Abstract
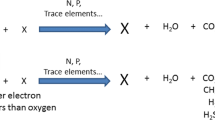
Microbial pollutant removal capabilities can be determined and exploited to accomplish bioremediation of hydrocarbon-polluted environments. Thus, increasing knowledge on environmental behavior of different petroleum products can lead to better bioremediation strategies. Biodegradation can be enhanced by adding biosurfactants to hydrocarbon-degrading microorganism consortia. This work aimed to improve petroleum products biodegradation by using a biosurfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis. The produced biosurfactant was added to biodegradation assays containing crude oil, diesel, and kerosene. Biodegradation was monitored by a respirometric technique capable of evaluating CO2 production in an aerobic simulated wastewater environment. The biosurfactant yielded optimal surface tension reduction (30.9 mN m−1) and emulsification results (46.90 % with kerosene). Biodegradation successfully occurred and different profiles were observed for each substance. Precise mathematical modeling of biosurfactant effects on petroleum degradation profile was designed, hence allowing long-term kinetics prediction. Assays containing biosurfactant yielded a higher overall CO2 output. Higher emulsification and an enhanced CO2 production dataset on assays containing biosurfactants was observed, especially in crude oil and kerosene.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amund, O. O., & Adebiyi, A. G. (1991). Effect of viscosity on the biodegradability of automotive lubricant oils. Tribology International, 24, 235–237.
Arima, K., Kakinuma, A., & Tamura, G. (1968). Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by B. subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 31, 488–494.
Ashis, K. M., & Das, K. (2010). Microbial surfactants and their potential applications. In R. Sen (Ed.), Advances in experimental medicine and biology (pp. 54–64). USA: Springer.
Ashrafizadeh, S. N., & Kamran, M. (2010). Emulsification of heavy crude oil in water for pipeline transportation. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 71, 205–211.
Atlas, R. M. (1981). Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiological Reviews, 45, 180–209.
Atlas, R. M., & Bartha, R. (1992). Hydrocarbon biodegradation and oil-spill bioremediation. Advances in Microbial Ecology, 12, 287–338.
Atlas, R. M., & Hazen, T. C. (2011). Oil biodegradation and bioremediation: a tale of the two worst spills in U.S. history. Environmental Science and Technology, 45, 6709–6715.
Balba, M. T., Al Awadhi, N., & Al Daher, R. (1998). Bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil: microbiological methods for feasibility, assessment and field evaluation. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 3, 155–164.
Banat, I. M. (1994). Biosurfactants production and possible uses in microbial enhanced oil recovery and oil pollution remediation: a review. Bioresource Technology, 51, 1–12.
Banat, I. M., Makkar, R. S., & Cameotra, S. S. (2000). Potential applications of microbial surfactants. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 53, 495–508.
Barros, F. F. C., Quadros, C. P., Júnior, M. R. M., & Pastore, G. M. (2007). Surfactina: propriedades químicas, tecnológicas e funcionais para aplicações em alimentos. Quimica Nova, 30, 409–414.
Bartha, R., & Pramer, D. (1965). Features of flask and method for measurement of the persistence and biological effects of pesticides in soil. Soil Science, 100, 68–70.
Benedik, M. J., Gibbs, P. R., Riddle, R. R., & Wilson, R. C. (1998). Microbial denitrogenation of fossil fuels. Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 390–395.
Benincasa, M., Marques, A., Pinazo, A., & Manresa, A. (2010). Rhamnolipid surfactants: alternative substrates, new strategies. In R. Sen (Ed.), Advances in experimental medicine and biology (pp. 170–184). USA: Springer.
Bordoloi, N. K., & Konwar, B. K. (2009). Bacterial biosurfactant in enhancing solubility and metabolism of petroleum hydrocarbons. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170, 495–505.
Bragg, J. R., Prince, R. C., Harner, E. J., & Atlas, R. M. (1994). Effectiveness of bioremediation for the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Nature, 368, 413–418.
Cai, Q., Zhang, B., Chen, B., Zhu, Z., Lin, W., & Cao, T. (2014). Screening of biosurfactant producers from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sources in cold marine environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 86, 402–410.
