Abstract
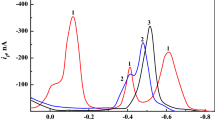
A new electrochemical adsorptive stripping voltammetry method was developed for the determination of trace amounts of copper in food and water samples. The study of electrochemical behavior of Cu ion indicated that Cu(II) and Schiff base formed a complex in H3BO4–NaOH buffer solution (pH = 7.25). An accumulation potential of −100 mV (vs Ag/AgCl) was applied while the solution was stirred for 60 s. The response curve was recorded by scanning the potential, and the peak current of −0.31 V (vs Ag/AgCl) was recorded. The peak current and concentration of copper accorded with linear relationship in the range of 0.04–120 ng mL−1. The relative standard deviation (for 12 ng mL−1 of copper) was 1.73 %, and the detection limit was 0.007 ng mL−1. The possible interference of some common ions was studied. The proposed method was applied to the determination of copper in water, rice, wheat, tea, milk, and tomato with satisfactory results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, S., Bahiraei, A., & Farmany, A. (2010a). Quantification of sub-nanomolar levels of aluminum by adsorptive stripping voltammetry using rubeanic acid as a selective chelating agent. Electroanalysis, 22, 1889–1893.
Abbasi, S., Farmany, A., Gholivand, M. B., Naghipour, A., Abbasi, F., & Khani, H. (2009). Kinetic-spectrophotometry method for determination of ultra trace amounts of aluminum in food samples. Food Chemistry, 116, 1019–1023.
Abbasi, S., Khodarahmian, K., & Farmany, A. (2012). Quantification of sub-nanomolar levels of penicillin G by differential pulse adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Drug Testing and Analysis, 4(2), 140–4.
Abbasi, S., Farmany, A., & Mortazavi, S. S. (2010b). Ultrasensitive simultaneous quantification of nanomolar level of Cd and Zn by cathodic adsorptive stripping voltammetry in some real samples. Electroanalysis, 22, 2884–2888.
Abbasi, S., Khodarahmian, K., & Farmany, A. (2011). Ultra sensitive quantification of thiourea at nanomolar level by catalytic-kinetic differential pulse voltammetry. Electroanalysis, 23, 2386–2391.
Anzano, J. M., & Gonzalez, P. (2000). Determination of ion and copper in peanuts by flame atomic absorption spectrometry using acid digestion. Microchemical Journal, 64(2), 141–145.
Bella, S. D., & Fragalà, I. (2002). Two-dimensional characteristics of the second-order nonlinear optical response in dipolar donor–acceptor coordination complexes. New Journal of Chemistry, 26, 285.
Bella, S. D. (2001). Second-order nonlinear optical properties of transition metal complexes. Chemical Society Reviews, 30, 355.
Keypour, H., Prichard, R. G., & Parish, R. V. (1997). Isolation of ternary complex precursors and partially condensed intermediates to macrocyclic complexes of nickel(II) and copper(II). Transition Metal Chemistry, 23, 609–614.
Korupoju, S. R., Mangayarkarasi, N., Ameerunisha, S., Valente, E. J., & Zacharias, P. S. (2000). Formation of dinuclear macrocyclic and mononuclear cyclic complexes of a new trinuclear hexaazatriphenolic Schiff base macrocycle: structure and NLO properties. Journal of the Chemical Society Dalton Transactions, 2000, 2845.
Mikuła, B., & Puzio, B. (2007). determination of trace metals by ICP-OES in plant materials after preconcentration of 1,10-phenanthroline complexes on activated carbon. Talanta, 71, 136–140.
Rezaei, B., Sadeghi, E., & Meghdadi, S. (2009). Nano-level determination of copper with atomic absorption spectrometry after pre-concentration on N, N-(4-methyl-1,2-phenylene)diquinoline-2-carboxamide–naphthalene. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 787–792.
Tobiasz, A., Walas, S., Trzewik, B., Grzybek, P., Zaitz, M. M., Gawin, M., & Mrowiec, H. (2009). Cu(II)-imprinted styrene-divinylbenzene beads as a new sorbent for flow injection-flame atomic absorption determination of copper. Microchemical Journal, 93, 87–92.
WHO (2003). Copper in drinking water. Background document for preparation of WHO guidelines for drinking water quality. Geneva, (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/88)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support to this research, which was provided by Ilam University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goudarziafshar, H., Nikoorazm, M., Mortazavi, S.S. et al. Ultra-sensitive quantification of copper in food and water samples by electrochemical adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Environ Monit Assess 185, 8823–8829 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3215-2