Abstract
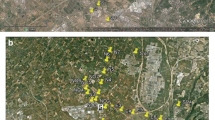
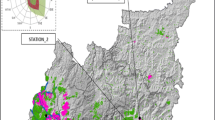
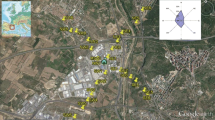
This paper presents a 10-year overview of the dioxins and furans (PCDD/Fs) content in soils in the province of Trento (Italy). The aim was to compare the results found in the Valsugana valley where there is a steel-making plant with other locations within the province. During 2002 and from 2005 to 2010, campaigns were carried out in order to obtain a background reference in terms of micropollutants, in view of the possible construction of a municipal solid waste (MSW) incinerator in Trento. In 2009, a campaign was performed for the environmental characterization of the Valsugana valley, the town of Trento and its surroundings, in order to help assess the impact of the steel-making plant. In 2012, another campaign was carried out by the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering of Trento, in order to monitor the soils in the area around the steel mill. All the campaigns showed relatively low concentrations of PCDD/Fs, both in protected areas and in the areas close to the industrial plants. No critical situations were identified, as also confirmed by an estimation of the potential daily PCDD/F intake by children subject to accidental ingestion of soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APPA - Agenzia Provinciale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente. (2010). Impatto dell’acciaieria di Borgo Valsugana sulla salute e sull’ambiente.
ATSDR. (2011). http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ToxProfiles/tp104-c1.pdf.
Caserini, S., & Monguzzi, A. M. (2002). PCDD/Fs emissions inventory in the Lombardy Region: results and uncertainties. Chemosphere, 48(8), 779–786.
Chen, M., Huang, P., & Chen, L. (2013). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from Urumqi, China: distribution, source contributions, and potential health risks. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(7), 5639–5651.
Deng, L. F., Yuan, H. R., Huang, H. Y., Noriyuki, K., & Chen, Y. (2012). The formation and control of secondary pollutants during thermal treatment of municipal solid waste. Advanced Materials Research, 518–523, 3257–3262.
Domingo, J. L., Schuhmacher, M., Granero, S., & De Kok, H. A. M. (2001). Temporal variation of PCDD/PCDF levels in environmental samples collected near an old municipal waste incinerator. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 69(2), 175–193.
Domotorova, M., Sejakova, Z. S., Koc, A., Conka, K., Chovancova, J., & Fabišikova, A. (2012). PCDDs, PCDFs, dioxin-like PCBs and indicator PCBs in soil from five selected areas in Slovakia. Chemosphere, 89, 480–485.
Douay, F., Pelfrêne, A., Planque, J., Fourrier, H., Richard, A., Roussel, H., & Girondelot, B. (2013). Assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants living near a former lead smelter. Part 1: metal concentrations in soils, agricultural crops, and homegrown vegetables. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(5), 3665–3680.
EU. (2000). Directive 2000/76/EC of the European Parliament and of the Coucil of 4 December 2000 on the incineration of waste. Available from http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:2000L0076:20001228:EN:PDF. Accessed October 2013.
Halse, A. K., Eckhardt, S., Schlabach, M., Stohl, A., & Breivik, K. (2013). Forecasting long-range atmospheric transport episodes of polychlorinated biphenyls using FLEXPART. Atmospheric Environment, 71, 335–339.
Hassanin, A., Lee, R. G. M., Steinnes, E., & Jones, K. C. (2005). PCDD/Fs in Norwegian and U.K. soils: implications for sources and environmental cycling. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 4784–4792.
Inyang, H. I., & Bae, S. (2007). The aero-geochemistry of cities and regions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 130(1–3), 1–2.
Lg., D. (2013). 152/2006 - Legislative Decree of 3 April 2006 n. 152 -“Environmental Regulations”, Available from: http://www.camera.it/parlam/leggi/deleghe/06152dl.htm Accessed October.
Loganathan, B. G., & Masunaga, S., (2009). PCBs, dioxins, and furans: Human exposure and health effects. In R. C. Gupta (Ed.), Handbook of toxicology of chemical warfare agents, (pp. 245–253). Elsevier.