Calvo, C., Manzanera, M., Silva-Castro, G. A., Uad, I., & González-López, J. (2008). Application of bioemulsifiers in soil oil bioremediation processes—future prospects. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3634–3640.
Cerón-Camacho, R., Martínez-Palou, R., Chávez-Gómez, B., Cuéllar, F., Bernal-Huicochea, C., Clavel, J. C., & Aburto, J. (2013). Synergistic effect of alkyl-O-glucoside and -cellobioside biosurfactants as effective emulsifiers of crude oil in water. A proposal for the transport of heavy crude oil by pipeline. Fuel, 110, 310–317.
CETESB - Companhia de Tecnologia e Saneamento Ambiental. (1990). Solos - determinação da biodegradação de resíduos - método respirométrico de bartha – standard procedure L6.350. São Paulo: CETESB.
Chaîneau, C. H., Rougeux, G., Yéprémian, C., & Oudot, J. (2005). Effects of nutrient concentration on the biodegradation of crude oil and associated microbial populations in the soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37, 1490–1497.
Chen, H., & Juang, R. (2008). Recovery and separation of surfactin from pretreated fermentation broths by physical and chemical extraction. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 28, 39–46.
Chouksey, M. K., Kadam, A. N., & Zingde, M. D. (2004). Petroleum hydrocarbon residues in marine environment of Bassein-Mumbai. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 637–647.
Christofi, N., & Ivshina, I. B. (2002). Microbial surfactants and their use in field studies of soil remediation. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 93, 915–936.
Cooper, D. G., & Goldenberg, B. G. (1987). Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 53, 224–229.
Cooper, D. G., MacDonald, C. R., Duff, S. J. B., & Kosaric, N. (1981). Enhanced production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by continuous product removal and metal cation additions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 42, 408–412.
Das, K., & Mukherjee, A. K. (2007). Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum-oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1339–1345.
Das, P., Mukherjee, A. K., & Sen, R. (2008). Improved bioavailability and biodegradation of a model polyaromatic hydrocarbon by a biosurfactant producing bacterium of marine origin. Chemosphere, 72, 1229–1234.
Dehghan-Noudeh, G., Housaindokht, M., & Bazzaz, B. S. F. (2005). Isolation, characterization, and investigation of surface and hemolytic activities of a lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633. The Journal of Microbiology, 43, 272–276.
Desai, J. D., & Banat, I. M. (1997). Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 61, 47–64.
Difco. (1984). Difco manual. Detroit: Difco Laboratories.
Dutta, T. K., & Harayama, S. (2000). Fate of crude oil by the combination of photooxidation and biodegradation. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 1500–1505.
Feitkenhauer, H., Muller, R., & Markl, H. (2003). Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and long chain alkanes at 70 °C by Thermus and Bacillus spp. Biodegradation, 14, 367–372.
Fiúza, A. M. A., & Vila, M. C. C. (2004). An insight into soil bioremediation through respirometry. Environment International, 31, 179–183.
Frazer, A. C., Coschigano, P. W., & Young, L. Y. (1995). Toluene metabolism under anaerobic conditions: a review. Anaerobe, 1, 293–303.
Garrett, R. M., Rothenburger, S. J., & Prince, R. C. (2003). Biodegradation of fuel oil under laboratory and arctic marine conditions. Spill Science and Technology Bulletin, 8, 297–302.
Georgiou, G., Lin, S., & Sharma, M. M. (1992). Surface active compounds from micro-organisms. Biotechnology Advances, 10, 60–65.
Gong, G., Zheng, Z., Chen, H., Yuan, C., Wang, P., Yao, L., & Yu, Z. (2009). Enhanced production of surfactin by Bacillus subtilis e8 mutant obtained by ion beam implantation. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 47, 23–31.
Graves, A., Lang, C., & Leavitt, M. (1991). Respirometric analysis of the biodegradation of organic contaminants in soil and water. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 29, 813–826.
Haferburg, D., Hommel, R., Claus, R., & Kleber, H. (1986). Extracellular microbial lipids as biosurfactants. Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology, 33, 53–93.
Harayama, S., Kishira, H., Kasai, Y., & Shutsubo, K. (1999). Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1, 63–70.
