Abstract
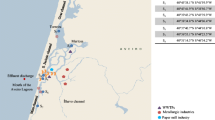
In spite of its outstanding ecological and touristic importance the Ria Formosa Lagoon shows signs of anthropogenic pollution. Nonetheless, until the present survey no studies had ever documented the measurement of natural and pharmaceutical estrogens (17β-estradiol, estrone, and 17α-ethynylestradiol), xenoestrogenic industrial pollutants (4-octylphenol, 4-nonylphenol, and their mono and diethoxylates and bisphenol A), phytoestrogens (formononetin, biochanin A, daidzein, genistein), and sitosterol in this area. The 17 compounds measured herein are known as endocrine disrupters (EDCs) and act over the endocrine system even in few amounts (ng L−1–μg L−1). Thus to conclude about the influx of EDCs in the lagoon, water samples were taken every 2 months, during 1 year (2010), in low tide at nine sites distributed along the coastline. Water samples (1 L) were preconcentrated in the Oasis HLB cartridges and cleaned in silica cartridges before their analysis by GC-MS. Data showed the ubiquitous presence of potentially hazardous amounts of estrogens (particularly of ethynylestradiol, up to 24.3 ng L−1), nonylphenol (up to 547 ng L−1), and sitosterol (up to 12,300 ng L−1), mainly in summer, suggesting that the increase of the local number of inhabitants (tourists), the rise of the water temperature (up to 26 °C), and the blooming of local flora may interfere with the water quality parameters. This makes the lagoon a potential model to study. Taking into account the data, it was concluded that there are conditions for the occurrence of endocrine disruption in aquatic animals, even in areas included in the natural park of the Formosa. Besides, both the high amounts of un-ionized ammonia (up to 0.3 mg L−1) and phosphates (up to 1.6 mg L−1) my pose risks for local fauna and humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newton, A., & Mudge, S. M. (2003). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 57, 73–85.
Calixto, V. F. C., Alves, J., Botelho J. (2011). In Boletim Informativo - Newsletter, ed. Sociedade Polis Litoral Ria Formosa (info@polislitoralriaformosa.pt), Olhão, Portugal, pp. 1–12.
Ferreira, J. G., Simas, T., Nobre, A., Silva, M. C., Shifferegger, K., Lencart-Silva, J. (2003). In Identification of sensitive areas and vulnerable zones in transitional and coastal Portuguese systems. Application of the United States National estuarine eutrophication assessment to the Minho, Lima, Douro, Ria de Aveiro, Mondego, Tagus, Sado, Mira, Ria Formosa and Guadiana systems, ed. INAG and IMAR, pp. 1–151.
Bebianno, M. J., & Barreira, L. A. (2009). Ecotoxicol and Environmental Safety, 72, 1849–1860.
Carvalho, P. N., Rodrigues, P. N. R., Basto, M. C. P., & Vasconcelos, M. (2009). Chemosphere, 75, 595–600.
Vasconcelos, P., Gaspar, M. B., & Barroso, C. M. (2010). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 12, 1823–1832.
David, A., Fenet, H., & Gomez, E. (2009). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 953–960.
Bebianno, M. J., Géret, F., Hoarau, P., Serafim, M. A., Coelho, M. R., Gnassia-Barelli, M., et al. (2004). Biomarkers: Biochemical indicators of exposure, response, and susceptibility to chemicals, 9, 305–330.
Dionisio, L. P. C., Rheinheimer, G., & Borrego, J. J. (2000). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 186–193.
Gamito, S. (2008). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 77, 710–720.
Mudge, S. M., Bebianno, M. J. A. F., East, J. A., & Barreira, L. A. (1999). Water Research, 33, 1038–1048.
Newton, A., & Mudge, S. M. (2005). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 62, 405–414.
Newton, A., Oliveira, P. S., Icely, J. D., & Foster, P. A. (2010). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 12, 355–360.
Hoerger, C. C., Wettstein, F. E., Hungerbuhler, K., & Bucheli, T. D. (2009). Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 6151–6157.
Clotfelter, E. D., McNitt, M. M., Carpenter, R. E., & Summers, C. H. (2010). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry, 36, 933–943.
Rocha, M. J., Ribeiro, C., & Ribeiro, M. (2011). International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 91, 1191–1205.
Duarte, P., Azevedo, B., Guerreiro, M., Ribeiro, C., Bandeira, R., Pereira, A., et al. (2008). Hydrobiologia, 611, 115–132.
Ribeiro, C., Tiritan, M. E., Rocha, E., & Rocha, M. J. (2007). Journal of Liquid Chromatography and Related Technologies, 30, 2729–2746.
