Abstract
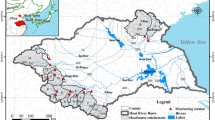
Water eutrophication in subtropical regions of southern China threatens watershed health and is of major concern. However, annual phosphorus (P) loading and its dominant causes are still unclear, especially at the watershed scale. In this study, we investigated dynamic P loadings and associated factors (e.g., land use, livestock production, and runoff depth) in ten watersheds that varied in area from 9 to 5,212 ha in a hilly area of Hunan Province, China. A flowmeter was installed at the outlet of each watershed, and total P (TP) and soluble P (SP) concentrations were monitored periodically from June 2010 to October 2012. The results showed that annual P loadings (APLs) in the ten watersheds ranged from 22.8 to 247.8 kg P/km2 and that P loss primarily occurred from April to June of each year during the main rainfall season in the study area. In addition, the average eutrophication (>0.05 mg P/L) ratio for stream waters was 86.7 % during the study period, which was indicative of a potentially serious condition for the local water environments. Annual P loadings were linearly related to livestock density (LD; R = 0.92, p < 0.01), whereas the eutrophication ratio of stream water was significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with LD (R = 0.61), percentage cropland (R = 0.71), and percentage forest cover (R = −0.68). Thus, it is concluded that the control of livestock production has the greatest potential for reducing P loadings in watersheds in this subtropical area. This will be beneficial to the amelioration and protection of local environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APL:
-
Annual phosphorus loading
- ER:
-
Eutrophication ratio
- LD:
-
Livestock density
- RD:
-
Runoff depth
- SP:
-
Soluble phosphorus
- TP:
-
Total phosphorus
References
Alexander, R. B., Smith, R. A., & Schwarz, G. E. (2000). Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature, 403, 758–761.
Baker, D. B., Richards, R. P., Kramer, J. W. (2007). Phosphorus trading between point and nonpoint sources: inapplicability for many stream eutrophication problems in Ohio. http://www.allacademic.com/meta/p175420_index.html.
Carpenter, S. R. (2008). Phosphorus control is critical to mitigating eutrophication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(32), 11039–11040.
Caruso, B. S. (2000). Comparative analysis of New Zealand and US approaches for agricultural nonpoint source pollution management. Environmental Management, 25(1), 9–22.
Centner, T. J., Wetzstein, M. E., & Mullen, J. D. (2008). Small livestock producers with diffuse water pollutants: adopting a disincentive for unacceptable manure application practices. Desalination, 226, 66–71.
Chen, H. Y., Teng, Y. G., Wang, J. S., Song, L. T., & Zhou, Z. Y. (2012). Pollution load and source apportionment of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus in Jinjiang River watershed. Transactions of the CSAE, 28(5), 213–219.
Chow, V., Maidment, D., & Mays, L. (1988). Applied hydrology (p. 588). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., et al. (2009). Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323, 1014–1015.
Drewry, J. J., Newham, L. T. H., & Greene, R. S. B. (2011). Index models to evaluate the risk of phosphorus and nitrogen loss at catchment scales. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 639–649.
Eastman, M., Gollamudi, A., Stämpfli, N., Madramootoo, C. A., & Sarangi, A. (2010). Comparative evaluation of phosphorus losses from subsurface and naturally drained agricultural fields in the Pike River watershed of Quebec. Canada Agricultural Water Management, 97, 596–604.
Gao, Y., Zhu, B., Wang, T., & Wang, Y. (2012). Seasonal change of non-point source pollution-induced bioavailable phosphorus loss: a case study of Southwestern China. Journal of Hydrology, 420–421, 373–379.
Han, L. N., Li, Y. Y., Shi, H., Zou, G. H., Yu, H. B., Xiao, R. L., et al. (2012). Study on comparison of different aquatic plant on nitrogen and phosphorus ecological control measures in drainage ditch of cropland in southern China. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 33(1), 117–120.
Howarth, R. W., & Marino, R. (2006). Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: evolving views over three decades. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 364–376.
Huang, J. L., Lin, J., Zhang, Y. Z., Li, Q. S., & Hong, H. S. (2013). Analysis of phosphorus concentration in a subtropical river basin in southeast China: Implications for management. Ocean & Coastal Management, 81, 29–37.
Kara, E. L., Heimerl, C., Killpack, T., Van de Bogert, M. C., Yoshida, H., & Carpenter, S. R. (2012). Assessing a decade of phosphorus management in the Lake Mendota, Wisconsin watershed and scenarios for enhanced phosphorus management. Aquatic Sciences, 74, 241–253.
Kato, T., Kuroda, H., & Nakasone, H. (2009). Runoff characteristics of nutrients from an agricultural watershed with intensive livestock production. Journal of Hydrology, 368, 79–87.
Kellogg, R. L., Lander, C. H., Moffitt, D. C., & Gollehon, N. (2000). Manure nutrients relative to the capacity of cropland and pastureland to assimilate nutrients: spatial and temporal trends for the United States. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service and Economic Research Service.
Krupa, M., Tate, K. W., van Kessel, C., Sarwar, N., & Linquist, B. A. (2011). Water quality in rice-growing watersheds in a Mediterranean climate. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 144, 290–301.
Lam, Q. D., Schmalz, B., & Fohrer, N. (2011). The impact of agricultural best management practices on water quality in a North German lowland catchment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 183, 351–379.
Makarewicz, J. C., D’Aiuto, P. E., & Bosch, I. (2007). Elevated nutrient levels from agriculturally dominated watersheds stimulate metaphyton growth. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 33(2), 437–448.
