Abstract
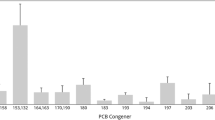
The aim of this study was to detect the presence and determine the residue levels of DDT, lindane, endrin and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the liver of wild boars from the area of West Pomerania, NW Poland; to determine the activity of glutathione S-transferase (GST) as a biomarker of biological response and to assess the toxicological risk for consumers of the wild boar offal. The presence of pesticide residues and PCBs was found in all examined liver samples. The highest concentration was observed for endrin, and then, the descending order was PCBs >DDTs >lindane >dl-PCBs. The mean hepatic concentrations of endrin, PCBs, DDTs and lindane were 117.28, 78.59, 67.95 and 7.24 ng/g lipid weight, respectively. Among the dioxin-like PCB congeners, 118 and 156 were dominant in liver samples. The mean toxic equivalent (TEQ) level calculated for dl-PCBs was 2.10 ± 1.11 pg WHO-PCB-TEQ/g. There was a statistically significant (p < 0.05) negative correlation between the concentration of lindane, DDTs and PCBs (as a sum of indicator congeners) in the liver and in the activity of GST. However, GST activities showed no significant correlation with any of the dl-PCBs. In five boar liver samples, the levels of certain organochlorine compounds exceeded the maximum residue levels (MRLs). In one sample, the MRLs were exceeded simultaneously for PCBs, endrin and DDTs and in another one—for endrin and DDTs. In the remaining three samples, only PCB levels were exceeded.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baubet, E., Bonenfant, C., & Brandy, S. (2004). Diet of the wild boar in the French Alps. Galemys, S16, 101–113.
Bouwman, H., van den Berg, H., & Kylin, H. (2011). DDT and malaria prevention: addressing the paradox. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119(6), 744–747.
Bradford, M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive assay of protein utilizing the principle of dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Breivik, K., Sweetman, A., Pacyna, J. M., & Jones, K. C. (2002). Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners—a mass balance approach 1. Global production and consumption. The Science of the Total Environment, 290(1), 181–198.
Dip, R., Hegglin, D., Deplazes, P., Dafflon, O., Koch, H., & Naegeli, H. (2003). Age-and sex-dependent distribution of persistent organochlorine pollutants in urban foxes. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(13), 1608–1612.
Dvorská, A., Lammel, G., & Holoubek, I. (2009). Recent trends of persistent organic pollutants in air in central Europe—Air monitoring in commination with air mass trajectory statistics as a tool to study the effectivity of regional chemical policy. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 1280–1287.
Falandysz, J. (1999). Polichlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in an environment: chemistry, toxicity, analysis, concentrations and risk assessment. Gdańsk: Fundacja Rozwoju Uniwersytetu Gdańskiego.
Fitzpatrick, P. J., O’Halloran, J., Sheehan, D., & Walsh, A. R. (1997). Assessment of a glutathione S-transferase and related proteins in the gill and digestive gland of Mytilus edulis (L.), as potential organic pollution biomarkers. Biomarkers, 2, 51–56.
Genov, P. (1981). Food composition of wild boar in North-eastern and Western Poland. Acta Theriologica, 26, 185–205.
Greco, L., Serrano, R., Blanes, M., Serrano, E., & Capri, E. (2010). Bioaccumulation markers and biochemical responses in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) raised under different environmental conditions. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 38–45.
Gregoraszczuk, E., Augustowska, K., & Ptak, A. (2004). Environmental xenoestrogens causes endocrine alterations associated with early fetal loss. Polish Journal of Endocrinology, 6, 819–824.
Hamed, R. R., Farid, N. M., Elowa, S. E., & Asdalla, A. M. (2003). Glutathione related enzyme levels of freshwater fish as bioindicators of pollution. Environmentalist, 23, 313–322.
Hoekstra, P. F., Braune, B. M., Wong, C. S., Williamson, M., Elkin, B., & Muir, D. C. (2003). Profile of persistent chlorinated contaminants, including selected chiral compounds, in wolverine (Gulo gulo) livers from the Canadian Arctic. Chemosphere, 53(5), 551–560.
Holoubek, I., Klánová, J., Jarkovský, J., Kubík, V., & Helešic, J. (2007). Trends in background levels of persistent organic pollutants at Kosetice observatory, Czech Republic. Part II Aquatic and terrestrial environments 1996–2005. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 9, 564–571.
Hoshi, H., Minamoto, N., Iwata, H., Shiraki, K., Tatsukawa, R., Tanabe, S., et al. (1998). Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in wild terrestrial mammals and birds from Chubu region, Japan: interspecies comparison of the residue levels and compositions. Chemosphere, 36(15), 3211–3221.
Jaward, F., Farrar, N., Harner, T., Sweetman, A., & Jones, K. (2004). Passive air sampling of PCBs, PBDEs, and organochlorine pesticides across Europe. Environmental Science and Technology, 38(1), 34–41.
Kocan, A., Petrik, J., Jursa, S., Chovancova, J., & Drobna, B. (2001). Environmental contamination with polychlorinated biphenyls in the area of their former manufacture in Slovakia. Chemosphere, 43(4–7), 595–600.
Kumar, K., Priya, M., Sajwan, K., Kõlli, R., & Roots, O. (2009). Residues of persistent organic pollutants in Estonian soils (1964-2006). Estonian Journal of Earth Sciences, 58(2), 109–123.
Langer, P. (2010). The impacts of organochlorines and other persistent pollutants on thyroid and metabolic health. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 31(4), 497–518.
Naccari, F., Giofrè, F., Licata, P., Martino, D., Calò, M., & Parisi, N. (2004). Organochlorine pesticides and PCBs in wild boars from Calabria (Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96(1–3), 191–202.
