Abstract
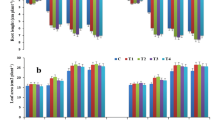
The tannery effluents contain a high concentration of chromium (Cr). It drastically reduces the crop yield when used for irrigation purpose. A huge volume of tannery effluents is available as irrigation for crop production. It is negatively affecting germination as well as yield of the crop. The wheat seeds were exposed to five different concentrations of Cr (0, 20, 40, 80, and 100 ppm). In Petri plates, 100 seeds were placed and the germination percent was recorded after 72 hour (h). Root elongation and coleoptile growth were measured at 72, 120, 168, and 240 h. Results showed that the germination percent of the test crop decreased with increasing Cr levels. It decreased by 6, 14, 30, and 37 % under the Cr concentration of 20, 40, 80, and 100 ppm, respectively. The root elongation was more sensitive than the coleoptile growth. The negative correlation was found between Cr levels and root elongation as well as coleoptile growth. These growth parameters were significantly affected up to 80 ppm of Cr level. The wheat growers using tannery effluent as irrigation should be well treated prior to application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, T., & Singh, M. V. (2002). Thermodynamics of chromium sorption in soil groups of India. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 72(11), 654–658.
Andjelković, D. H., Andjelković, T. D., Nikolić, R. S., Purenović, M. M., Blagojević, S. D., Bojić, A. L., et al. (2012). Leaching of chromium from chromium contaminated soil—a speciation study and geochemical modelling. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 77(1), 119–129.
Arun, K. S., Cervantes, C., Loza-Tavera, H., & Avudainayagam, S. (2005). Chromium toxicity in plants. Environment International, 31(739), 753.
Babel, S., & Opiso, E. M. (2007). Removal of Cr from synthetic wastewater by sorption into volcanic ash soil. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(1), 99–107.
Barcel, J., Poschenrieder, C., & Gunse, J. (1985). Effect of chromium VI on mineral element composition of bush beans. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 8(211), 217.
Barcelo, J., & Poschenrieder, C. H. (1990). Plant water relations as affected by heavy metal stress: a review. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 13(1), 37.
Bartlett, R.J., & James, B.R. (1996). Chromium. In Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Soltanpour, P.N., Tabatabai, M.A., Johnston, CT., & Sumner, M.E. (Eds.), Method of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods (Soil Science Society of America, book series no. 5) (pp. 683–701). Madison: ASA-SSSA.
Bingham, F. T., Pereyea, F. J., & Jarrell, W. M. (1986). Metal toxicity to agriculture crops. Metal Ions in Biological Systems, 20, 119–156.
Chang, A. C., Granato, T. C., & Page, A. L. (1992). A methodology for establishing phytotoxicity criteria for chromium, copper, nickel and zinc in agricultural land application of municipal sewage sludges. Journal Environmental Quality, 21, 521–536.
Dakiky, M., Khami, A., Manassra, A., & Mereb, M. (2002). Selective adsorption of chromium(VI) in industrial wastewater using low-cost abundantly available adsorbents. Advances in Environmental Research, 6(4), 533–540.
Dey, S. K., Jena, P. P., & Kundu, S. (2009). Antioxidative efficiency of Triticum aestivum L. exposed to chromium stress. Journal of Environmental Biology, 30(4), 539–544.
Dube, B. K., Tewari, K., Chatterjee, J., & Chatterjee, C. (2003). Excess chromium alters uptake and translocation of certain nutrients in citrullus. Chemosphere, 53(9), 1147–1153.
Jain, R., Srivastava, S., Madan, V. K., & Jain, R. (2000). Influence of chromium on growth and cell division of sugarcane. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 5(3), 228–231.
Jun, R., Ling, T., & Guanghua, Z. (2009). Effects of chromium on seed germination, root elongation and coleoptile growth in six pulses. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 6(4), 571–578.
Kar, D., Sur, P., Mandal, S. K., Saha, T., & Kole, R. K. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(1), 119–124.
Nath, K., Saini, S., & Sharma, Y. K. (2005). Chromium in tannery industry effluent and its effect on plant metabolism and growth. Journal of Environmental Biology, 26(2), 197–204.
