Abstract
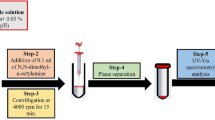
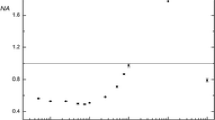
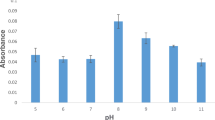
In this research, a microfunnel-assisted headspace liquid-phase microextraction technique has been used in combination with hydride generation to determine arsenic (As) by UV–Vis spectrophotometry. The method is based on the reduction of As to arsine (AsH3) in acidic media by sodium tetrahydroborate (NaBH4) followed by its subsequent reaction with silver diethyldithiocarbamate (AgDDC) to give an absorbing complex at 510 nm. The complexing reagent (AgDDC) has been dissolved in a 1:1 (by the volume ratio) mixture of chloroform/chlorobenzene microdroplet and exposed to the generated gaseous arsine via a reversed microfunnel in the headspace of the sample solution. Several operating parameters affecting the performance of the method have been examined and optimized. Acetonitrile solvent has been added to the working samples as a sensitivity enhancement agent. Under the optimized operating conditions, the detection limit has been measured to be 0.2 ng mL−1 (based on 3sb/m criterion, n b = 8), and the calibration curve was linear in the range of 0.5–12 ng mL−1. The relative standard deviation for eight replicate measurements was 1.9 %. Also, the effects of several potential interferences have been studied. The accuracy of the method was validated through the analysis of JR-1 geological standard reference material. The method has been successfully applied for the determination of arsenic in raw and spiked soft drink and water samples with the recoveries that ranged from 91 to 106 %.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbab-Zavar, M. H., & Hashemi, M. (2000). Evaluation of electrochemical hydride generation for spectrophotometric determination of As(III) by silver diethyldithiocarbamate. Talanta, 52, 1007–1014.
Arbab-Zavar, M. H., Chamsaz, M., & Heidari, T. (2010). Speciation and analysis of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by electrochemical hydride generation spectrophotometric method. Analytical Sciences, 26, 107–110.
Ayotte, J. D., Montgomery, D. L., Flanagan, S. M., & Robinson, K. W. (2003). Arsenic in groundwater in Eastern New England: occurrence, controls, and human health implications. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 2075–2083.
Chamsaz, M., Arbab-Zavar, M. H., & Nazari, S. (2003). Determination of arsenic by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry using headspace liquid phase microextraction after in situ hydride generation. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 18, 1279–1282.
Chen, W. F., Parette, R., Zou, J. Y., Cannon, F. S., & Dempsey, B. A. (2007). Arsenic removal by iron-modified activated carbon. Water Research, 41, 1851–1858.
Chen, L. W. L., Lu, X., & Le, X. C. (2010). Complementary chromatography separation combined with hydride generation–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for arsenic speciation in human urine. Analytica Chimica Acta, 675, 71–75.
Correia, C. L. T., Gonçalves, R. A., Azevedo, M. S., Vieira, M. A., & Campos, R. C. (2010). Determination of total arsenic in seawater by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 96, 157–160.
D’Ulivo, A., Dedina, J., Mester, Z., Sturgeon, R. E., Wang, Q., & Welz, B. (2011). Mechanisms of chemical generation of volatile hydrides for trace element determination (IUPAC technical report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 83, 1283–1340.
Dedina, J., & Tsalev, D. L. (1995). Hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry. New York: Wiley.
dos Santos, W. N. L., Cavalcante, D. D., Macedo, S. M., Nogueira, J. S., & da Silva, E. G. P. (2013). Slurry sampling and HG AFS for the determination of total arsenic in rice samples. Food Analytical Methods, 6, 1128–1132.
El-Hadri, F., Morales-Rubio, A., & de la Guardia, M. (2007). Determination of total arsenic in soft drinks by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 105, 1195–1200.
Fragueiro, S., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2006). Hydride generation-headspace single-drop microextraction-electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry method for determination of selenium in waters after photoassisted prereduction. Talanta, 68, 1096–1101.
Gil, R. A., Ferr’ua, N., Salonia, J. A., Olsina, R. A., & Martinez, L. D. (2007). On-line arsenic co-precipitation on ethyl vinyl acetate turning-packed mini-column followed by hydride generation-ICP OES determination. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 143, 431–436.
Hashemi, M., & Modasser, P. (2007). Sequential spectrophotometric determination of inorganic arsenic species by hydride generation from selective medium reactions and colour bleaching of permanganate. Talanta, 73, 166–171.