Naso, B., Zaccaroni, A., Perrone, D., Ferrante, M., Severino, L., Stracciari, G., et al. (2004). Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in European roe deer Capreolus capreolus resident in a protected area in Northern Italy. The Science of the Total Environment, 328(1–3), 83–93.
Richardson, K. L., Lopez Castro, M., Gardne, S. C., & Schlenk, D. (2010). Polychlorinated biphenyls and biotransformation enzymes in three species of sea turtles from the Baja California Peninsula of Mexico. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 58(1), 183–193.
Rolecki, R. (2002). Toxicological characteristics of permanent organic pollutants and routes of human exposure Report GF-POL-INV-R15 under the GEF project GF/POL/01/004. http://ios.info.pl/gef/doc/GF-POL-INV-R15.PDF. Accessed 12.11.2002.
Routti, H., Letcher, R., Arukwe, A., van Bavel, B., Yoccoz, N., Chu, S., et al. (2008). Biotransformation of PCBs in relation to phase I and II xenobiotic-metabolizing enzyme activities in ringed seals (Phoca hispida) from Svalbard and the Baltic Sea. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(23), 8952–8958.
Růžičková, P., Klánová, J., Čupr, P., Lammel, G., & Holoubek, I. (2008). An assessment of air-soil exchange of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides across Central and Southern Europe. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(1), 179–185.
Safe, S. (1994). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implication for risk assessment. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 24(2), 87–149.
Sheehan, D., Meade, G., Foley, V. M., & Dowd, C. A. (2001). Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochemical Journal, 360, 1–16.
Shore, R., Casulli, A., Bologov, V., Wienburg, C., Afsar, A., Toyne, P., et al. (2001). Organochlorine pesticide, polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metal concetrations in wolves (Canis lapus L.) from north-west Russia. The Science of the Total Environment, 280(1–3), 45–54.
Smith, A. G. (1991). Chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides. In W. J. Hayes Jr. & E. R. Laws Jr. (Eds.), Handbook of pesticide toxicology. Volume 2, Classes of pesticides (pp. 731–916). Toronto: Academic.
Struciński, P. (2009). 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane. Podstawy i Metody Oceny Środowiska Pracy, 3(61), 75–126.
Suutari, A., Ruokojärvi, P., Hallikainen, A., & Laaksonen, S. (2009). Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and polychlorinated biphenyls in semi-domesticated reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) and wild moose (Alces alces) meat in Finland. Chemosphere, 75(5), 617–622.
Suutari, A., Hallikainen, A., Ruokojärvi, P., Kiviranta, H., Nieminen, M., & Laaksonen, S. (2012). Persistent organic pollutants in Finnish reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus L.) and moose (Alces alces). Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 54(1), 11.
Tian, X., Song, E., Pi, R., Zhu, R., Liu, L., Ma, X., et al. (2012). Polychlorinated biphenyls and their different level metabolites as inhibitors of glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 198(1–3), 1–8.
Tomza, A., Witczak, A., & Ciereszko, W. (2006). Uptake of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in freshwater mussels Anodonta complanata from the lower Odra River. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 15(4), 603–608.
Tomza-Marciniak, A. (2013). Residues of organochlorine pesticides and PCBs in wild boars from an area which once contained a landfill of obsolete pesticides and other chemicals. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin (in press).
Tomza-Marciniak, A., & Witczak, A. (2010). Distribution of endocrine-disrupting pesticides in water and fish from the Oder River, Poland. Acta Ichthyologica et Piscatoria, 40(1), 1–9.
Tomza-Marciniak, A., Pilarczyk, B., Wieczorek-Dąbrowska, M., Bąkowska, M., Witczak, A., & Hendzel, D. (2011). Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) residues in European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) and red deer (Cervus elaphus) from north-western Poland. Chemistry and Ecology, 27(6), 493–501.
Tomza-Marciniak, A., Pilarczyk, B., Bąkowska, M., Tylkowska, A., Marciniak, A., Ligocki, M., et al. (2012). Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs) residues in suburban red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from West Pomerania region (Poland)—preliminary study. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 24(1), 193–199.
Turrio-Baldassarri, L., Alivernini, S., Carasi, S., Casella, M., Fuselli, S., Iacovella, N., et al. (2009). PCB, PCDD and PCDF contamination of food of animal origin as the effect of soil pollution and the cause of human exposure in Brescia. Chemosphere, 76(2), 278–285.
van den Berg, M., Birnbaum, L. S., Denison, M., De Vito, M., Farland, W. F. M., Fiedler, H., et al. (2006). The 2005 World Health Organization revaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicological Science, 93, 223–241.
Wania, F., & Mackay, D. (1996). Tracking the distribution of persistent organic pollutants. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 390–396.
WHO. (1992). Endrin (Environmental Health Criteria 130). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Witczak, A., & Abdel-Gawad, H. (2012). Comparison of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls residues in vegetables, grain and soil from organic and conventional farming in Poland. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B-Pesticides Food Contaminants and Agricultural Wastes, 47(4), 343–354.
Zasadowski, A., Wyszyńska, A., & Wysoki, A. (2003). Evaluation of the contamination degree of roe-deer with cadmium and polychlorinated biphenyls in Warmia and Mazury district. Polish Journal of Veterinary Science, 6, 93–97.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Ms Diana Hendzel for help in obtaining material for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomza-Marciniak, A., Marciniak, A., Pilarczyk, B. et al. Wild boar (Sus scrofa) as a bioindicator of organochlorine compound contamination in terrestrial ecosystems of West Pomerania Province, NW Poland. Environ Monit Assess 186, 229–238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3368-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3368-z