Abstract
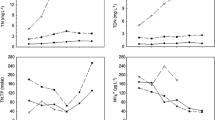
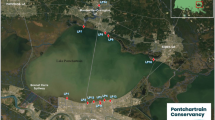
The increasing incidence of toxic cyanobacterial blooms, together with the difficulties to reliably predict cyanobacterial toxin (e.g. microcystins) concentration, has created the need to assess the predictive ability and variability of the cyanobacterial biomass–microcystin relationship, which is currently used to assess the risk to human and ecosystems health. To achieve this aim, we assessed the relationship between cyanobacterial biomass and microcystin concentration on a spatiotemporal scale by quantifying the concentration of cyanobacterial biomass and microcystin in eight lakes over 9 months. On both a temporal and spatial scale, the variability of microcystin concentration exceeded that of cyanobacterial biomass by up to four times. The relationship between cyanobacterial biomass and microcystin was weak and site specific. The variability of cyanobacterial biomass only explained 25 % of the variability in total microcystin concentration and 7 % of the variability of cellular microcystin concentration. Although a significant correlation does not always imply real cause, the results of multiple linear regression analysis suggest that the variability of cyanobacterial biomass and cellular microcystin concentration is influenced by salinity and total phosphorus, respectively. The weak cyanobacterial biomass–microcystin relationship, coupled with the fact that microcystin was present in concentrations exceeding the WHO drinking water guidelines (1 μg L−1) in most of the collected samples, emphasizes the high risk of error connected to the traditional indirect microcystin risk assessment method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shehri, A. M. (2010). Toxin-producing blooms of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa in rainwater ponds in Saudi Arabia. Oceanological and Hydrobiological Studies, 39(4), 171–187.
ANZECC (2000). Australian and New Zealand guideline for fresh and marine water quality. Canberra: ANZECC
Baldia, S. F., Conaco, M. C. G., Nishijima, T., Imanishi, S., & Harada, K. (2003). Microcystin production during algal bloom occurrence in Laguna de Bay, the Philippines. Fisheries Science, 69(1), 110–116.
Ballot, A., Pflugmacher, S., Wiegand, C., Kotut, K., & Krienitz, L. (2003). Cyanobacterial toxins in Lake Baringo, Kenya. Limnologica—Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 33(1), 2–9.
Barrington, D. J., & Ghadouani, A. (2008). Application of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of toxic cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton from wastewater. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(23), 8916–8921.
Barrington, D. J., Ivey, G. N., & Ghadouani, A. (2011). Environmental factors and the application of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of toxic cyanobacteria from waste stabilization ponds. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 137(10).
Beutler, M., Wiltshire, K. H., Meyer, B., Moldaenke, C., Luring, C., Meyerhofer, M., et al. (2002). A fluorometric method for the differentiation of algal populations in vivo and in situ. Photosynthesis Research, 72(1), 39–53.
Briand, E., Gugger, M., Francois, J. C., Bernard, C., Humbert, J. F., & Quiblier, C. (2008). Temporal variations in the dynamics of potentially microcystin-producing strains in a bloom-forming Planktothrix agardhii (cyanobacterium) population. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(12), 3839–3848.
Briand, J. F., Jacquet, S., Flinois, C., Avois-Jacquet, C., Maisonnette, C., Leberre, B., et al. (2005). Variations in the microcystin production of Planktothrix rubescens (Cyanobacteria) assessed from a four-year survey of Lac du Bourget (France) and from laboratory experiments. Microbial Ecology, 50(3), 418–428.
Carmichael, W. W., Azevedo, S. M. F. O., An, J. S., Molica, R. J. R., Jochimsen, E. M., Lau, S., et al. (2001). Human fatalities from cyanobacteria: chemical and biological evidence for cyanotoxins. Environmental and Health Perspective, 109(7), 663–668.
Carrasco, D., Moreno, E., Sanchis, D., Wormer, L., Paniagua, T., Cueto, A. D., et al. (2006). Cyanobacterial abundance and microcystin occurrence in Mediterranean water reservoirs in Central Spain: microcystins in the Madrid area. Journal of Phycology, 41(3), 281–291.
Chen, J., Han, F., Wang, F., Zhang, H. M., & Shi, Z. (2012). Accumulation and phytotoxicity of microcystin–LR in rice (Oryza sativa). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 76(2), 193–199.
Chen, J., Xie, P., Li, L., & Xu, J. (2009). First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicological Sciences, 108(1), 81–89.
Chorus, I., & Bartram, J. (1999). Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. London: E & FN Spon.
Clesceri, L. S., Greenberg, A. E., & Eaton, A. D. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th Ed. Washington, DC: American Public Health Association
Davis, J. A., Rosich, R. S., Bradley, J. S., Growns, J. E., Schmidt, L. G., & Cheal, F. (1993). Wetland classification on the basis of water quality and invertebrate community data. Wetlands of the Swan Coastal Plain, 6, 242. Water Authority of Western Australia.
