Abstract
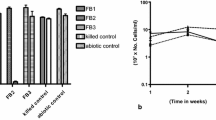
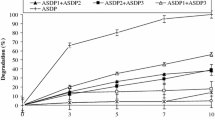
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) utilizing bacteria were isolated from soils of seven sites of Mathura refinery, India. Twenty-six bacterial strains with different morphotypes were isolated. These strains were acclimatized to utilize a mixture of four polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, i.e., anthracene, fluorene, phenanthrene, and pyrene, each at 50 mg/L concentration as sole carbon source. Out of total isolates, 15 potent isolates were subjected to 16S rDNA sequencing and identified as a member of diverse genera, i.e., Bacillus, Acinetobacter, Stenotrophomonas, Alcaligenes, Lysinibacillus, Brevibacterium, Serratia, and Streptomyces. Consortium of four promising isolates (Acinetobacter, Brevibacterium, Serratia, and Streptomyces) were also investigated for bioremediation of PAH mixture. This consortium was proved to be efficient PAH degrader resulting in 40–70 % degradation of PAH within 7 days. Results of this study indicated that these genera may play an active role in bioremediation of PAHs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annweiler, E., Materna, A., Safinowski, M., Kappler, A., Richnow, H. H., Michaelis, W., & Meckenstock, R. U. (2000). Anaerobic degradation of 2-methylnaphthalene by a sulfate-reducing enrichment culture. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 66, 5329–5333.
Arulazahan, P., & Vasudevan, N. (2011). Role of nutrients in the utilization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by halotolerant bacterial strain. Journal of Environmental Science, 23, 282–287.
Baboshin, M., Akimov, V., Baskunov, B., Born, T. L., Khan, S. U., & Golovleva, L. (2008). Conversion of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingomonas sp. VKM B-2434. Biodegradation, 19, 567–576.
Boonchan, S., Britz, M. L., & Stanley, G. A. (1998). Surfactant- enhanced biodegradation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 59, 482–494.
Boopathy, R. (2000). Factors limiting bioremediation technologies. Bioresource Technology, 74, 63–67.
Bull, A. T., Goodfellow, M., & Slater, J. H. (1992). Biodiversity as a source of innovation in biotechnology. Annual Reviews of Microbiology, 46, 219–252.
Bushnell, L. D., & Haas, H. F. (1941). The utilization of certain hydrocarbons by microorganisms. Journal of Bacteriology, 41, 653–673.
Charles, T. C., & Nester, E. W. (1993). A chromosomally encoded two-component sensory transduction system is required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Journal of Bacteriology, 175, 6614–6625.
Chaudhary, P., Sharma, R., Singh, S. B., Chaudhary, P., Sharma, R., Singh, S. B., & Lata. (2011). Bioremediation of PAH by Streptomyces sp. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 86, 268–271.
Chaudhary, P., Singh, S. B., Chaudhry, S., & Lata. (2012). Impact of PAH on biological health parameters of soils of an Indian refinery and adjoining agricultural area-A case study. Environmental Assessment and Monitoring, 184(2), 1145–1156.
Chhatre, S., Purohit, H., Shanker, R., & Khanna, P. (1996). Bacterial consortia for crude oil spill remediation. Water Science and Technology, 34, 187–193.
Cybulski, Z., Dziurla, E., Kaczorek, E., & Olszanowski, A. (2003). The influence of emulsifiers on hydrocarbon biodegradation by Pseudomondacea and Bacillaea strains. Spill Science Technology Bulletin, 8, 503–507.
De Carvalho, C. C. C. R., Parreno-Marchante, B., Neumann, G., da Fonseca, M. M. R., & Heipieper, H. J. (2005). Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 to growth on n-alkanes, alcohols and terpenes. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 67, 383–388. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1750-z.
Di Gennaro, P., Rescalli, E., Galli, E., Sello, G., & Bestetti, G. (2001). Characterization of Rhodococcus opacus R7, a strain able to degrade naphthalene and o-xylene isolated from a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Research Microbiology, 152(7), 641–651. doi:10.1016/S0923-2508(01)01243-8.
Edwards, U., Rogall, T., Blocker, H., Emde, M., & Böttger, E. C. (1989). Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acid Research, 19(19), 7843–7853.
Farhadian, M., Vachelard, C., Duchez, D., & Larroche, C. (2008). In situ bioremediation of monoaromatic pollutants in groundwater: a review. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5296–5308. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.025.
