Abstract
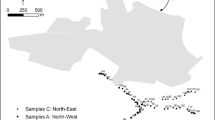
The transfer of lead, cadmium, zinc, mercury, copper and molybdenum from soil to the tissues of small mammals inhabiting differently polluted areas in Slovenia was investigated. Metals were determined in soil samples and in the livers of 139 individuals of five small mammal species, collected in 2012 in the vicinity of a former lead smelter, the largest Slovenian thermal power plant, along a main road and in a control area. The area in the vicinity of former lead smelter differs considerably from other study areas. The soil from that area is heavily polluted with Pb and Cd. The mean metal concentrations in the liver, irrespective of species, varied in the following ranges—Pb: 0.40–7.40 mg/kg fw and Cd: 0.27–135 mg/kg fw and reached effect concentrations at which toxic effects can be expected in a significant proportion of the livers of the small mammal specimens (Pb 40 %, Cd 67 %). These findings indicate that the majority of small mammals trapped in the area of the former lead smelter are at risk of toxic effects due to the very high bioaccumulation of Pb and Cd in the organism. On the contrary, Pd and Cd concentrations in the livers of small mammals sampled in the vicinity of the thermal power plant and along the main road were comparable with reference values and considerably lower than effect concentrations. Additionally, the study suggests that Apodemus flavicollis and Myodes glareolus are very suitable biomonitors of metal pollution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham, K. G., Al-Eisa, N. A., & Farhood, M. H. (2011). Risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and wild Libyan jird Meriones libycus in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Environmental Biology, 32, 813–819.
Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S. (2013). Forest biomonitoring of the largest Slovene thermal power plant with respect to reduction of air pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 1809–1823.
Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S., & Pokorny, B. (2013). Lead and cadmium in mushrooms from the vicinity of two large emission sources in Slovenia. Science of the Total Environment, 443, 944–954.
Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S., Poličnik, H., Ramšak, R., Mavec, M., & Pokorny, B. (2010). Ecological remediation of the Šoštanj Thermal Power Plant with respect to sustainable development of the Šalek Valley, Slovenia. Thermal Science, 14(3), 773–782.
Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S., Mazej Grudnik, Z., & Pokorny, B. (2011). Heavy metals and arsenic concentrations in ten fish species from the Šalek lakes (Slovenia): assessment of potential human health risk due to fish consumption. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 2647–2662.
Bennet, J. R., Kaufman, C. A., Koch, I., Sova, J., & Reimer, K. J. (2007). Ecological risk assessment of lead contamination at rifle and pistol ranges using techniques to account for site characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, 374, 91–101.
Beyer, W. N., & Storm, G. (1995). Ecotoxicological damage from zinc smelting at Palmerton, Pennsylvania. In D. J. Hoffman, B. A. Rattner, G. A. Burton, & J. C. Cairns (Eds.), Handbook of toxicology (pp. 569–608). Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc.
Beyer, W. N., Pattee, O. H., Sileo, L., Hoffman, D. J., & Mulhern, B. M. (1985). Metal contamination in wildlife living near two zinc smelters. Environmental Pollution, 38(A), 63–86.
Chmiel, K. M., & Harisson, R. M. (1981). Lead content of small mammals at a roadside site in relation to the pathways of exposure. The Science of the Total Environment, 17, 145–154.
Cooke, J. A., & Johanson, M. S. (1996). Cadmium in small mammals. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentration (pp. 377–399). Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc.
Cooke, J. A., Andrews, S. M., & Johnson, M. S. (1990). Lead, zinc, cadmium, and fluoride in small mammals from contaminated grassland established on fluorspar tailings. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 51, 43–54.
Damek-Poprawa, M., & Sawicka-Kapusta, K. (2003). Damage to the liver, kidney, and testis with reference to burden of heavy metals in yellow-necked mice from areas around steelworks and zinc smelter in Poland. Toxicology, 168, 1–10.
Damek-Poprawa, M., & Sawicka-Kapusta, K. (2004). Histopatological changes in liver, kidneys, and testes of bank voles environmentally exposed to heavy metals emissions from the steelworks and zinc smelter in Poland. Environmental Research, 96, 72–78.
Eisler, R. (1987). Mercury hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebtrates: a synoptic review. US fish and Wildlife Service, Biological Report USFWS 85/1.10, Laurel, MD.
Getz, L. L., Verner, L., & Prather, M. (1977). Lead concentrations in small mammals living near highways. Environmental Pollution, 13, 151–157.
Hamers, T., van den Berg, J. H. M., van Gestel, C. A. M., van Schooten, F., & Murk, A. J. (2006). Risk assessment of metals and organic pollutants for herbivorous and carnivorous small mammal food chains in a polluted floodplain (Biesbosch, The Netherlands). Environmental Pollution, 144, 581–595.