Harvey, S., Elashvili, I., Valdes, J. J., Kamely, D., & Chakrabarty, A. M. (1990). Enhanced removal of Exxon Valdez spilled oil from Alaskan gravel by a microbial surfactant. Biotechnology, 8, 228–230.
Ibrahima, M. L., Ijahb, U. J. J., Mangaa, S. B., Bilbisc, L. S., & Umara, S. (2013). Production and partial characterization of biosurfactant produced by crude oil degrading bacteria. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 81, 28–34.
Ilori, M. O., Amobi, C. J., & Odocha, A. C. (2005). Factors affecting biosurfactant production by oil degrading Aeromonas sp., isolated from a tropical environment. Chemosphere, 61, 985–992.
Jacques, R. J. S., Okeke, B. C., Bento, F. M., Teixeira, A. S., Peralba, M. C. R., & Camargo, F. A. O. (2008). Microbial consortium bioaugmentation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2637–2643.
Javaheri, M., Jenneman, G. E., McInerney, M. J., & Knapp, R. M. (1985). Anaerobic production of a biosurfactant by Bacillus licheniformis JF-2. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 50, 698–700.
Jovančićević, B., Antić, M., Pavlović, I., Vrvić, M., Beškoski, V., Kronimus, A., & Schwarzbauer, J. (2008). Transformation of petroleum saturated hydrocarbons during soil bioremediation experiments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 190, 299–307.
Juhasz, A. L., & Naidu, R. (2000). Bioremediation of high-molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review of the microbial degradation of benzo[a]pyrene. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 45, 57–88.
Karhu, M., Kaakinen, J., Kuokkanen, T., & Rämö, J. (2009). Biodegradation of light fuel oils in water and soil as determined by the manometric respirometric method. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 197, 3–14.
Kernanshani, A., Kararnanev, D., & Margaritis, A. (2006). Kinetic modeling of the biodegradation of the aqueous p-xylene in the immobilized soil bioreactor. Engineering Journal, 27, 204–211.
Kosaric, N. (2001). Biosurfactants and their application for soil bioremediation. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 39, 295–304.
Lee, R. F. (1999). Agents which promote and stabilize water-in-oil emulsions. Spill Science and Technology Bulletin, 5, 117–26.
Li, X., Li, P., Lin, X., Zhang, C., Li, Q., & Gong, Z. (2008). Biodegradation of aged polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) by microbial consortia in soil and slurry phases. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150, 21–26.
Lopes, P. R. M., & Bidoia, E. D. (2009). Evaluation of the biodegradation of different types of lubricant oil in liquid medium. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology, 52, 1285–1290.
Maier, R. M. (2003). Biosurfactants: evolution and diversity. Advances in Applied Microbiology, 52, 101–121.
Mandri, T., & Lin, J. (2007). Isolation and characterization of engine oil degrading indigenous micro-organisms in Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. African Journal of Biotechnology, 6, 23–26.
Manning, F. C., & Thompson, R. E. (1995). Oilfield processing—crude oil. Oklahoma: PennWell.
Martínez-Palou, R., Mosqueira, M. L., Zapata-Rendón, B., Mar-Juárez, E., Bernal-Huicochea, C., Clavel-López, J., & Aburto, J. (2011). Transportation of heavy and extra-heavy crude oil by pipeline: a review. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 75, 274–282.
Medina-Bellver, J. I., Marin, P., Delgado, A., Rodriguez-Sanchez, A., Reyes, E., Ramos, J. L., & Marques, S. (2005). Evidence for in situ crude oil biodegradation after the prestige oil spill. Environmental Microbiology, 7, 773–779.
Membre, J. M., Thurette, J., & Catteau, M. (1996). Modeling the growth, survival and death of Listeria monocytogenes. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 82, 345–350.
Merck (Ed.). (1976). The Merck index: an encyclopedia of chemicals and drugs. New Jersey: Merck.
Millioli, V. S., & Sobral, E. F. (2007). Biorremediação de solo contaminado com óleo cru: Avaliação da adição de ramnolipídio quanto à toxicidade e a eficiência de biodegradação. Campinas: 4° PDPETRO.
