Abstract
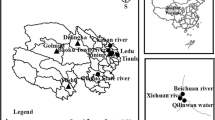
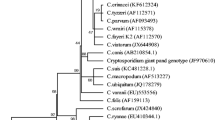
Human wastewater and livestock can contribute to contamination of surface water with Cryptosporidium and Giardia. In countries where a substantial proportion of drinking water is produced from surface water, e.g., Belgium, this poses a constant threat on drinking water safety. Our objective was to monitor the presence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in different water catchment sites in Belgium and to discriminate between (oo)cysts from human or animal origin using genotyping. Monthly samples were collected from raw water and purified drinking water at four catchment sites. Cryptosporidium and Giardia were detected using USEPA method 1623 and positive samples were genotyped. No contamination was found in purified water at any site. In three catchments, only low numbers of (oo)cysts were recovered from raw water samples (<1/liter), but raw water samples from one catchment site were frequently contaminated with Giardia (92 %) and Cryptosporidium (96 %), especially in winter and spring. Genotyping of Giardia in 38 water samples identified the presence of Giardia duodenalis assemblage AI, AII, BIV, BIV-like, and E. Cryptosporidium andersoni, Cryptosporidium suis, Cryptosporidium horse genotype, Cryptosporidium parvum, and Cryptosporidium hominis were detected. The genotyping results suggest that agriculture may be a more important source of surface water contamination than human waste in this catchment. In catchment sites with contaminated surface water, such as the Blankaart, continuous monitoring of treated water for the presence of Cryptosporidium and Giardia would be justified and (point) sources of surface water contamination should be identified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agullo-Barcelo, M., Oliva, F., & Lucena, F. (2013). Alternative indicators for monitoring Cryptosporidium oocysts in reclaimed water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 20(7), 4448–4454.
Ajonina, C., Buzie, C., Ajonina, I. U., Basner, A., Reinhardt, H., Gulyas, H., et al. (2012). Occurrence of Cryptosporidium in a wastewater treatment plant in north Germany. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health A, 75(22–23), 1351–1358.
Ajonina, C., Buzie, C., & Otterpohl, R. (2013). The detection of Giardia cysts in a large-scale wastewater treatment plant in Hamburg, Germany. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health A, 76(8), 509–514.
Barwick, R. S., Levy, D. A., Craun, G. F., Beach, M. J., & Calderon, R. L. (2000). Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United States, 1997–1998. MMWR CDC Surveillance Summaries, 49(4), 1–21.
Bodley-Tickell, A. T., Kitchen, S. E., & Sturdee, A. P. (2002). Occurrence of Cryptosporidium in agricultural surface waters during an annual farming cycle in lowland UK. Water Research, 36(7), 1880–1886.
Briancesco, R., & Bonadonna, L. (2005). An Italian study on Cryptosporidium and Giardia in wastewater, fresh water and treated water. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 104(1–3), 445–457.
Burnet, J. B. (2012). PhD Thesis Université de Liège, Belgium. Dynamique spatio-temporelle de Cryptosporidium et de Giardia dans un réservoir d’eau potable et son bassin versant: cas des lacs de barrage de la Haute-Sure (Grand-Duché de Luxembourg) (partially in French).
Carmena, D., Aguinagalde, X., Zigorraga, C., Fernandez-Crespo, J. C., & Ocio, J. A. (2007). Presence of Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts in drinking water supplies in northern Spain. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 102(3), 619–629.
Castro-Hermida, J. A., Garcia-Presedo, I., Almeida, A., Gonzalez-Warleta, M., Da Costa, J. M., & Mezo, M. (2009). Detection of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia duodenalis in surface water: a health risk for humans and animals. Water Research, 43(17), 4133–4142.
Castro-Hermida, J. A., Garcia-Presedo, I., Gonzalez-Warleta, M., & Mezo, M. (2010). Cryptosporidium and Giardia detection in water bodies of Galicia, Spain. Water Research, 44(20), 5887–5896.
Chalmers, R. M., Robinson, G., Elwin, K., Hadfield, S. J., Thomas, E., Watkins, J., et al. (2010). Detection of Cryptosporidium species and sources of contamination with Cryptosporidium hominis during a waterborne outbreak in north west Wales. Journal of Water Health, 8(2), 311–325.
DiGiorgio, C. L., Gonzalez, D. A., & Huitt, C. (2002). Cryptosporidium and Giardia recoveries in natural waters by using environmental protection agency method 1623. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 68, 5952–5955.
Eurostat. (2013). http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/statistics_explained/index.php/Water_statistics.