Mari, M., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., & Domingo, J. L. (2009). Exposure to heavy metals and PCDD/Fs by the population living in the vicinity of a hazardous waste landfill in Catalonia, Spain: health risk assessment. Environment International, 35(7), 1034–1039.
Martinez, K., Abad, E., & Rivera, J. (2006). Surveillance programme on dioxin levels in soils in the Campo de Gibraltar (Southwest Spain). Chemosphere, 65(3), 382–389.
Pandey, J. S., Kumar, R., & Wate, S. R. (2008). Dioxin uptake by Indian plant species. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 143(1–3), 51–58.
Paustenbach, D. J., & Kerger, B. D. (2013). The University of Michigan Dioxin Exposure Study: estimating residential soil and house dust exposures to young children. Chemosphere, 91, 200–204.
Rada, E. C., & Ragazzi, M. (2008). Critical analysis of PCDD/F emissions from anaerobic digestion. Water Science and Technology, 58(9), 1721–1725.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., Panaitescu, V., & Apostol, T. (2006). The role of bio-mechanical treatments of waste in the dioxin emission inventories. Chemosphere, 62(3), 404–410.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., Zardi, D., Laiti, L., & Ferrari, A. (2011). PCDD/F enviromental impact from municipal solid waste bio-drying plant. Chemosphere, 84(3), 289–295.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., Chistè, A., Schiavon, M., Tirler, W., Tubino, M., Antonacci, G., Todeschini, I., Toffolon, M., (2012). A contribution to the evolution of the BAT concept in the steelmaking sector. Proceedings of Sustainable Technology for Environmental Protection, 1–8.
Rada, E. C., Ragazzi, M., & Schiavon, M. (2014). Assessment of the local role of a steel making plant by POPs deposition. Chemosphere, 110, 53–61.
Ragazzi, M., Rada, E. C., Tubino, M., Marconi, M., Chistè, A., & Girelli, E. (2012). Deposition near a sintering plant: preliminary comparison between two methods of measurements by deposimeters. UPB Scientific Bulletin, Series D, 74(1), 205–210.
Ragazzi, M., Tirler, W., Angelucci, G., Zardi, D., & Rada, E. C. (2013). Management of atmospheric pollutants from waste incineration processes: the case of Bozen. Waste Management and Research, 31(3), 235–240.
Rong, Z., Li, K., & Yin, H. (2010). Pilot study of the polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans level in agricultural soil in Shanghai, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 171(1–4), 493–500.
Schiavon, M., Ragazzi, M., & Rada, E. C. (2013). A proposal for a diet-based local PCDD/F deposition limit. Chemosphere, 93(8), 1639–1645.
Schuhmacher, M., Granero, S., Llobet, J. M., de Kok, H. A. M., & Domingo, J. L. (1997). Assessment of baseline levels of PCDD/F in soils in the neighbourhood of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere, 35(9), 1947–1958.
Schuhmacher, M., Agramunt, M. C., Rodriguez-Larena, M. C., Diaz-Ferrero, J., & Domingo, J. L. (2002). Baseline levels of PCDD/Fs in soil and herbage samples collected in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere, 46(9–10), 1343–1350.
Stanek, E. J., Calabrese, E. J., & Zorn, M. (2001). Soil ingestion distributions for Monte Carlo risk assessment in children. Human and Ecology Risk Assessment, 7(2), 357–368.
Su, S., & Hui, Y. (2012). The PCDD/Fs levels of air, soil and sediments in Southern China. Advanced Materials Research, 518–523, 1636–1639.
Thron, R. W. (1996). Direct and indirect exposure to air pollution. Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, 114, 281–285.
Tzimas, E. & Peteves, S.D., (2010). NOx and dioxin emissions from waste incineration plants. Energy Technology Observatory. Institute for Energy, Available from http://www.jrc.nl/, Accessed October 2013.
Wirling, J. (2005). Reducing dioxin emissions in electric steel mills. MPT International (Metallurgical Plant and Technology), 1, 36–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rada, E.C., Ragazzi, M., Marconi, M. et al. PCDD/Fs in the soils in the province of Trento: 10 years of monitoring. Environ Monit Assess 187, 4114 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4114-x