StatSoft I.(2007). In Book STATISTICA (data analysis software system).
Hopkins, F. E., & Mudge, S. M. (2004). Environmental Forensics, 5, 213–223.
Mudge, S. M., & Bebianno, M. J. (1997). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34, 163–170.
Mes, T., Zeeman, G., & Lettinga, G. (2005). Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 4, 275–311.
Jobling, S., & Tyler, C. R. (2003). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 75, 2219–2234.
Gomes, T., Gonzalez-Rey, M., & Bebianno, M. J. (2009). Ecotoxicology, 18, 1104–1109.
Safe, S. H. (2000). Environmental Health Perspectives, 108, 487–493.
Zoller, U. (2006). Environmental International, 32, 269–272.
D. 2003/53/EC (2003). In Book of the amending for the 26th time Council Directive 76/769/EEC relating to restrictions on the marketing and use of certain dangerous substances and preparations (nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylate and cement),ed. Official Journal of the European Union, pp. L178/24-L178/27.
Maria, V. L., Santos, M. A., & Bebianno, M. J. (2009). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Toxicology & Pharmacology, 150, 196–208.
Serpa, D., Jesus, D., Falcão, M., Cancela da Fonseca, L.(2005). In Ria Formosa ecosystem: socio-economic approach., ed. IPIMAR, (http://ipimar-iniap.ipimar.pt), 28, pp. 1–50.
Rocha, M. J., Cruzeiro, C., Ferreira, C., & Rocha, E. (2012a). Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 94(2), 252–261.
Rocha, M. J., Ribeiro, R., Ribeiro, C., Couto, C., & Rocha, E. (2012b). Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 94(2), 262–274.
Arditsoglou, A., & Voutsa, D. (2008). Environmental Pollution, 156, 316–324.
Soares, A., Guieysse, B., Jefferson, B., Cartmell, E., & Lester, J. N. (2008). Environmental International, 34, 1033–1049.
Erickson, B. E. (2002). Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 140–145.
Azevedo, D., Lacorte, S., Viana, P., & Barceló, D. (2000). Chromatographia, 53, 113–118.
Quirós, L., Céspedes, R., Lacorte, S., Viana, P., Raldúa, D., Barcelò, D., et al. (2005). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 389–395.
Céspedes, R., Lacorte, S., Raldúa, D., Ginebreda, A., Barceló, D., & Piña, B. (2005). Chemosphere, 61, 1710–1719.
Vethaak, A. D., Lahr, J., Kuiper, R. V., Grinwis, G. C. M., Rankouhi, T. R., Giesy, J. P., et al. (2002). Toxicology, 181, 147–150.
Crain, D. A., Eriksen, M., Iguchi, T., Jobling, S., Laufer, H., LeBlanc, G. A., et al. (2007). Reproductive Toxicology, 24, 225–239.
Benassayag, C., Perrot-Applanat, M., & Ferre, F. (2002). Journal of Chromatography B, 777, 233–248.
Guimaraes, M., Cunha, A. H., Nzinga, R. L., & Marques, J. F. (2012). Journal for Nature Conservation, 20, 30–40.
Mackova, Z., Koblovska, R., & Lapcik, O. (2006). Phytochemistry, 67, 849–855.
Kiparissis, Y., Gordon, C. B., Metcalfe, T. L., & Metcalfe, C. D. (2003). Environmental Health Perspectives, 111, 1158–1163.
Kime, D. E. (1998). In Endocrine disruption in fish, ed. Springer, City.
Volkman, J. K., Revill, A. T., Holdsworth, D. G., & Fredericks, D. (2008). Organic Geochemistry, 39, 689–710.
Falcão, M., Fonseca, L., Serpa, D., Matias, D., Joaquim, S. (2003). In Development of an information technology tool for the management of European southern lagoons under the influence of river-basin runoff. Synthesis Report Ria Formosa, ed. INIAP/IPIMAR - National Research Institute for Fisheries and Sea City, pp. 1–38.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by FEDER funds through the Competitiveness and Trade Expansion Program—COMPETE and by National Funds provided by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), via the project PTDC/MAR/70436/2006. Acknowledgements are also due to the Administração da Região Hidrográfica do Algarve I.P (AHR-Algarve, Portugal) that provided us important technical information about the Ria Formosa Lagoon and to Francisco Arenas Parra and Carolina Caldas for their help in statistics and water processing, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, M.J., Cruzeiro, C., Reis, M. et al. Determination of seventeen endocrine disruptor compounds and their spatial and seasonal distribution in Ria Formosa Lagoon (Portugal). Environ Monit Assess 185, 8215–8226 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3168-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3168-5