Abstract
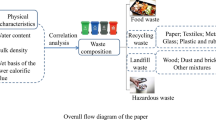
This paper provides a comprehensive characterization of mineral waste such as fly ash, bottom ash, slag and construction demolition (C&D) collected from four different thermal power plants, three steel plants and three C&D waste generation sites in India. To determine utilisation potential and environmental concerns, as received fly ash, bottom ash, slag and C&D waste were analysed for physico-chemical, mineralogical and morphological properties. The physico-chemical properties analysed include pH, moisture content, acid insoluble residue, loss on ignition(LOI), carbon content, fineness, chloride content, sulphate content, reactive silica content, XRF and heavy metal analysis. Morphological and mineralogical characteristics were investigated using scanning electron microscopy–energy dispersive X-ray. Particle size distribution was obtained using particle size analyser. The material analysed has different compositions and were selected with a view to determine their suitability for different applications in cement and concrete industry and for further research studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antiohos, S., & Tsimas, S. (2006) Reactive silica of fly ash as an indicator for the mechanical performance of blended cements. Measuring, monitoring and modeling concrete properties. Part 4, pp. 403–409.
Bangur, H. M. (2009). Cement industry needs policy on fly ash, June 1. http://www.projectsmonitor.com/OPED/cement-industry-needs-policy-on-fly-ash, Accessed 2 Feb 2010.
Bhattacharjee, U., & Kandpal, T. C. (2002). Potential of fly ash utilisation in India. Energy, 27, 151–166.
Bolwerk, R. (2004). Co-processing of waste and energy efficiency by cement plants. Vienna: IPPC Conference.
Das, B., Prakash, S., Reddy, P. S. R., & Misra, V. N. (2007). An overview of utilization of slag and sludge from steel industries. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 50(1), 40–57.
Farag, L. M., & Abbas, M. (1995). Practical limits for chorine cycles in dry process cement plants with precalcining and tertiary air ducting. Zement Kalk Gips, 48(1), 22–26.
Glasser, F. P., Kindness, A., & Stronach, S. A. (1999). Stability and solubility relationships in AFM phases: part I. Chloride, sulfate, and hydroxide. Cement and Concrete Research, 29(6), 861–866.
Hower, J. C., Mastalerz, M., Drobniak, A., Mardon, S., & Lis, G. (2011) Chemical properties and petrographic composition of coal and fly ash. Indiana Geological Survey, Indian University.
Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM) (2008, 2009). http://ibm.nic.in/slagironandsteel.pdf. Accessed 2 January, 2012.
Katyal, N. K. (2008). Development of rapid method for the estimation of reactive silica in fly ash. Cement and Concrete Research, 38(1), 104–106.
Lankford, W. T., Samways, J. N. L., Craven, R. F., & McGannon, H. E. (1985). The making, shaping and treating of steel (10th ed., p. 1572). Pittsburgh: United States Steel Corporation.
Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF), Report of the Committee to Evolve Road Map on Management of Wastes in India, New Delhi, March, 2010. http://moef.nic.in/downloads/public-information/Roadmap-Mgmt-Waste.pdf.
Norton, G. A., Markuszewski, R., & Shanks, H. R. (1986). Morphological and chemical characterization of iron-rich fly ash fractions. Environmental Science and Technology, 20(4), 409–413.
Pappu, A., Saxena, M., & Asolekar, S. R. (2007). Solid wastes generation in India and their recycling potential in building materials. Building and Environment, 42, 2311–2320.
Paya, J., Monzo, J., Peris-Mora, E., Borrachero, M. V., Tercero, R., & Pinillos, C. (1995). Early-strength development of Portland cement mortars containing air classified fly ash. Cement and Concrete Research, 25(6), 449–456.
Prasad B., & Mondal K. (2008). Trace metals leaching in Indian Fly ash. Journal of Environmental science & Engineering, 50(2), 127–132.
Sarkar, A., Rano, R., Udaybhanu, G., & Basu, A. K. (2006). A comprehensive characterisation of fly ash from a thermal power plant in Eastern India. Fuel Processing Technology, 87, 259–277.
Singh, S. P., Tripathy D. P., & Ranjit P. G. (2008). Performance evaluation of cement stabilized fly ash-GBFS mixes as a highway construction material. Waste management, 28, 1331–1337.
Sushil S., & Batra V. S. (2006). Analysis of fly ash trace metal content and disposal in three thermal power plants in India. Fuel, 85, 2676–2679.
TIFAC report on (2001) Utilisation of waste from construction industry. Code No: TMS150.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the supports from the Indo-Norwegian BILAT Project coordinated by SINTEF Building and Infrastructure. The authors would like to thank the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute India for providing facilities and equipment for these research studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gedam, V.V., Jha, R., Labhasetwar, P. et al. A comprehensive physico-chemical, mineralogical and morphological characterization of Indian mineral wastes. Environ Monit Assess 185, 6343–6352 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3029-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3029-7