Davis, T. W., Berry, D. L., Boyer, G. L., & Gobler, C. J. (2009). The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae, 8(5), 715–725.
Dignum, M., Matthijs, H. C. P., Pel, R., Laanbroek, H. J., Mur, L. R., et al. (2005). Nutrient limitation of freshwater cyanobacteria—tools to monitor phosphorus limitation at the individual level. In J. Huisman, H. C. P. Matthijs, & P. M. Visser (Eds.), Harmful cyanobacteria. the Netherlands: Springer.
Eisentraeger, A., Dott, W., Klein, J., & Hahn, S. (2003). Comparative studies on algal toxicity testing using fluorometric microplate and Erlenmeyer flask growth-inhibition assays. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 54(3), 346–354.
Frank, C. A. P. (2002). Microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in recreational waters in southwestern Germany. Environmental Toxicology, 17(4), 361–366.
Geis, S. W., Fleming, K. L., Korthals, E. T., Searle, G., Reynolds, L., & Karner, D. A. (2000). Modifications to the algal growth inhibition test for use as a regulatory assay. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 19(1), 36–41.
Ghadouani, A., & Coggins, L. X. (2011). Science, technology and policy for water pollution control at the watershed scale: current issues and future challenges. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 36(9–11), 335–341.
Ghadouani, A., Pinel-Alloul, B., Plath, K., Codd, G. A., & Lampert, W. (2004). Effects of Microcystis aeruginosa and purified microcystin–LR on the feeding behavior of Daphnia pulicaria. Limnology and Oceanography, 49(3), 666–679.
Ghadouani, A., Pinel-Alloul, B., & Prepas, E. E. (2003). Effects of experimentally induced cyanobacterial blooms on crustacean zooplankton communities. Freshwater Biology, 48(2), 363–381.
Ghadouani, A., Pinel-Alloul, B., & Prepas, E. E. (2006). Could increased cyanobacterial biomass following forest harvesting cause a reduction in zooplankton body size structure? Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 63, 2308–2317.
Ghadouani, A., & Smith, R. E. H. (2005). Phytoplankton distribution in Lake Erie as assessed by a new in situ spectrofluorometric technique. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 31(Supplement 2), 154–167.
Graham, J. L., Jones, J. R., Jones, S. B., Downing, J. A., & Clevenger, T. E. (2004). Environmental factors influencing microcystin distribution and concentration in the Midwestern United States. Water Research, 38(20), 4395–4404.
Ha, J. H., Hidaka, T., & Tsuno, H. (2011). Analysis of factors affecting the ratio of microcystin to chlorophyll-a in cyanobacterial blooms using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Environmental Toxicology, 26(1), 21–28.
Halstvedt, C. (2008). On the effect of abiotic environmental factors on production of bioactive oligopeptides in field populations of Planktothrix spp. (Cyanobacteria). Journal of Plankton Research, 30(5), 607–617.
Harada, K., Kondo, F., & Lawton, L. A. (1999). Laboratory analysis of cyanotoxins. In I. Chorus & J. Bartram (Eds.), Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management (pp. 363–367). London: E & FN Spon on behalf of the World Health Organization.
Havens, K. E. (2007). Chapter 33: Cyanobacteria blooms—effects on aquatic ecosystems. In: Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: state of the science and research needs (Vol. 619, pp. 733–747). New York: Springer.
HC (2010). Guidelines for Canadian drinking water quality: summary table. Ottawa: Health Canada.
Hillebrand, H., Durselen, C., Kirschtel, D., Pollingher, U., & Zohary, T. (1999). Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology, 35(2), 403–424.
Hobson, P., & Fallowfield, H. (2003). Effect of irradiance, temperature and salinity on growth and toxin production by Nodularia spumigena. Hydrobiologia, 493(1–3), 7–15.
Hotto, A. M., Satchwell, M. F., Berry, D. L., Gobler, C. J., & Boyer, G. L. (2008). Spatial and temporal diversity of microcystins and microcystin-producing genotypes in Oneida Lake, NY. Harmful Algae, 7(5), 671–681.
ISO (2005). Determination of microcystins: method using solid phase extraction (SPE) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet (UV) detection. Geneva: ISO
Izydorczyk, K., Jurczak, T., Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A., Skowron, A., Mankiewicz-Boczek, J., & Tarczynska, M. (2008). Influence of abiotic and biotic factors on microcystin content in Microcystis aeruginosa cells in a eutrophic temperate reservoir. Journal of Plankton Research, 30(4), 393–400.