Ogundiran, O. O., & Afolabi, T. A. (2008). Assessment of the physicochemical parameters and heavy metals’ toxicity of leachates from municipal solid waste open dumpsite. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 5(2), 243–250.
Oliveira, H. (2012). Chromium as an environmental pollutant: insights on induced plant toxicity. Journal of Botany. doi:10.1155/2012/375843.
López-Luna, J. L., Gonzalez-Chavez, M. C., Esparza-Garcia, F. J., & Rodriguez-Vazquez, R. (2009). Toxicity assessment of soil amended with tannery sludge, trivalent chromium and hexavalent chromium, using wheat, oat and sorghum plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(2–3), 829–834.
Parmar, N. G., Vithalani, S. D., & Chanda, S. V. (2002). Alteration in growth and peroxidase activity by heavy metals in Phaseolus seedlings. Acta Physiologia Plantarum, 24(1), 89–95.
Peralta, J. R., Gardea-Torresdey, J. L., & Tiemann, K. J. (2001). Uptake and effects of five heavy metals on seed germination and plant growth in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66(6), 727–734.
Saha, J. K., Panwar, N., & Singh, M. V. (2013). Risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of a susceptible agro-ecological system amended with municipal solid waste compost. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 61(1), 15–22.
Sahu, R. K., Katiyar, S., Yadav, A. K., Kumar, N., & Srivastava, J. (2008). Toxicity assessment of industrial effluent by bioassays. CLEAN Soil Air Water, 36(5–6), 517–520.
Scoccianti, V., Crinelli, R., Tirillini, B., Mancinelli, V., & Speranza, A. (2006). Uptake and toxicity of Cr(III) in celery seedlings. Chemosphere, 64(10), 1695–1703.
Shanker, A. K., Cervantes, C., Tavera, H. L., & Avudainayagam, S. (2005). Chromium toxicity in plants. Journal of Environment International, 31(739), 753.
Sharma, D. C., & Forster, C. F. (1995). Column studies into the adsorption of chromium (VI) using sphagnum moss peat. Bioresource Technology, 52(261), 267.
Shrestha, R., Fischer, R., & Sillanpää, M. (2007). Investigations on different positions of electrodes and their effects on the distribution of Cr at the water sediment interface. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(4), 413–420.
Singh, A. P., & Rao, D. P. (2013). Assessment of tannery effluent: a case study of Kanpur in India. European Chemical Bulletin, 2(7), 461–464.
Srivastava, S., & Thakur, I. S. (2006). Evaluation of bioremediation and detoxification potentiality of Aspergillus niger for removal of hexavalent chromium in soil microcosm. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38(7), 1904–1911.
Sundaramoorthy, P., Chidambaram, A., Ganesh, K. S., Unnikannan, P., & Baskaran, L. (2010). Chromium stress in paddy: (i) nutrient status of paddy under chromium stress; (ii) phytoremediation of chromium by aquatic and terrestrial weeds. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 333(8), 597–607.
UNIDO (2002). Industrial policy and the environment in Pakistan (NC/PAK/97/018). Vienna: United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO). 11 Dec 2000.
UNIDO (2005). Cost of tanned waste treatment, 15th session of the leather and leather products industry panel Leon, Mexico. Vienna: United Nations Industrial Development Organization.
Venkateswaran, P., Vellaichamy, S., & Palanivelu, K. (2007). Speciation of heavy metals in electroplating industry sludge and wastewater residue using inductively coupled plasma. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(4), 497–504.
Wong, J. W. C., Lai, K. M., Su, D. S., & Fang, M. (2001). Availability of heavy metals for Brassica chinensis grown in an acidic loamy soil amended with a domestic and an industrial sewage sludge. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 128(3–4), 339–353.
Zayed, A. M., & Terry, M. (2003). Chromium in the environment: factors affecting biological remediation. Plant and Soil, 249(1), 139–156.
Zeid, M. (2001). Responses of Phaseolus vulgaris to chromium and cobalt treatments. Biologia Plantarum, 44(1), 111–115.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dotaniya, M.L., Das, H. & Meena, V.D. Assessment of chromium efficacy on germination, root elongation, and coleoptile growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) at different growth periods. Environ Monit Assess 186, 2957–2963 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3593-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3593-5