Gurjeet, P., Kothiyal, N. C., & Kumar, V. (2014). Bioremediation of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) from soil using Sphingobium indicum, Sphingobium japonicum and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacterial strains under aerobic conditions. Journal of Environmental Research and Development, 8, 396–405.
Hamamura, N., Ward, D. M., & Inskeep, W. P. (2013). Effects of petroleum mixture types on soil bacterial population dynamics associated with the biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil environments. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 85, 168–178.
Haritash, A. K., & Kaushik, C. P. (2009). Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): a review. Journal of Hazardous Material, 169, 1–15.
Herrenkohl, M. J., Lunz, J. D., Sheets, R. G., & Wakeman, J. S. (2001). Environmental impacts of PAH and oil release as a NAPL or as contaminated pore water from the construction of a 90-cm in situ isolation cap. Environmental Science Technology, 35, 4927–4932.
Juhasz, A. L., Stanley, G. A., & Britz, M. L. (2000). Microbial degradation and detoxification of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strain VUN 10,003. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 30, 396–401.
Kanaly, R. A., & Harayama, S. (2000). Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Journal of Bacteriology, 182, 2059–2067.
Kang, H., Hwang, S. Y., Kim, Y. M., Kim, E., Kim, Y. S., & Kim, S. K. (2003). Degradation of phenanthrene and naphthalene by a Burkholderia species strain. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 49, 39–144.
Kim, Y. H., Engesser, K. H., & Cerniglia, C. E. (2003). Two polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon o-quinone reductases from a pyrene-degrading Mycobacterium. Archives of Biochemistry Biophysics, 416, 209–217.
Krauss, M., Wilcse, W., & Zech, W. (2000). Availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) to earthworms in urban soils. Environmental Science Technology, 34, 4335–4340.
Lindstrom, J. E., Barry, R. P., & Braddock, J. F. (1999). Long-term effect on microbial communities after a sub artic oil spill. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 31, 1677–1689.
Mukherjee, S., Das, P., & Sen, R. (2009). Rapid quantification of a microbial surfactant by a simple turbidometric method. Journal of Microbiology Methods, 76, 38–42.
Nam, J. J., Song, B. H., Eom, K. C., Lee, S. H., & Smith, A. (2003). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in agricultural soils in South Korea. Chemosphere, 50, 1281–1289.
Pandey, G., & Jain, R. K. (2002). Bacterial chemotaxis toward environmental pollutants: role in bioremediation. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 68, 5789–5795.
Pumphrey, G. M., & Madsen, E. L. (2007). Naphthalene metabolism and growth inhibition by naphthalene in Polaromonas naphthalenivorans strain CJ2. Microbiology, 153, 3730–3738. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2007/010728-0.
Rengarajan, T., Rajendran, P., Nandakumar, N., Lokeshkumar, B., Rajendran, P., & Nishigaki, I. (2015). Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with special focus on cancer. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 5, 182–189.
Schluep, M., Imboden, D. M., Galli, R., & Zeyer, J. (2001). Mechanisms affecting the dissolution of non aqueous phase liquids into the aqueous phase in slow stirring batch system. Environmental Toxicology Chemistry, 20, 459–466.
Sharma, M., & Rawat, M. K. (2013). Study on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and poly chlorinated biphenyls yearly based concentration in waste oil-sludge at Mathura-Agra Region. Journal of Current Chemical & Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(1), 16–22.
Shiaris, M. P. (1989). Seasonal biotransformation of naphthalene, phenanthrene and benzo (a) pyrene in superficial estuarine sediments. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 55, 1391–1399.
Watanabe, K. (2001). Microorganisms relevant to bioremediation. Current Opinions in Biotechnology, 12, 237–241.
Wick, L. Y., Colangelo, T., & Harms, H. (2001). Kinetics of mass transfer-limited bacterial growth on solid PAHs. Environmental Science Technology, 35, 354–361.
Wong, J. W. C., Fang, M., Zhao, Z., & Xing, B. (2004). Effect of surfactants on solubilization and degradation of phenanthrene under thermophilic conditions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 2015–2025.
Zhang, W., Wang, H., Zhang, R., Yu, X. Z., Qian, P. Y., & Wong, M. H. (2010). Bacterial communities in PAH contaminated soils at an electronic-waste processing center in China. Ecotoxicology, 19, 96–104.
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance provided by the Indian council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi through AMAAS network project is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are also grateful to the division of Microbiology and Agricultural chemicals for providing the necessary facilities to undertake this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, P., Sahay, H., Sharma, R. et al. Identification and analysis of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)—biodegrading bacterial strains from refinery soil of India. Environ Monit Assess 187, 391 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4617-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4617-0