Henze, G., Wagner, W., & Sander, S. (1997). Speciation of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) by cathodic stripping voltammetry. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 358, 741–744.
Ilander, A., & Vaisane, A. (2011). The determination of antimony and arsenic concentrations in fly ash by hydride generation inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 689, 178–183.
Leal, L. O., Ferrer, L., Forteza, R., & Cerd, V. (2011). Multicommutation flow techniques in the hydride generation-atomic fluorescence determination of arsenic. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 30, 761–770.
Liang, P., Peng, L. L., & Yan, P. (2009). Speciation of As(III) and As(V) in water samples by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction separation and determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchimica Acta, 166, 47–52.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Matusiewicz, H., & Ślachcińsk, M. (2012). Development of a new hybrid technique for inorganic arsenic speciation analysis by microchip capillary electrophoresis coupled with hydride generation microwave induced plasma spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 102, 61–67.
Mishra, D., Mehta, A., & Flora, S. J. (2008). Reversal of arsenic-induced hepatic apoptosis with combined administration of DMSA and its analogues in guinea pigs: role of glutathione and linked enzymes. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 21, 400–407.
Pal, A., & Maji, S. K. (2006). Spectrophotometric determination of arsenic via nanogold formation in micellar medium. Indian Journal of Chemistry, 45A, 1178–1182.
Pena-Pereira, F., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2010). Colorimetric assay for determination of trimethylamine-nitrogen (TMA-N) in fish by combining headspace-single-drop microextraction and microvolume UV–vis spectrophotometry. Food Chemistry, 119, 402–407.
Reyes-Salas, E. O., Dosal-Gomez, M. A., Barcelo-Quintal, M. H., & Manzanilla-Cano, J. A. (2002). Simultaneous determination of nickel, cobalt, antimony, and arsenic in an aqueous sample by differential pulse polarography. Analytical Letters, 35, 123–133.
Shariati-Feizabadi, V., Yamini, Y., & Bahramifar, N. (2003). Headspace solvent microextraction and gas chromatographic determination of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 489, 21–31.
Shen-Tu, C., Fan, Y., Hou, Y., Wang, K., & Zh, Y. (2008). Arsenic species analysis by ion chromatography–bianode electrochemical hydride generator–atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1213, 56–61.
Sun, Y. C., & Yang, J. Y. (1999). Simultaneous determination of arsenic(III, V), selenium(IV, VI), and antimony(III, V) in natural water by coprecipitation and neutron activation analysis. Analytica Chimica Acta, 395, 293–300.
Sun, H., Liu, X., & Miao, Y. (2011). Speciation analysis of trace inorganic arsenic in dietary supplements by slurry sampling hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Analytical Methods, 4, 251–257.
Tyburska, A., Jankowski, K., & Rodzi, A. (2011). Determination of arsenic and selenium by hydride generation and headspace solid phase microextraction coupled with optical emission spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 66, 517–521.
Ulusoy, H. I., Akçay, M., Ulusoy, S., & Gürkan, R. (2011). Determination of ultra trace arsenic species in water samples by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 703, 137–144.
World Health Organization. (1988). WHO food additives, Series no. 24. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yu, C. H., Cai, Q. T., Guo, Z. X., Yang, Z. G., & Khoo, S. B. (2003). Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry study of the retention behavior of arsenic species on various solid phase extraction cartridges and its application in arsenic speciation. Spectrochimica Acta B, 58, 1335–1351.
Yuan, C. G., He, B., Gao, E. L., Lu, J. X., & Jiang, G. B. (2007). Evaluation of extraction methods for arsenic speciation in polluted soil and rotten ore by HPLC-HG-AFS analysis. Microchimica Acta, 159, 175–182.
Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Li, L., Huang, Y., & Cao, J. (2010). Eggshell membrane-based solid-phase extraction combined with hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry for trace arsenic(V) in environmental water samples. Talanta, 80, 1907–1912.
Zhang, Y., Qiang, S., Sun, J., Song, M., & Hang, T. (2013). Liquid chromatography–hydride generation–atomic fluorescence spectrometry determination of arsenic species in dog plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Realgar and Niu Huang Jie Du. Journal of Chromatography B, 917–918, 93–99.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ferdowsi University of Mashhad for the financial supports of this work under grant no. 21317 dated on 8 May 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemniaye-Torshizi, R., Ashraf, N. & Arbab-Zavar, M.H. Hydride generation coupled to microfunnel-assisted headspace liquid-phase microextraction for the determination of arsenic with UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Environ Monit Assess 186, 8381–8389 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4011-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4011-3