Hunter, B. A., Johnson, M. S., & Thompson, D. J. (1989). Ecotoxicology of cooper and cadmium in a contaminated grassland ecosystem. Tissue distribution and age accumulation in small mammals. Journal of Applied Ecology, 26, 89–99.
Ieradi, L. A., Cristaldi, M., Mascanzoni, D., Cardarelli, E., Gross, R., & Campanella, L. (1996). Genetic damage in urban mice exposed to traffic pollution. Environmental Pollution, 92, 601–614.
Jelenko, I., & Pokorny, B. (2010). Historical biomonitoring of fluoride pollution by determining fluoride concentrations in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.) antlers and mandibles in the vicinity of the largest Slovene thermal power plant. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 430–438.
Johansson, C., Norman, M., & Burman, L. (2009). Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 4681–4688.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2001). Trace elements in soils and plants (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press, LLC.
Kopušar, N., Mazej Grudnik, Z., Savinek, K., & Poličnik, H. (2011). Biomonitoring kakovosti zraka v bližini prometnic in možni ukrepi za zmanjšanje njegovega negativnega vpliva na zdravje ljudi. Velenje: ERICo (in Slovene).
Levengood, J. M., & Heske, E. J. (2008). Heavy metal exposure, reproductive activity, and demographic patterns in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) inhabiting a contaminated floodplain wetland. Science of the Total Environment, 389, 320–328.
Lewis, L. A., Poppenga, R. J., Davidson, W. R., Fisher, J. R., & Morgan, K. A. (2001). Lead toxicosis and trace element levels in wild birds and mammals at a firearms training facility. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41, 208–214.
Ma, W. C. (1989). Effect of soil pollution with metallic lead pellets on lead bioaccumulation and organ/body weight alternations in small mammals. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 18, 617–622.
Ma, W. C. (1996). Lead in mammals. In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.), Environmental contaminants in wildlife (pp. 281–296). New York: Lewis publishers.
Ma, W. C., Denneman, W., & Faber, J. (1991). Hazardous exposure of ground-living small mammals to cadmium and lead in contaminated terrestrial ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 18, 266–270.
Marques, C. C., Sánchez-Chardi, A., Gabriel, S. I., Nadal, J., Viegas-Crespo, A. M., & Da Luz Mathias, M. (2007). How does the great white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula, respond to long-term heavy metal contamination?—a case study. Science of the Total Environment, 376, 128–133.
Martiniaková, M., Omelka, R., Grookopf, B., & Jančová, A. (2010). Yellow-necked mice (Apodemus flavicollis) and bank voles (Myodes glareolus) as zoomonitors of environmental contamination at a polluted area in Slovakia. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 2010, 52–58.
Mazej, Z., Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S., & Pokorny, B. (2010). Heavy metal concentrations in food chain of Lake Velenjsko jezero, Slovenia: an artificial lake from mining. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58, 998–1007.
Mertens, J., Luyssaert, S., Verbeeren, S., Vervaeke, P., & Lust, N. (2001). Cd and Zn concentrations in small mammals and willow leaves on disposal facilities for dredged material. Environmental Pollution, 115, 17–22.
Metcheva, R., Teodorova, S., & Topashka-Ancheva, M. (2003). A comparative analyses of the heavy metal loading of small mammals in different region of Bulgaria I: monitoring points and bioaccumulation features. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54, 176–187.
Official Gazzete of the Republic of Slovenia, no. 68/1996.
Okati, N., & Rezaee, M. (2013). Heavy metals concentrations in different tissues of Persian Jird (Meriones persicus) in Sistan region. International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Science, 5(10), 1272–1276.
Pokorny, B., & Ribarič Lasnik, C. (2000). Lead, cadmium and zinc in tissues of roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) near the lead smelter in the Koroška region (north Slovenia). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 64, 20–26.
Pokorny, B., Glinšek, A., & Ribarič Lasnik, C. (2004). Roe deer antlers as a historical bioindicator of lead pollution in the Šalek Valley, Slovenia. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 49, 175–189.
Pokorny, B., Jelenko, I., Kierdorf, U., & Kierdorf, H. (2009). Roe deer antlers as historical bioindicators of lead pollution in the vicinity of a lead smelter, Slovenia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 203, 317–324.
Poličnik, H., Batič, F., & Ribarič Lasnik, C. (2004). Monitoring of short-term heavy metal deposition by accumulation in epiphytic lichens (Hypogymnia physodes (L.) Nyl.). Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 49, 223–230.
Poličnik, H., Simončič, P., & Batič, F. (2008). Monitoring air quality with lichens: a comparison between mapping in forest sites and in open areas. Environmental Pollution, 151, 395–400.
Reinecke, A. J., Reinecke, S. A., Musilbono, D. H., & Champan, A. (2000). The transfer of lead (Pb) from earthworms to shrews (Myosorex varius). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 392–397.
Ribarič Lasnik, C., Eržen, I., Kugonič, N., Pokorny, B., Končnik, D., Svetina, M., et al. (2002). Primerjalna študija onesnaženosti okolja v Zgornji Mežiški dolini med stanji v letih 1989 in 2001. Velenje: ERICo Velenje (in Slovene).