Makarewicz, J. C., Lewis, T. W., Bosch, I., Noll, M. R., Herendeen, N., Simon, R. D., et al. (2009). The impact of agricultural best management practices on downstream systems: soil loss and nutrient chemistry and flux to Conesus Lake, New York, USA. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 35, 23–36.
McDowell, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Folmar, G. (2003). Modification of phosphorus export from an eastern USA catchment by fluvial sediment and phosphorus inputs. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 99, 187–199.
Meng, C., Li, Y. Y., Xu, X. G., Gao, R., Wang, Y., Zhang, M. Y., et al. (2013). A case study on non-point source pollution and environmental carrying capacity of animal raising production in subtropical watershed. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33(2), 635–643.
MEPC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of China), National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), Ministry of Agriculture of China (MAC). (2010). First national pollution census bulletin of (2007). http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2010-02/10/content_1532174.htm.
MEPPRC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China). (2002). Water and wastewater monitoring analysis method (4th ed.). Beijing: China Environmental Science.
Mulholland, P. J., Helton, A. M., Poole, G. C., Hall, R. O., Hamilton, S. K., Peterson, B. J., et al. (2008). Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature, 452, 202–205.
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36.
Némery, J., Garnier, J., & Morel, C. (2005). Phosphorus budget in the Marne Watershed (France): urban vs. diffuse sources, dissolved vs. particulate forms. Biogeochemistry, 72, 35–66.
Ng Kee Kwong, K. F., Bholah, A., Volcy, L., & Pynee, K. (2002). Nitrogen and phosphorus transport by surface runoff from a silty clay loam soil under sugarcane in the humid tropical environment of Mauritius. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 91, 147–157.
Noll, M. R., & Magee, E. A. (2009). Quantification of phosphorus sources to a small watershed: a case study of Graywood Gully, Conesus Lake, NY. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 35, 50–55.
Pärn, J., Pinay, G., & Mander, Ü. (2012). Indicators of nutrients transport from agricultural catchments under temperate climate: a review. Ecological Indicators, 22, 4–15.
Pionke, H. B., Gburek, W. J., Schnabel, R. R., Sharpley, A. N., & Elwinger, G. F. (1999). Seasonal flow, nutrient concentrations and loading patterns in stream flow draining an agricultural hill-land watershed. Journal of Hydrology, 220, 62–73.
Pote, D. H., Daniel, D. C., Sharpley, A. P., & Nichols, D. J. (1996). Relating extractable soil phosphorus to phosphorus losses in runoff. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 855–859.
Qin, H. L., Quan, Z., Liu, X. L., Li, M. D., Zong, Y., Wu, J. S., et al. (2010). Phosphorus status and risk of phosphate leaching loss from vegetable soils of different planting years in suburbs of Changsha, China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 9(11), 1641–1649.
Rao, N. S., Easton, Z. M., Schneiderman, E. M., Zion, M. S., Lee, D. R., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2009). Modeling watershed-scale effectiveness of agricultural best management practices to reduce phosphorus loading. Journal of Environmental Management, 90, 1385–1395.
Schelske, C. L. (2009). Eutrophication: focus on phosphorus. Science, 324, 722.
Schindler, D. W. (1977). Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science, 195, 260–262.
Schindler, D. W., & Hecky, R. E. (2009). Eutrophication: more nitrogen data needed. Science, 324, 721–722.
Schindler, D. W., Hecky, R. E., Findlay, D. L., Stainton, M. P., Parker, B. R., Paterson, M. J., et al. (2008). Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(32), 11254–11258.
Schoumans, O. F., & Groenendijk, P. (2000). Modeling soil phosphorus levels and phosphorus from agricultural land in the Netherlands. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 111–116.
Schröder, J. J., Scholefield, D., Cabral, F., & Hofman, G. (2004). The effects of nutrient losses from agriculture on ground and surface water quality: the position of science in developing indicators for regulation. Environmental Science & Policy, 7, 15–23.
Shafqat, M. N., & Pierzynski, G. M. (2011). Bioavailable phosphorus in animal waste amended soils: using actual crop uptake and P mass balance approach. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 8217–8224.
Sharpley, A. N., Kleinman, P. J. A., & Weld, J. L. (2004). Environmental soil phosphorus indices. In M. R. Carter & E. G. Gregorich (Eds.), Soil sampling and methods of analysis, Canadian Society of Soil Science. Boca Raton: CRC.
Sileika, A. S., & Gaigalis, K. (2005). Factors affecting N and P losses from small catchments (Lithuania). Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 102, 359–374.
Soil Survey Staff. (1975). Soil taxonomy. Washington, D.C.: USDA-NRCS, US Government Printing Office.
Ter Braak, C. J. F. (2002). Biometris—quantitative methods in the life and earth sciences. Wageningen: Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Centre.
Turner, R. E., & Rabalais, N. N. (2004). Suspended sediment, C, N, P, and Si yields from the Mississippi River basin. Hydrobiologia, 511, 79–89.
Wei, M. J., & Shen, C. (2009). http://finance.chinanews.com/cj/cj-hbht/news/2009/11-05/1948982.Shtml.
Yang, J. L., & Zhang, G. L. (2003). Quantitative relationship between land use and phosphorus losses in subtropical hilly regions of China. Pedosphere, 13(1), 67–74.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Science Fund of China (41171396), the National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2012BAD14B17), and the Creative Research Teams Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-T07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Meng, C., Gao, R. et al. Study on phosphorus loadings in ten natural and agricultural watersheds in subtropical region of China. Environ Monit Assess 186, 2717–2727 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3573-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3573-9