Jayatissa, L. P., Silva, E. I. L., McElhiney, J., & Lawton, L. A. (2006). Occurrence of toxigenic cyanobacterial blooms in freshwaters of Sri Lanka. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 29(2), 156–164.
Jean, M. J., Diane, C. C., Eugene, B. W., Hardy, F. J., & Michele, C. (2000). Environmental factors associated with a toxic bloom of Microcystis aeruginosa. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(1), 231–240.
Joung, S.-H., Oh, H.-M., Ko, S.-R., & Ahn, C.-Y. (2010). Correlations between environmental factors and toxic and non-toxic Microcystis dynamics during bloom in Daechung Reservoir, Korea. Harmful Algae, 10(2), 188–193.
Kann, J., & Smith, V. H. (1999). Estimating the probability of exceeding elevated pH values critical to fish populations in a hypereutrophic lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 56(12), 2262–2270.
Kardinaal, W. E. A., & Visser, P. M. (2005). Dynamics of cyanobacterial toxins—sources of variability in microcystin concentration. In J. Huisman, H. C. P. Matthijs, & P. M. Visser (Eds.), Harmful cyanobacteria (pp. 41–63). the Netherlands: Springer.
Kemp, A. S. (2009). Freshwater cyanoprokaryota blooms in the Swan Coastal Plain wetlands: ecology, taxonomy and toxicology. Ph.D. thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Perth.
Komarek, J., & Hauer, T. (2011). CyanoDB.cz on-line database of cyanobacterial genera. Univ. of South Bohemia & Inst. of Botany AS CR. http://www.cyanodb.cz.
Kotak, B. G., Lam, A., Prepas, E. E., & Hrudey, S. E. (2000). Role of chemical and physical variables in regulating microcystin–LR concentration in phytoplankton of eutrophic lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(8), 1584–1593.
Kotut, K., Ballot, A., Wiegand, C., & Krienitz, L. (2010). Toxic cyanobacteria at Nakuru sewage oxidation ponds—a potential threat to wildlife. Limnologica, 40(1), 47–53.
Lawton, L. A., Edwards, C., & Codd, G. A. (1994). Extraction and high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of microcystins in raw and treated waters. Analyst, 119(7), 1525–1530.
Liu, Y. M., Chen, W., Li, D. H., Huang, Z. B., Shen, Y. W., & Liu, Y. D. (2011). Cyanobacteria–cyanotoxin-contaminations and eutrophication status before Wuxi Drinking Water Crisis in Lake Taihu, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 23(4), 575–581.
Maske, S., Sangolkar, L., & Chakrabarti, T. (2010). Temporal variation in density and diversity of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in lakes at Nagpur (Maharashtra State), India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 169(1–4), 299–308.
Meriluoto, J., & Codd, G. (2005). Toxic—cyanobacterial monitoring and cyanotoxin analysis (Vol. 65, Acta Academiae Aboensis Ser. B, Mathematica et physica). Åbo: Åbo Akademi University Press.
Mooney, K., Floyd, S., Foy, R., & Elliott, C. (2011). Initial studies on the occurrence of cyanobacteria and microcystins in Irish lakes. Environmental Toxicology, 26(5), 566–570.
Naselli-Flores, L., Barone, R., Chorus, I., & Kurmayer, R. (2007). Toxic cyanobacterial blooms in reservoirs under a semiarid Mediterranean climate: the magnification of a problem. Environmental Toxicology, 22(4), 399–404.
Nasri, H., Bouaicha, N., & Harche, M. K. (2007). A new morphospecies of Microcystis sp forming bloom in the Cheffia dam (Algeria): seasonal variation of microcystin concentrations in raw water and their removal in a full-scale treatment plant. Environmental Toxicology, 22(4), 347–356.
NHMRC (2011). National water quality management strategy: Australian drinking water guidelines 6. (Vol. 1). Canberra: National Health and Medical Research Council.
Okello, W., Portmann, C., Erhard, M., Gademann, K., & Kurmayer, R. (2010). Occurrence of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in Ugandan freshwater habitats. Environmental Toxicology, 25(4), 367–380.
Orr, P. T., & Jones, G. J. (1998). Relationship between microcystin production and cell division rates in nitrogen-limited Microcystis aeruginosa cultures. Limnology and Oceanography, 43(7), 1604–1614.
Orr, P. T., Jones, G. J., & Douglas, G. B. (2004). Response of cultured Microcystis aeruginosa from the Swan River, Australia, to elevated salt concentration and consequences for bloom and toxin management in estuaries. Marine and Freshwater Research, 55(3), 277–283.
Palikova, M., Mares, J., Kopp, R., Hlavkova, J., Navratil, S., Adamovsky, O., et al. (2011). Accumulation of microcystins in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L., and effects of a complex cyanobacterial bloom on the dietetic quality of muscles. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87(1), 26–30.