Fayer, R. (2004). Cryptosporidium: a water-borne zoonotic parasite. Veterinary Parasitology, 126(1–2), 37–56.
Geurden, T., Claerebout, E., Vercruysse, J., & Berkvens, D. (2004). Estimation of diagnostic test characteristics and prevalence of Giardia duodenalis in dairy calves in Belgium using a Bayesian approach. International Journal for Parasitology, 34, 1121–1127.
Geurden, T., Berkvens, D., Geldhof, P., Vercruysse, J., & Claerebout, E. (2006). A Bayesian approach for the evaluation of six diagnostic assays and the estimation of Cryptosporidium prevalence in dairy calves. Veterinary Research, 37(5), 671–682.
Geurden, T., Berkvens, D., Martens, C., Casaert, S., Vercruysse, J., & Claerebout, E. (2007). Molecular epidemiology with subtype analysis of Cryptosporidium in calves in Belgium. Parasitology, 134(Pt.14), 1981–1987.
Geurden, T., Geldhof, P., Levecke, B., Martens, C., Berkvens, D., Casaert, S., et al. (2008). Mixed Giardia duodenalis assemblage A and E infections in calves. International Journal for Parasitology, 38(2), 259–264.
Geurden, T., Levecke, B., Caccio, S. M., Visser, A., De Groote, G., Casaert, S., et al. (2009). Multilocus genotyping of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in non-outbreak related cases of diarrhoea in human patients in Belgium. Parasitology, 136(10), 1161–1168.
Hanninen, M. L., Horman, A., Rimhanen-Finne, R., Vahtera, H., Malmberg, S., Herve, S., et al. (2005). Monitoring of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in the Vantaa River basin, southern Finland. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 208(3), 163–171.
Hansen, J. S., & Ongerth, J. E. (1991). Effects of time and watershed characteristics on the concentration of Cryptosporidium oocysts in river water. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 57(10), 2790–2795.
Helmi, K., Skraber, S., Burnet, J. B., Leblanc, L., Hoffmann, L., & Cauchie, H. M. (2011). Two-year monitoring of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia occurrence in a recreational and drinking water reservoir using standard microscopic and molecular biology techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 179, 163–175.
Herwaldt, B. L., Craun, G. F., Stokes, S. L., & Juranek, D. D. (1992). Outbreaks of waterborne disease in the United States, 1989–1990. Journal of American Water Works Association, 84, 129–135.
Horman, A., Rimhanen-Finne, R., Maunula, L., von Bonsdorff, C. H., Torvela, N., Heikinheimo, A., et al. (2004). Campylobacter spp., Giardia spp., Cryptosporidium spp., noroviruses, and indicator organisms in surface water in southwestern Finland, 2000–2001. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 70(1), 87–95.
Isaac-Renton, J., Moorehead, W., & Ross, A. (1996). Longitudinal studies of Giardia contamination in two community drinking water supplies: cysts levels, parasite viability, and health impact. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 62, 47–54.
Johnson, D. W., Pieniazek, N. J., Griffin, D. W., Misener, L., & Rose, J. B. (1995). Development of a PCR protocol for sensitive detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts in water samples. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 61(11), 3849–3855.
Julio, C., Sa, C., Ferreira, I., Martins, S., Oleastro, M., Angelo, H., et al. (2012). Waterborne transmission of Giardia and Cryptosporidium at river beaches in southern Europe (Portugal). Journal of Water Health, 10, 484–496.
Keeley, A., & Faulkner, B. R. (2008). Influence of land use and watershed characteristics on protozoa contamination in a potential drinking water resources reservoir. Water Research, 42, 2803–2813.
Ketelaars, H. A. M., Medema, G. J., van Breemen, L. W. C. A., van der Kooij, D., Nobel, P. J., & Nuhn, P. (1995). Occurrence of Cryptosporidium oocysts and Giardia cysts in the River Meuse and removal in the Biesbosch reservoirs. Journal of Water Supply Research and Technology, 44(Suppl. 1), 108–111.
Kramer, M. H., Herwaldt, B. L., Craun, G. F., Calderon, R. L., & Juranek, D. D. (1996). Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United States, 1993–1994. MMWR CDC Surveillance Summaries, 45(1), 1–33.
Lalle, M., Pozio, E., Capelli, G., Bruschi, F., Crotti, D., & Caccio, S. M. (2005). Genetic heterogeneity at the giardin locus among human and animal isolates of Giardia duodenalis and identification of potentially zoonotic sub genotypes. International Journal for Parasitology, 35, 207–213.