Montagnolli, R. N., Lopes, P. R. M., & Bidoia, E. D. (2009). Applied models to biodegradation kinetics of lubricant and vegetable oils in wastewater. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 63, 297–305.
Monteiro, A. S., Miranda, T. T., Lula, I., Denadai, A. M. L., Sinisterra, R. D., Santoro, M. M., & Santos, V. L. (2011). Inhibition of Candida albicans CC biofilms formation in polystyrene plate surfaces by biosurfactant produced by Trichosporon montevideense CLOA72. Colloids and Surfaces B, 84, 467–476.
Muller-Hurtig, R., Wagner, F., Blaszczyk, R., & Kosaric, N. (1993). Biosurfactants production, properties and applications. New York: Kosaric Marcel Dekker.
Mulligan, C. N. (2005). Environmental applications of biosurfactants. Environmental Pollution, 133, 183–198.
Nadarajah, N., Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2002). De-emulsification of petroleum oil emulsion by a mixed bacterial culture. Process Biochemistry, 37, 1135–1141.
Nitschke, M., Ferraz, C., & Pastore, G. M. (2004). Selection of micro-organisms for biosurfactant production using agroindustrial wastes. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 35, 81–85.
Norman, R. S., Frontera-Suau, R., & Morris, P. J. (2002). Variability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide expression during crude oil degradation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68, 5096–5103.
Obayori, O. S., Hori, M. O., Adebusoye, S. A., Oyetibo, G. O., Omotayo, A. E., & Amund, O. O. (2009). Degradation of hydrocarbons and biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas sp. strain LP1. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25, 1615–1623.
Okoh, A. I., & Trejo-Hernandez, M. R. (2006). Remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon polluted systems: exploiting the bioremediation strategies. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5, 2520–2525.
Oluwole, O. S., Makinde, S. C. O., & Philips, D. A. (2005). The impact of spent engine oil pollution on the growth of Celosia argentea. Dissertation, Lagos State University.
Pala, D. M., Carvalho, D. D., Pinto, J. C., & Sant’Anna, G. L. (2006). A suitable model to describe bioremediation of a petroleum-contaminated soil. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 58, 254–260.
Perfumo, A., Rancich, I., & Banat, I. M. (2010). Possibilities and challenges for biosurfactants use in petroleum industry. In R. Sen (Ed.), Advances in experimental medicine and biology (pp. 135–145). USA: Springer.
Peters, K. E., Walters, C. C., & Moldowan, J. M. (2005). The biomarker guide, biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum exploration and earth history. USA: Cambridge Univ. Press.
Prince, R. C., & Walters, C. C. (2007). Biodegradation of oil hydrocarbons and its implications for source identification. Canada: Academic.
Queiroga, C. L., Nascimento, L. R., & Serra, G. E. (2003). Evaluation of paraffin biodegradation and biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis in the presence of crude oil. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 34, 321–324.
Radwan, S. S., Al-Awadhi, H., Sorkhoh, N. A., & El-Nemr, I. M. (1998). Rhizospheric hydrocarbon-utilizing micro-organisms as potential contributors to phytoremediation for the oily Kuwaiti desert. Microbiological Research, 153, 247–251.
Readman, J. W., Fowler, S. W., Villeneuve, J. P., Cattini, C., Oregioni, B., & Mee, L. D. (1992). Oil and combustion-product contamination of the Gulf marine environment following the war. Nature, 358, 662–665.
Rosenberg, E., & Ron, E. Z. (1997). Bioemulsans: microbial polymeric emulsifier. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 8, 313–316.
Sanscartier, D., Reimer, K., Koch, I., Laing, T., & Zeeb, B. (2009). An investigation of the ability of a 14C-labeled hydrocarbon mineralization test to predict bioremediation of soils contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons. Biochemical Journal, 13, 92–101.
Sasaki, T., Maki, H., Ishihara, M., & Harayama, S. (1998). Vanadium as an internal marker to evaluate microbial degradation of crude oil. Environmental Science and Technology, 22, 3618–3621.
Schmidt, S. K., Simkins, S., & Alexander, M. (1985). Models for the kinetics of biodegradation of organic compounds not supporting growth. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 50, 323–331.