Pavlova, V., Babica, P., Todorova, D., Bratanova, Z., & Maršálek, B. (2006). Contamination of some reservoirs and lakes in Republic of Bulgaria by microcystins. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 34(5), 437–441.
Reichwaldt, E. S., & Ghadouani, A. (2012). Effects of rainfall patterns on toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a changing climate: between simplistic scenarios and complex dynamics. Water Research, 46(5), 1372–1393.
Rinta-Kanto, J. M., Konopko, E. A., DeBruyn, J. M., Bourbonniere, R. A., Boyer, G. L., & Wilhelm, S. W. (2009). Lake Erie Microcystis: relationship between microcystin production, dynamics of genotypes and environmental parameters in a large lake. Harmful Algae, 8(5), 665–673.
Sabart, M., Pobel, D., Briand, E., Combourieu, B., Salencon, M. J., Humbert, J. F., et al. (2010). Spatiotemporal variations in microcystin concentrations and in the proportions of microcystin-producing cells in several Microcystis aeruginosa populations. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76(14), 4750–4759.
Srivastava, A., Choi, G.-G., Ahn, C.-Y., Oh, H.-M., Ravi, A., & Asthana, R. (2012). Dynamics of microcystin production and quantification of potentially toxigenic Microcystis sp. using real-time PCR. Water Research, 46(3), 817–827.
Tonk, L. L., Bosch, L. K., Visser, L. P., & Huisman, L. J. (2007). Salt tolerance of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 46(2), 117–123.
Utermöhl, H. (1958). Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Mitt. int. Verein. theor. angew. Limnology, 9, 1–38.
Vasconcelos, V., Martins, A., Vale, M., Antunes, A., Azevedo, J., Welker, M., et al. (2011). First report on the occurrence of microcystins in planktonic cyanobacteria from Central Mexico. Toxicon, 56(3), 425–431.
Vezie, C., Rapala, J., Vaitomaa, J., Seitsonen, J., & Sivonen, K. (2002). Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth of toxic and nontoxic Microcystis strains and on intracellular microcystin concentrations. Microbial Ecology, 43(4), 443–454.
Watzin, M. C., Miller, E. B., Shambaugh, A. D., & Kreider, M. A. (2006). Application of the WHO alert level framework to cyanobacterial monitoring of Lake Champlain, Vermont. Environmental Toxicology, 21(3), 278–288.
WHO (1998). Cyanobacterial toxins: microcystin–LR. In: Guidelines for drinking water quality. (2nd Ed., Vol. 2, pp. 95–110). Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2003). Algae and cyanobacteria in freshwater: guidelines for safe recreational water environments (pp. 136–154). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wilhelm, S. W., Farnsley, S. E., LeCleir, G. R., Layton, A. C., Satchwell, M. F., DeBruyn, J. M., et al. (2011). The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae, 10(2), 207–215.
Wu, S., Wang, S., Yang, H., Xie, P., Ni, L., & Xu, J. (2008). Field studies on the environmental factors in controlling microcystin production in the subtropical shallow lakes of the Yangtze River. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(4), 329–334.
Wu, S. K., Xie, P., Liang, G. D., Wang, S. B., & Liang, X. M. (2006). Relationships between microcystins and environmental parameters in 30 subtropical shallow lakes along the Yangtze River, China. Freshwater Biology, 51(12), 2309–2319.
Yang, H., Xie, P., Xu, J., Zheng, L., Deng, D., Zhou, Q., et al. (2006). Seasonal variation of microcystin concentration in Lake Chaohu, a shallow subtropical lake in the People's Republic of China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 77(3), 367–374.
Znachor, P. P., Jurczak, P. T., Komarkova, P. J., Jezberova, P. J., Mankiewicz, P. J., Kastovska, P. K., et al. (2006). Summer changes in cyanobacterial bloom composition and microcystin concentration in eutrophic Czech reservoirs. Environmental Toxicology, 21(3), 236–243.
Zurawell, R. W., Chen, H. R., Burke, J. M., & Prepas, E. E. (2005). Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. Part B, Critical Reviews, 8(1), 1–37.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Australian Research Council’s Linkage Project funding scheme (LP0776571) and the Water Corporation of Western Australia. We wish to thank Matthew Timmins and Ricarda Fenske from Metabolomics Australia at The University of Western Australia for their assistance in the operation of LC-MS, Professor Pierre Legendre and Laura Firth for their valuable statistical advice and Liah Coggins for her help in the editing of the manuscript. During the study, S.C. Sinang was supported by a scholarship from Sultan Idris Education University (UPSI) and Malaysia Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinang, S.C., Reichwaldt, E.S. & Ghadouani, A. Spatial and temporal variability in the relationship between cyanobacterial biomass and microcystins. Environ Monit Assess 185, 6379–6395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3031-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3031-0