Roodbergen, M., Klok, C., & Van Der Hout, A. (2008). Transfer of heavy metals in food chain earthworm Black-tailed godwit (Limosa limosa): comparison of polluted and reference site in the Netherlands. Science of the Total Environment, 406, 407–412.
Salińska, A., Włostowski, T., & Zambrzycka, E. (2012). Effect of dietary cadmium and/or lead on histopathological changes in the kidneys and liver of bank voles Myodes glareolus kept in different group densities. Ecotoxicology, 21, 2235–2243.
Salińska, A., Włostowski, T., & Oleńska, E. (2013). Differential susceptibility to cadmium-induced liver and kidney injury in wild and laboratory-bred bank voles Myodes glareolus. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 65, 324–331.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., & López-Fuster, M. (2009). Metal and metalloid accumulation in shrews (Soricomorpha, Mammalia) from two protected Mediterranean costal sites. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1243–1248.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., & Nadal, J. (2007). Bioaccumulation of metals and effects of landfill pollution in small mammals. Part II. The great white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula. Chemosphere, 68, 703–711.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., López-Fuster, M., & Nadal, J. (2007a). Bioaccumulation of lead, mercury, and cadmium in the greater white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula, from the Elba Delta (NE Spain): sex- and age-dependent variation. Environmental Pollution, 145, 7–14.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., Marques, C. C., Nadal, J., & Da Luz Mathias, M. (2007b). Metal bioaccumulation in the greater white-toothed shrew, Crocidura russula, inhabiting an abandoned pyrite mine site. Chemosphere, 67, 121–130.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., Peñarroja-Matutano, C., Oliveira Riberio, C. A., & Nadal, J. (2007c). Bioaccumulation of metals and effects of a landfill in small mammals. Part II. The wood mouse, Apodemus sylvaticus. Chemosphere, 70, 101–109.
Sánchez-Chardi, A., Oliveira Riberio, C. A., & Nadal, J. (2009). Metals in liver and kidneys and the effects of chronic exposure to pyrite mine pollution in the shrew Crocidura russula inhabiting the protected wetland of Doñana. Chemosphere, 76, 387–394.
Scheifler, R., Coeurdassier, M., Morilhat, C., Bernard, N., Faivre, B., Flicoteaux, P., et al. (2006). Lead concentrations in feathers and blood of common blackbirds (Turdus merula) and in earthworms inhabiting unpolluted and moderately polluted urban areas. Science of the Total Environment, 371, 197–205.
Schleich, C. E., Beltrame, M. O., & Antenucci, C. D. (2010). Heavy metal accumulation in the subterranean rodent Ctenomys talarum (Rodentia: Ctenomydae) from areas with different risk of contamination. Folia Zoologica, 59(2), 104–114.
Shore, R. F., & Rattner, B. A. (Eds.). (2001). Ecotoxicology of wild mammals. Chichester: Wiley.
Sneddon, J., Clemente, R., Riby, P., & Lepp, N. W. (2009). Source-pathway-receptors investigation of the fate of trace elements derived from shot-gun pellets discharged in terrestrial ecosystems managed for game shooting. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2663–2669.
Stansley, W., & Rosce, D. E. (1996). The uptake and effects of lead in small mammals and frogs at a trap and skeet range. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 30, 220–226.
STATSOFT. (2006). Statistica for Windows 7.1. Tulsa, StatSoft.
Sutherland, R. A., & Tolosa, C. A. (2000). Multi-element analysis of road-deposited sediment in an urban drainage basin, Honolulu, Hawaii. Environmental Pollution, 110, 483–495.
Świergosz-Kowalewska, R., Gramatyka, M., & Reczyński, W. (2005). Metal distribution and interactions in tissues of shrews (Sorex ssp.) from copper and zinc-contaminated areas in Poland. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 1519–1529.
Topashka-Ancheva, M., Metcheva, R., & Teodorova, S. (2003). A comparative analysis of the heavy metal loading of small mammals in different regions of Bulgaria II: chromosomal aberrations and blood pathology. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54, 188–193.
Wijnhoven, S., Leuven, R. S. E. W., Van Der Velde, G., & Eijsackers, H. J. P. (2008). Toxicological risk for small mammals in a diffusely and moderatory polluted floodplain. Science of the Total Environment, 406, 401–406.
Wlostowski, T., Krasowska, A., & Bonda, E. (2003). An iron-rich diet protects the liver and kidneys against cadmium-induced injury in the bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54, 194–198.
Acknowledgements
The study was financed by the Slovene Research Agency through the project No. L1-4320.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al Sayegh Petkovšek, S., Kopušar, N. & Kryštufek, B. Small mammals as biomonitors of metal pollution: a case study in Slovenia. Environ Monit Assess 186, 4261–4274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3696-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3696-7