs provide a vast area to expand not only this important socio-economic but also pollution-prone activity. Nutrient mass budget, water quality monitoring, hydrodynamic characterization, and elemental/stable isotopic composition of end-member products were measured in cage aquaculture and other reservoir areas in order to determine the relative effects on reservoir conditions. Nutrient budgets showed that 34 % of the artificial feed was lost to the water column but water quality monitoring and isotopic composition analysis suggested that the cages were not extensively impacting the water quality probably because of the physiographic and hydrodynamic features of the cage site.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abery, N. W., Sukadi, F., Budhiman, A. A., Kartamihardja, E. S., Koeshendrajana, S., Buddhiman, D., & De Silva, S. S. (2005). Fisheries and cage culture of three reservoirs in west Java, Indonesia; a case study of ambitious development and resulting interactions. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 12, 315–330.
Alves, R. C. P. & Baccarin, A. E. (2006). Efeito da produção de peixes em tanques-rede sobre sedimentação de material em suspensão e de nutrientes no córrego da Arribada (UHE Nova Avanhandava, Baixo rio Tietê, SP). In M. G., Nogueira, R., Henry, A., Jorcin. (Eds.) Ecologia de reservatórios: impactos potenciais, ações de manejo e sistemas em cascata. (pp. 329–347) Ed. São Carlos: Rima Editora.
An, K., & Kim, D. (2003). Response of reservoir water quality to nutrient from streams and in-lake fish farms. Water Air Soil Pollution, 149, 27–49.
APHA. American Public Health Association (2005). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (21ªed). Washington, DC: American Public Association.
Araújo-Lima, C., Forsberg, B. R., Victoria, R., & Martinelli, L. (1986). Energy sources for detritivorous fishes in the Amazon. Science, 234, 1256–1258.
Beveridge, M. (1996). Cage aquaculture. Blackwell Science Ltd: Fishing News Books, Oxford.
Carter, C. G., Houlihan, D. F., & Owen, S. F. (1998). Protein synthesis, nitrogen excretion and long-term growth of juvenile Pleuronectes flesus. Journal of Fish Biology, 53, 272–284.
Chen, Y. S., Beveridge, M. C. M., & Telfer, T. C. (2000). Settling rate characteristics and nutrient content of the faeces of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., and the implications for modeling of solid waste dispersion. Aquaculture Research, 30, 395–398.
Costello, M. J., Collier, L., Dowse, J., & Quigley, D. (2004). Long-term environmental monitoring shows no impact from salmon cage farming in Lough Allen, an Irish freshwater lake. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy - Section B, Biology and Environment, 104, 19–42.
Cornel, G. E., & Whoriskey, F. G. (1993). The effects of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cage culture on the water quality, zooplankton, benthos and sediments of Lac du Passage, Quebec. Aquaculture, 109, 101–117.
Dempster, T., Sanchez-Jerez, P., Bayle-Sempere, J., & Kingsford, M. (2004). Extensive aggregations of wild fish at coastal sea-cage fish farms. Hydrobiologia, 525, 245–248.
Fernandes, M., Angove, M., Sedawie, T., & Cheshire, A. (2007). Dissolved nutrient release from solid wastes of southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii, Castelnau) aquaculture. Aquaculture Research, 38, 388–397.
Figueredo, C. C., & Giane, A. (2005). Ecological interactions between Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, L.) and the phytoplanktonic community of the Furnas Reservoir (Brazil). Freshwater Biology, 50, 1391–1403.
Foy, R. H., & Rosell, R. (1991). Loadings of nitrogen and phosphorus from a Northern Ireland fish farm. Aquaculture, 96, 17–30.
France, R. L. (1995). Carbon-13 enrichment in benthic compared to planktonic algae: food web implications. Marine Ecology Progress and Series, 124, 307–312.
Gaiser, T., Krol, M. S., Frischkorn, H., & Araujo, J. C. (2003). Global change and regional impacts: water availability and vulnerability of ecosystems and society in the semi-arid Northeast of Brazil. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer Verlag.
Gowen, R. J., & Bradbury, N. B. (1987). The ecological impact of salmonid farming in coastal waters: a review. Oceanography and Marine Biology, 25, 563–575.
Guo, L., & Li, Z. (2003). Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus from fish cage-culture on the communities of a shallow lake in middle Yangtze River basin of China. Aquaculture, 226, 201–212.
Halver, J. E., & Hardy, R. W. (2002). Fish nutrition. USA: Elsevier Science.
Hakanson, L., Carlsson, L., & Johansson, T. (1998). A new approach to calculate the phosphorus load to lakes from fish farm emissions. Aquacultural Engineering, 17, 149–166.
Hargreaves, J. A. (1998). Nitrogen biogeochemistry of aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture, 166, 181–212.
Harrison, J. A., Maranger, R. J., Alexander, R. B., Giblin, A. E., Jacinthe, P. A., Mayorga, E., Seitzinger, S. P., Sobota, D. J., & Wollheim, W. M. (2009). The regional and global significance of nitrogen removal in lakes and reservoirs. Biogeochemistry, 93, 143–157.
Hedges, J. I., Clark, W. A., Quay, P. D., Richey, J. E., Devol, A. H., & Santos, U. M. (1986). Composition and fluxes of particulate organic material in the Amazon river. Limnology and Oceanography, 1986(31), 717–738.
Hevia, M., Rosenthal, H., & Gowen, R. J. (1996). Modelling benthic deposition under fish cages. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 12, 71–74.
Hubaux, A., & Vox, G. (1970). Decision and detection limits for linear calibration curves. Analytical Chemistry, 42, 849–855.
Islam, S. (2005). Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: review and analysis toward model development. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 48–61.