Lee, S. H., Levy, D. A., Craun, G. F., Beach, M. J., & Calderon, R. L. (2002). Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United States, 1999–2000. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 51(8), 1–47.
Levecke, B., Geldhof, P., Claerebout, E., Dorny, P., Vercammen, F., Caccio, S. M., et al. (2009). Molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in captive nonhuman primates reveals mixed assemblage A and B infections and novel polymorphisms. International Journal for Parasitology, 139, 1595–1601.
Levy, D. A., Bens, M. S., Craun, G. F., Calderon, R. L., & Herwaldt, B. L. (1998). Surveillance for waterborne-disease outbreaks—United States, 1995–1996. MMWR CDC Surveillance Summaries, 47(5), 1–34.
MacKenzie, W. R., Hoxie, N. J., Proctor, M. E., Gradus, M. S., Blair, K. A., Peterson, D. E., et al. (1994). A massive outbreak in Milwaukee of Cryptosporidium infection transmitted through the public water supply. New England Journal of Medicine, 331, 161–167.
McCuin, R. M., & Clancy, J. L. (2003). Modifications to United States environmental protection agency methods 1622 and 1623 for detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts and Giardia cysts in water. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 69(1), 267–274.
Mons, C., Dumetre, A., Gosselin, S., Galliot, C., & Moulin, L. (2009). Monitoring of Cryptosporidium and Giardia river contamination in Paris area. Water Research, 43(1), 211–217.
Morgan, U. M., Monis, P. T., Xiao, L., Limor, J., Sulaiman, I., Raidal, S., et al. (2001). Molecular and phylogenetic characterisation of Cryptosporidium from birds. International Journal for Parasitology, 31(3), 289–296.
Obiri-Danso, K., & Jones, K. (1999). Distribution and seasonality of microbial indicators and thermophilic campylobacters in two freshwater bathing sites on the River Lune in northwest England. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 87(6), 822–832.
Ong, C., Moorehead, W., Ross, A., & Isaac-Renton, J. (1996). Studies of Giardia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. in two adjacent watersheds. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 62(8), 2798–2805.
Ongerth, J. E., Hunter, G. D., & DeWalle, F. B. (1995). Watershed use and Giardia cyst presence. Water Research, 29, 1295–1299.
Payment, P., & Franco, E. (1993). Clostridium perfringens and somatic coliphages as indicators of the efficiency of drinking water treatment for viruses and protozoan cysts. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 59, 2418–2424.
Peng, M.M., Matos, O., Gatei, W., Das, P., Stantic-Pavlinic, M., Bern, C., et al. (2001). A comparison of cryptosporidium subgenotypes from several geographic regions. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, (Suppl.), 28S–31S.
Pozio, E., Rezza, G., Boschini, A., Pezzotti, P., Tamburrini, A., Rossi, P., et al. (1997). Clinical cryptosporidiosis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-induced immunosuppression: findings from a longitudinal study of HIV-positive and HIV-negative former injection drug users. Journal of Infectious Disease, 176(4), 969–975.
Radio Télévision Belge Francophone (RTBF). (2008). http://www.rtbf.be/info/societe/detail_eau-impropre-a-la-consommation-a-saint-hubert?id=5225223.
Risebro, H. L., Doria, M. F., Andersson, Y., Medema, G., Osborn, K., Schlosser, O., et al. (2007). Fault tree analysis of the causes of waterborne outbreaks. Journal of Water Health, 5(Suppl 1), 1–18.
Robertson, L. J., & Gjerde, B. (2001). Occurrence of Cryptosporidium oocysts and Giardia cysts in raw waters in Norway. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 29(3), 200–207.
Scientific Institute for Public Health (WIV-ISP). (2010). https://www.wiv-isp.be/epidemio/epinl/plabnl/plabannl/index10.htm.
Shaw, N. J., Villegas, L. F., Eldred, B. J., Gaynor, D. H., Warden, P. S., & Pepich, B. V. (2008). Modification to EPA method 1623 to address a unique seasonal matrix effect encountered in some U.S. source waters. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 75, 445–448.
Sischo, W. M., Atwill, E. R., Lanyon, L. E., & George, J. (2000). Cryptosporidia on dairy farms and the role these farms may have in contaminating surface water supplies in the northeastern United States. Preventive Veterinary Medicine, 43, 253–267.
Slifko, T. R., Smith, H. V., & Rose, J. B. (2000). Emerging parasite zoonoses associated with water and food. International Journal for Parasitology, 30(12–13), 1379–1393.