Semple, K. T., Doik, K. J., Wick, L. Y., & Harms, H. (2007). Microbial interactions with organic contaminants in soils: definitions, processes and measurement. Environmental Pollution, 150, 166–176.
Singh, A., Van Hamme, J. D., & Ward, O. P. (2007). Surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology: part 2. Application aspects. Biotechnology Advances, 25, 99–121.
Solano-Serena, F., Marchal, M. R., Lebeault, R. J. M., & Vandecasteele, J. P. (1999). Biodegradation of gasoline: kinetics, mass balance and fate of individual hydrocarbons. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 86, 1008–1016.
Stallwood, B., Shears, J., Williams, P. A., & Hughes, K. A. (2005). Low temperature bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil using biostimulation and bioaugmentation with a pseudomonas sp. from maritime Antarctica. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 99, 794–802.
Tjessen, K., Pedersen, D., & Aaberg, A. (1984). On the environmental fate of a dispersed crude oil in sea-immersed plastic columns. Water Research, 9, 1129–1136.
Urum, K., & Pekdemir, T. (2004). Evaluation of biosurfactants for crude oil contaminated soil washing. Chemosphere, 57, 1139–1150.
Uysal, A., & Turkman, A. (2011). Biodegradation of 4-chlorophenol in biosurfactant supplemented activated sludge. In: Current research, technology and education topics in applied microbiology and microbial biotechnology - microbiology book series 2. Spain: Formatex Research Center.
Vater, J. (1986). Lipopeptides, an attractive class of microbial surfactants. Progress in Colloid and Polymer Science, 72, 12–18.
Volkering, F., Breure, A. M., & Rulkens, W. H. (1998). Microbiological aspects of surfactant use for biological soil remediation. Biodegradation, 8, 401–417.
West, C. C., & Harwell, J. H. (1992). Surfactant and subsurface remediation. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 2324–2330.
Widdel, F., & Rabus, R. (2001). Anaerobic biodegradation of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 12, 259–276.
Wolfe, D. A., Hameedi, M. J., Galt, J. A., Watabayashi, G., Short, J., O’Clair, C. E., Rice, S. A., Michel, J., & Payne, J. R. (1994). The fate of oil spilled from the Exxon Valdez. Environmental Science and Technology, 28, 560–568.
Wu, Y., Chiang, C., & Lu, C. (2004). Respirometric evaluation by graphical analysis for microbial systems. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 92, 137–152.
Xu, H. L., Chen, J. N., Wang, S. D., & Liu, Y. (2012). Oil spill forecast model based on uncertainty analysis: a case study of Dalian oil spill. Ocean Engineering, 54, 206–212.
Yanto, D. H. Y., & Tachibanac, S. (2013). Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons by a newly isolated Pestalotiopsis sp. NG007. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 85, 438–450.
Yemashova, N. A., Murygina, V. P., Zhukov, D. V., Zakharyantz, A. A., Gladchenko, M. A., Appanna, V., & Kalyuzhnyi, S. V. (2007). Biodeterioration of crude oil and oil derived products: a review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 6, 315–337.
Zhengkai, L., & Wrenn, B. A. (2008). Effects of ferric hydroxide on the anaerobic biodegradation kinetics and toxicity of vegetable oil in freshwater sediments. Water Research, 38, 3859–3868.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the thoughtful review and important insights provided by Sarah Mae Wachlin and Brent Perumal, providing comments on the manuscript in its entirety and working with the authors as we made revisions to the text. We alone, of course, take responsibility for the final text and any errors that appear therein. Our research group acknowledges CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico), FUNDUNESP (Fundação para o Desenvolvimento da UNESP), PRH-ANP/MCT (Programa de Formação de Recursos Humanos em Geologia do Petróleo e Ciências Ambientais Aplicadas ao Setor de Petróleo e Gás) and UNESP (Universidade Estadual Paulista “Julio de Mesquita Filho”) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montagnolli, R.N., Lopes, P.R.M. & Bidoia, E.D. Assessing Bacillus subtilis biosurfactant effects on the biodegradation of petroleum products. Environ Monit Assess 187, 4116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4116-8