Abstract
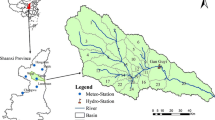
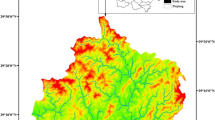
Water flow regulation is an important ecosystem service that significantly impacts on ecological quality and social benefits. With the aim of improving our understanding of ecosystems and proposing strategies for optimizing ecosystem services, a geographic information system (GIS)-based approach was designed to estimate and map regulated water flow in the Chongqing region of China. In this study, we applied the integrated valuation of environmental services and tradeoffs (InVEST) model and mathematical simulations to estimate the provision of the regulated water flow across space and time in 2000, 2005, and 2010. The results indicated that this ecosystem service had improved by 2.07 % from 2000 to 2010 as a result of human activities (such as vegetation restoration) and climatic interaction. Places with positive changes mainly occurred in high mountain areas, whereas places with negative changes were mainly distributed in resettlement areas along the Yangtze River. The type of ecosystem in areas with high mountains and steep slopes was a relatively minor contributor to the total service, but this ecosystem had the higher water flow regulation capacity. Moreover, with the increase in altitude and slope, the percentage contribution of forest increased significantly from 2000 to 2010; by contrast, the percentage contribution of cropland decreased rapidly. As for the impacts, the spatial variation of water flow regulation in the Chongqing region had a significant relation with climate and human activities at the regional scale. These results provided specific information that could be used to strengthen necessary public awareness about the protection and restoration of ecosystems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R. G., Pereira, L. S., Raes, D., & Smith, M. (1998). Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO irrigation and drainage paper 56. Rome: FAO.
Angert, A., Biraud, S., Bonfils, C., Henning, C. C., Buermann, W., Pinzon, J., Tucker, C. J., & Fung, I. (2005). Drier summers cancel out the CO2 uptake enhancement induced by warmer springs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 10823–10827.
Budyko, M. I. (1974). Climate and life. San Diego: Academic.
Bai, Y., Zhuang, C. W., Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., & Jiang, B. (2011). Spatial characteristics between biodiversity and ecosystem services in a human-dominated watershed. Ecological Complexity, 8(2), 177–183.
Beck, H. E., McVicar, T. R., van Dijk, A. I., Schellekens, J., de Jeu, R. A., & Bruijnzeel, L. A. (2011). Global evaluation of four AVHRR–NDVI data sets: intercomparison and assessment against Landsat imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 111, 2547–2563.
Canadell, J., Jackson, R. B., Ehleringer, J. B., Mooney, H. A., Sala, O. E., & Schulze, E. D. (1996). Maximum rooting depth of vegetation types at the global scale. Oecologia, 108(4), 583–595.
Costanza, R., D′Arge, R., de Groot, R., Farber, S., Grasso, M., Hannon, B., Limburg, K., Naeem, S., O′Neill, R. V., Paruelo, J., Raskin, R. G., Sutton, P., & van den Belt, M. (1997). The value of the world′s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature, 387, 253–260.
Chen, Z. H., & Wang, J. F. (2010). Land use and land cover change detection using satellite remote sensing techniques in the mountainous Three Gorges area, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(6), 1519–1542.
Chen, L., Xie, G. D., Zhang, C. S., Pei, S., & Fan, N. (2011). Modelling ecosystem water supply services across the Lancang river Basin. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 2(4), 322–327.
Daily, G. C. (Ed.). (1997). Nature’s services: societal dependence on natural ecosystems. Washington DC: Island Press.
De Groot, R. S., Wilson, M. A., & Boumans, R. M. J. (2002). A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecological Economics, 41, 393–408.
Droogers, P., & Allen, R. G. (2002). Estimating reference evapotranspiration under inaccurate data conditions. Irrigation and Drainage Systems, 16, 33–45.
Eklundh, L., & Olsson, L. (2003). Vegetation index trends for African Sahel 1982–1999. Geophysical Research Letters, 30, 1430–1433.
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., Chapin, F. S., Coe, M. T., Daily, G. C., Gibbs, H. K., Helkowski, J. H., Holloway, T., Howard, E. A., Kucharik, C. J., Monfreda, C., Patz, J. A., Prentice, I. C., Ramankutty, N., & Snyder, P. K. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309, 570–574.
Guo, Z. W., Xiao, X. M., & Li, D. M. (2000). An assessment of ecosystem services: water flow regulation and hydroelectric power production. Ecological Applications, 10(3), 925–936.
Guo, Z. W., Xiao, X. M., Gan, Y. L., & Zheng, Y. J. (2001). Ecosystem functions, services and their values—a case study in Xingshan county of China. Ecological Economics, 38, 141–154.
Guo, M., Wang, X. F., Li, J., Yi, K. P., Zhong, G. S., & Tani, H. (2012). Assessment of global carbon dioxide concentration using MODIS and GOSAT data. Sensors, 12, 16368–16389.
Hewlett, J. D. (1982). Principles of forest hydrology. Athens: University of Georgia Press.