Kiljunen, M., Grey, J., Sinisalo, T., Harrod, C., Immonen, H., & Jones, R. I. (2006). A revised model for lipid-normalizing δ13C values from aquatic organisms, with implications for isotope mixing models. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 1213–1222.
Lilyestrom, C. G., & Romaire, R. P. (1987). Diet and food assimilation by channel catfish and Malaysian prawns in polyculture as determined by stomach content analysis and stable carbon isotope ratios. Journal of World Aquaculture Society, 18, 278–288.
Liti, D. M., Fulanda, B., Munguti, J. M., Straif, M., Waidbacher, H., & Winkler, G. (2005). Effects of open-pond density and caged biomass of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.) on growth feed utilization, economic returns and water quality in fertilized ponds. Aquaculture Research, 36, 1535–1543.
Minagawa, M., & Wada, E. (1984). Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15 N and animal age. Geochimica and Cosmochimica Acta, 48, 1135–1140.
Molisani, M. M., Leite, L. J. A., & Farias, E. G. G. (2007). Tilapicultura cearense: uma reflexão sobre a capacidade de suporte dos reservatórios. Panorama da Aqüicultura, 17, 32–33.
Molisani, M. M., Barroso, H. S., Becker, H., Moreira, M. O. P., Hijo, C. A. G., Monte, T. M., & Vasconcellos, G. H. (2010). Trophic state, phytoplankton assemblages and limnological diagnosis of the castanhão reservoir, CE, Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensis, 22, 1–12.
Molisani, M. M., Becker, H., Barroso, H. S., Hijo, C. A. G., Monte, T. M., Vasconcellos, G. H., & Lacerda, L. D. (2013). The influence of Castanhão reservoir on nutrients and suspended matter transport during rainy season in the ephemeral Jaguaribe river (CE, Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Biology, 73, 115–123.
Parnell, A. C., Inger, R., Bearhop, S., & Jackson, A. L. (2010). Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. PloS One, 5(3), e9672.
Peterson, B. J., & Fry, B. (1987). Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18, 293–320.
Pinnegar, J. K., Polunin, N. V. C., Videler, J. J., & Wiljes, J. J. (2007). Daily carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus budgets for the Mediterranean planktivorous damselfish Chromis chromis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 352, 378–391.
Reid, G. K., Liutkus, M., Robinson, S. M. C., Chopin, T. R., Blair, T., Lander, T., Mullen, J., Page, F., & Moccia, R. D. (2009). A review of the biophysical properties of salmonid faeces: implications for aquaculture waste dispersal models and integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquaculture Research, 40, 257–273.
Rota, M. A. & Queiroz, J. F. (2003) Boas práticas de manejo para a produção de peixes em tanques-rede. Embrapa Pantanal, Documento 47.
Sarà, G., Scilipoti, D., Milazzo, M., & Modica, A. (2006). Use of stable isotopes to investigate dispersal of waste from fish farms as a function of hydrodynamics. Marine Ecology Progress and Series, 313, 261–270.
Sarà, G. (2007a). Ecological effects of aquaculture on living and non-living suspended fractions of the water column: a meta-analysis. Water Research, 41, 3187–3200.
Sarà, G. (2007b). A meta-analysis on the ecological effects of aquaculture on the water column: dissolved nutrients. Marine Environmental Research, 63, 390–408.
Simões, F. S., Moreira, A. M., Bisinoti, M. C., Gimenez, S. N. M., & Yabe, M. J. (2008). Water quality index as a simple indicator of aquaculture effects on aquatic bodies. Ecological Indicators, 8, 476–484.
Stigebrandt, A. (2011). Carrying capacity: general principles of model construction. Aquaculture Research, 42, 41–50.
Stirling, H. P., & Dey, T. (1990). Impact of intensive cage fish farming on the phytoplankton and periphyton of a Scottish freshwater loch. Hydrobiologia, 190, 193–214.
SRH Secretaria de Recursos Hídricos do Estado do Ceará. (2008). Programa de Açudes Estratégicos. http://www.srh.ce.gov.br. Accessed 10 May 2012.
Tacon, A. J. G., & Forster, I. P. (2003). Aquafeeds and the environment: policy implications. Aquaculture, 226, 181–189.
Tacon, A. G. J., & Halwart, M. (2007). Cage aquaculture: a global overview. In M. Halwart, D. Soto, & J. R. Artur (Eds.), Cage aquaculture—regional reviews and global overview (pp. 3–16). Roma: FAO Fisheries Technical.
Tavares, L. H. S., Millan, R. N., & Santeiro, R. M. (2010). Characterization of a plankton community in a fish farm. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensis, 22, 60–69.
Vander Zanden, M. J., Cabana, G., & Rasmussen, J. B. (1997). Comparing trophic position of freshwater fish calculated using stable nitrogen isotope ratio (δ15N) and literature dietary data. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 54, 1142–1158.
Wetzel, R. G., & Likens, G. E. (2000). Limnological analyses. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by DCR program from National Research Council of Brazil (CNPq) and Fundação Cearense de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (FUNCAP) (1514-14 CV. 016/2005, Proc. No. 222/04). FUNCAP/CNPq/UFC also provides PIBIC grants to undergraduate students Thiago M. do Monte and George H. Vasconcellos. We are grateful to the Departamento Nacional de Obras Contra a Seca (DNOCS/Ceará) to provide logistical help in the Castanhão reservoir. Thanks are due to the community of Curupati-peixe to make the information about the cage fish farming available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molisani, M.M., do Monte, T.M., Vasconcellos, G.H. et al. Relative effects of nutrient emission from intensive cage aquaculture on the semiarid reservoir water quality. Environ Monit Assess 187, 707 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4925-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4925-4