Abstract
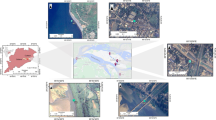
India's Unnao region is home to many leather-treatment facilities and related industries. Industrial and agricultural waste leads to heavy metal contamination that infiltrates groundwater and leads to human health hazards. This work measured the amount of heavy metal in groundwater at specific sites near the industrial facilities in Unnao and identified potential sources of contamination as anthropogenic or lithogenic. Groundwater samples were taken from 10 bore well sites chosen for depth and proximity to industry. Data obtained from sample sites was interpreted using a multivariate statistical analytical approach, i.e., principal component analysis, clustering analysis, and correlation analysis. The results of the multivariate analysis showed that cadmium, copper, manganese, nickel, lead, and zinc were correlated with anthropogenic sources, while iron and chromium were associated with lithogenic sources. These findings provide information on the possible sources of heavy metal contamination and could be a model for assessing and monitoring heavy metal pollution in groundwater in other locales. This study analyzed a selection of heavy metals chosen on the basis of industries located in the study area, which might not provide a complete range of information about the sources and availability of all heavy metals. Therefore, an extended investigation on heavy metal fractions will be developed in further studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Cluster analysis
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- CM:
-
Correlation matrix
- Cr:
-
Chromium
- Cu:
-
Copper
- GPS:
-
Global positioning satellite
- Hg:
-
Mercury
- km2 :
-
Square kilometer
- ml:
-
Milliliter
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- mg/L:
-
Milligrams per liter
- mS/cm:
-
Milli-Siemens per centimeter
- Ni:
-
Nickel
- Pb:
-
Lead
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- ppt:
-
Parts per thousand
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
- Zn:
-
Zinc
References
Ansari, A. A., Singh, I. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (1998). Organotin compounds in surface and pore waters of Ganga Plain in the Kanpur-Unnao industrial region, India. Science of The Total Environment, 223, 157–166.
Ansari, A. A., Singh, I. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (1999). Status of anthropogenically induced metal pollution in the Kanpur-Unnao industrial region of the Ganga Plain, India. Environmental Geology, 38, 25–33.
Ansari, A. A., Singh, I. B., & Tobschall, H. J. (2000). Role of monsoon rain on concentrations and dispersion patterns of metal pollutants in sediments and soils of the Ganga Plain, India. Environmental Geology, 39, 221–237.
Covelo, E. F., Vega, F. A., & Andrade, M. L. (2007). Simultaneous sorption and desorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in acid soils: II. Soil ranking and influence of soil characteristics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 862–870.
Einax, J. W., & Soldt, U. (1999). Geostatistical and multivariate statistical methods for the assessment of polluted soils—merits and limitations. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 46, 79–91.
Facchinelli, A., Sacchi, E., & Mallen, L. (2001). Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environmental Pollution, 114, 313–324.
Huamain, C. (2005). Environmental soil science. Beijing: Science Press.
Huamain, C., Chunrong, Z., Cong, T., & Yongguan, Z. (1999). Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: status and countermeasures. Ambio, 28, 130–134.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872.
Ministry of Water Resources (2013). The report of the committee on pollution caused by leather tanning industry to the water bodies/ground water in Unnao district of Uttar Pradesh, NIH Roorkee. http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/file/pollution%20caused%20by%20leather%20tannery%20industry%20in%20Unnao%20district.pdf
MSME (2012). Brief industrial profile of Unnao District U.P. Government of India. http://dcmsme.gov.in/dips/DIP%20Unnao.pdf.
Oliva, S. R., & Espinosa, A. J. F. (2007). Monitoring of heavy metals in topsoils, atmospheric particles and plant leaves to identify possible contamination sources. Microchemical Journal, 86, 131–139.
Richard, J.B., Gregory, C.A. (1985). Applied regression analysis and experimental design. Marcel Dekker. London: CRC Press.
Samuel, B. G., Neil, J. S., & Theresa, M. (2000). Using SPSS for Windows: analyzing and understanding data. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Srinivasa Gowd, S., Ramakrishna Reddy, M., & Govil, P. K. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 113–121.
Tuncer, G. T., Tuncel, S. G., Tuncel, G., & Balkas, T. I. (1993). Metal pollution in the Golden Horn, Turkey—contribution of natural and anthropogenic components since 1913. Water Science and Technology, 28, 59–64.
USEPA (2009). Drinking water contaminants. National primary drinking water regulations. EPA 816-F-09–0004.
Vankar, P. S., & Dwivedi, A. K. (2009). Raw skin preservation through sodium salts—a comparative analysis. Desalination, 249, 158–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, A.K., Vankar, P.S. Source identification study of heavy metal contamination in the industrial hub of Unnao, India. Environ Monit Assess 186, 3531–3539 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3636-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3636-6