Hargreaves, G. L., Hargreaves, G. H., & Riley, J. P. (1985). Agricultural benefits for Senegal river basin. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering ASCE, 111(2), 113–124.
Hargreaves, G. H. (1994). Defining and using reference evapotranspiration. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering ASCE, 120(6), 1132–1139.
Hillel, D. (1991). Out of the earth: civilization and the life of the soil. New York: Free Press.
Hunter, L. M., Manuel, D. J., Gonzalez, G., Matt, S., Kimberly, S. K., Richard, T., Thomas, C., Edwards, J., Robert, J. L., & Mary, C. (2003). Population and land use change in the California Mojave: natural habitat implications of alternative futures. Population Research and Policy Review, 22(4), 373–397.
Miao, C. Y., Ni, J. R., & Borthwick, A. G. L. (2010). Recent changes of water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow river basin, China. Progress in Physical Geography, 34(4), 541–561.
Miao, C. Y., Ni, J. R., Borthwick, A. G. L., & Yang, L. (2011). A preliminary estimate of human and natural contributions to the changes in water discharge and sediment load in the Yellow river. Global and Planetary Change, 76(3–4), 196–205.
Miao, C. Y., Duan, Q. Y., Sun, Q. H., Huang, Y., Kong, D. X., Yang, T. T., Ye, A. Z., Di, Z. H., & Gong, W. (2014). Assessment of CMIP5 climate models and projected temperature changes over Northern Eurasia. Environmental Research Letters, 9, 055007.
National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) (2005). The greenshelt construction project around the Three Gorges Reservoir (in Chinese). http://www.sdpc.gov.cn/zjgx/t20050715_36863.htm.
Piao, S. L., Fang, J. Y., & Guo, Q. H. (2001). Application of CASA model to the estimation of Chinese terrestrial net primary productivity. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 25, 603–608.
Qin, Y., Yi, S., Ren, S., Li, N., & Chen, J. (2014). Responses of typical grasslands in a semi-arid basin on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau to climate change and disturbances. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 1421–1431.
Semwal, R. L., Nautiyal, S., Sen, K. K., Rana, U., Maikhuri, R. K., Rao, K. S., & Saxena, K. G. (2004). Patterns and ecological implications of agricultural land-use changes: a case study from central Himalaya, India. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment, 102, 81–92.
Stockli, R., & Vidale, P. L. (2004). European plant phenology and climate as seen in a 20-year AVHRR land-surface parameter dataset. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25, 3303–3330.
Seto, K. C., Fragkias, M., Güneralp, B., & Reilly, M. K. (2011). A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE, 6(8), e23777.
Vitousek, P. M., Ehrlich, P. R., Ehrlich, A. H., & Matson, P. A. (1986). Human appropriation of the products of photosynthesis. Bioscience, 36, 368–373.
Wu, K., & Zhang, H. (2012). Land use dynamics, built-up land expansion patterns, and driving forces analysis of the fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, eastern China (1978-2008). Applied Geography, 34, 137–145.
Wang, S. X., Wu, B., & Yang, P. N. (2014). Assessing the changes in land use and ecosystem services in an oasis agricultural region of Yanqi Basin, Northwest China. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 186, 8343–8357.
Zhang, L., Dawes, W. R., & Walker, G. R. (2001). Response of mean annual evapotranspiration to vegetation changes at catchment scale. Water Resources Research, 37, 701–708.
Zhou, L. M., Tucker, C. J., Kaufmann, R. K., Slayback, D., Shabanov, N. V., & Myneni, R. B. (2001). Variations in northern vegetation activity inferred from satellite data of vegetation index during 1981 to 1999. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 106, 20069–20083.
Zhou, W. Z., Liu, G. H., Pan, J. J., & Feng, X. F. (2005). Distribution of available soil water capacity in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 15(1), 3–12.
Zhu, W. Q., Pan, Y. Z., He, H., Yu, D. Y., & Hu, H. B. (2006). Simulation of maximum light use efficiency for some typical vegetation types in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 457–463.
Zhang, J. X., Liu, Z. J., & Sun, X. X. (2009). Changing landscape in the three gorges reservoir area of Yangtze river from 1977 to 2005: Land use/land cover, vegetation cover changes estimated using multi-source satellite data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 11(6), 403–412.
Zhang, B., Li, W. H., Xie, G. D., & Xiao, Y. (2010). Water conservation of forest ecosystem in Beijing and its value. Ecological Economics, 69(7), 1416–1426.
Zhang, B., Xie, G. D., Yan, Y. P., & Yang, Y. G. (2011). Regional differences of water conservation in Beijing’s forest ecosystem. Journal of Forestry Research, 22(2), 295–300.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by National Key Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2009CB421105, 2006CB403402) and Special Foundation from State Key Laboratory of Urban and Regional Ecology. The authors gratefully thank editors and anonymous reviewers for their very helpful comments and constructive feedback.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Xiao, Q., Ouyang, Z. et al. Assessing changes in water flow regulation in Chongqing region, China. Environ Monit Assess 187, 362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4370-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4370-4