Smith, H. V., Caccio, S. M., Tait, A., McLauchlin, J., & Thompson, R. C. (2006a). Tools for investigating the environmental transmission of Cryptosporidium and Giardia infections in humans. Trends in Parasitology, 22(4), 160–167.
Smith, A., Reacher, M., Smerdon, W., Adak, G. K., Nichols, G., & Chalmers, R. M. (2006b). Outbreaks of waterborne infectious intestinal disease in England and Wales, 1992–2003. Epidemiology and Infection, 134(6), 1141–1149.
Sprong, H., Caccio, S. M., & van der Giessen, J. W. (2009). Identification of zoonotic genotypes of Giardia duodenalis. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 3(12), e558.
Stirling, R., Aramini, J., Ellis, A., Lim, G., Meyers, R., Fleury, M., et al. (2001). Waterborne cryptosporidiosis outbreak, North Battleford, Saskatchewan, Spring 2001. Canada Communicable Disease Report, 27(22), 185–192.
Sulaiman, I. M., Fayer, R., Bern, C., Gilman, R. H., Trout, J. M., Schantz, P. M., et al. (2003). Triosephosphate isomerase gene characterization and potential zoonotic transmission of Giardia duodenalis. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 9(11), 1444–1452.
Tallon, P., Magajna, B., Lofranco, C., & Leung, K. T. (2006). Microbial indicators of faecal contamination in water: a current perspective. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 166, 139–166.
Touron, A., Berthe, T., Gargala, G., Fournier, M., Ratajczak, M., Servais, P., et al. (2007). Assessment of faecal contamination and the relationship between pathogens and faecal bacterial indicators in an estuarine environment (Seine, France). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 1441–1450.
U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2005). http://www.epa.gov/microbes/documents/1623de05.pdf.
Van Dyke, M. I., Ong, C. S., Prystajecky, N. A., Isaac-Renton, J. L., & Huck, P. M. (2012). Identifying host sources, human health risk and indicators of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in a Canadian watershed influenced by urban and rural activities. Journal of Water Health, 10(2), 311–323.
WAC_V_A_001: https://esites.vito.be/sites/reflabos/2013/Online%20documenten/WAC_V_A_001.pdf.
WAC_V_A_007: https://esites.vito.be/sites/reflabos/2014/Online%20documenten/WAC_V_A_007.pdf.
Wallis, P. M., Erlandsen, S. L., Isaac-Renton, J. L., Olson, M. E., Robertson, W. J., & van Keulen, H. (1996). Prevalence of Giardia cysts and Cryptosporidium oocysts and characterization of Giardia spp. isolated from drinking water in Canada. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 62(8), 2789–2797.
Webber, C. (2002). Outbreak of giardiasis in bay of plenty and manawatu. In Annual Summary of Outbreaks in New Zealand 2001, Report for the Ministry of Health, pp. 38–39.
Wilkes, G., Edge, T., Gannon, V., Jokinen, C., Lyautey, E., Medeiros, D., et al. (2009). Seasonal relationships among indicator bacteria, pathogenic bacteria, Cryptosporidium oocysts, Giardia cysts, and hydrological indices for surface waters within an agricultural landscape. Water Research, 43, 2209–2223.
World Health Organisation (WHO). (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edition.
Xiao, L., Singh, A., Limor, J., Graczyk, T. K., Gradus, S., & Lal, A. (2001). Molecular characterization of cryptosporidium oocysts in samples of raw surface water and wastewater. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 67(3), 1097–1101.
Xiao, G., Qiu, Z., Qi, J., Chen, J. A., Liu, F., Liu, W., et al. (2013). Occurrence and potential health risk of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water Research, 47(7), 2431–2445.
Zuckerman, U., & Tzipori, S. (2006). Portable continuous flow centrifugation and method 1623 for monitoring of waterborne protozoa from large volumes of various water matrices. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 100, 1220–1227.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a doctoral scholarship for candidates from developing countries from Ghent University (Grant No. 01W05309). The authors would like to thank the Royal Meteorological Institute for providing daily rainfall data.
Conflict of interest
J. Paulussen, L. De Coster, and T. Schoemaker are (former) employees of The Water Group, a Belgian water supply company which owns the sampled catchment sites. The employees of the Watergroup were involved in sampling and in writing of the manuscript. T. Geurden is currently employed by Zoetis, a veterinary pharmaceutical company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehsan, A., Geurden, T., Casaert, S. et al. Occurrence and potential health risk of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in different water catchments in Belgium. Environ Monit Assess 187, 6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4157-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4157-z