Abstract
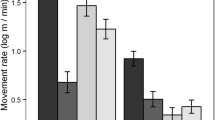
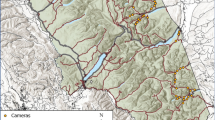
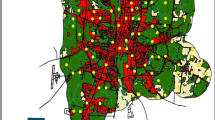
Drainage culverts are known to be used by a diverse number of species. To date, most studies looking at culvert usage have been restricted to the dry season. This seasonal bias has limited our understanding of how different species respond to culverts and, consequently, our ability to find effective ways to promote the use of culverts as aids to species movement. The main goal of this study was to examine the role of highway culverts for mesocarnivores throughout the year. We addressed (1) the seasonality of culvert use, (2) the relative importance of culvert structure, highway features, and surrounding landscape on culvert use, (3) the influence of the water depth and cover on culvert use, and (4) the effect of culvert structure on individual behavior. Fifteen culverts were monitored along 2 highways in southern Portugal using video-surveillance cameras and marble dust for 10 consecutive days per season. We used generalized linear mixed models to determine which factors most affected the culvert use and behavior by mesocarnivores. Our results highlight the effect of seasonality and water on culvert use. Culvert use was positively related with species activity throughout the year. All species (except otters (Lutra lutra)) were less likely to use culverts that contained water more than 3 cm deep or covering more than 70 % of the culvert base. Based on our results, future surveys and culvert retrofit design should address (1) the importance of seasonality in the interpretation of results and (2) the complementarity of culvert-specific features (water, ledges, and naturalization).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascensão, F., & Mira, A. (2006). Factors affecting culvert use by vertebrates along two stretches of roads in southern Portugal. Ecological Research, 22, 57–66.
Bates, D., Maechler, M., & Bolker, B. (2011). lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using S4 classes. R package version 0.999375-42. Retrieved April 4, 2012, from http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4.
Bissonette, J. A., & Adair, W. (2007). Restoring habitat permeability to roaded landscapes with isometrically-scaled wildlife crossings. Biological Conservation, 141, 482–488.
Blanco, J. C. (1998). Mamíferos de España: Insectívoros, quirópteros, primates y carnívoros de la Península Ibérica. Baleares y Canárias. Barcelona: GeoPlaneta.
Bolker, B. M., Brooks, M. E., Clark, C. J., Geange, S. W., Poulsen, J. R., Stevens, M. H. H., et al. (2009). Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 24(3), 127–135.
Cain, A. T., Tuovila, V. R., Hewitt, D. G., & Tewes, M. E. (2003). Effects of a highway and mitigation projects on bobcats in Southern Texas. Biological Conservation, 114, 189–197.
Cavalini, P., & Lovari, S. (1994). Home range, habitat selection and activity of the red fox in a Mediterranean coastal ecotone. Acta Theriologica, 39(3), 279–287.
Clevenger, A. P., Chruszcz, B., & Gunson, K. (2001). Drainage culverts as habitat linkages and factors affecting passage by mammals. Journal of Applied Ecology, 38, 1340–1349.
Dodd, N. L., Gagnon, J. W., Manzo, A. L., & Schweinsburg, R. E. (2007). Video-surveillance to assess highway use by elk in Arizona. Journal of Wildlife Management, 71(2), 637–645.
Epps, C. W., Palsbøll, P., Wehausen, J. D., Roderick, G., Ramey, I. I. R., & McCullough, D. R. (2005). Highways block gene flow and cause a rapid decline in genetic diversity of desert bighorn sheep. Ecology Letters, 8, 1029–1038.
Fahrig, L., & Rytwinski, T. (2009). Effects of roads on animal abundance: An empirical review and synthesis. Ecology and Society, 14(1), 21.
Forman, R., Sperling, D., Bissonette, J., Clevenger, A., Cutshall, C., Dale, V., et al. (2003). Road ecology—Science and solutions. USA: Island Press.
Grilo, C., Bissonette, J. A., & Santos-Reis, M. (2008). Response of carnivores to existing highway culverts and underpasses: Implications for road planning and mitigation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17, 1685–1699.
Grilo, C., Bissonette, J. A., & Santos-Reis, M. (2009). Spatial–temporal patterns in Mediterranean carnivore casualties: Consequences for mitigation. Biological Conservation, 142, 301–313.
Guisan, A., & Zimmermann, N. (2000). Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecological Modelling, 135, 147–186.
Hardy, A., Clevenger, A. P., Huijser, M., & Neale, G. (2003). An overview of methods and approaches for evaluating the effectiveness of wildlife crossing structures: Emphasizing the science in applied science. In C. L. Irwin, P. Garrett, & K. P. McDermott (Eds.), Proceedings of the international conference on ecology and transportation (pp. 319–330). Raleigh: Center for Transportation and Environment.
Hobbs, R. J. (1992). The role of corridors in conservation: Solution or bandwagon? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 7(11), 389–392.
Jaeger, J. A. G., Bowman, J., Brennan, J., Lenore, F., Bret, D., Bouchard, J., et al. (2005). Predicting when animal populations are at risk from roads: An interactive model of road avoidance behavior. Ecological Modelling, 185, 329–348.
Kruuk, H. (2006). Otters: Ecology, behaviour and conservation. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 288.
Mata, C., Hervás, I., Herranz, J., Suárez, F., & Malo, J. E. (2005). Complementary use by vertebrates of crossing structures along a fenced Spanish motorway. Biological Conservation, 124(3), 397–405.
Mata, C., Hervás, I., Herranz, J., Suárez, F., & Malo, J. E. (2008). Are motorway wildlife passages worth building? Vertebrate use of road-crossing structures on a Spanish motorway. Journal of Environmental Management, 88, 407–415.
Mata, C., Hervás, I., Herranz, J., Malo, J. E., & Francisco, S. (2009). Seasonal changes in wildlife use of motorway crossing structures and their implication for monitoring programmes. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 14(7), 447–452.
Mateus, A. R., Grilo, C., & Santos-Reis, M. (2011). Surveying drainage culvert use by carnivores: Sampling design and cost–benefit analyzes of track-pads vs. video-surveillance methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 181(1), 101–109.
Matos, H., Santos, M., Palomares, F., & Santos-Reis, M. (2009). Does riparian habitat condition influence mammalian carnivore abundance in Mediterranean ecosystems? Biodiversity and Conservation, 18, 373–386.
Ng, S. J., Dole, J., Sauvajot, R., Riley, S., & Valone, T. (2004). Use of highway undercrossings by wildlife in southern California. Biological Conservation, 115, 499–507.
Palomares, F., & Delibes, M. (1992). Circadian activity patterns of free-ranging large grey mongooses, Herpestes ichneumon in southwestern Spain. Journal of Mammalogy, 73, 173–177.
Palomares, F., & Delibes, M. (1993). Key habitats for Egyptian mongooses in Doñana National Park, southwestern Spain. Journal of Applied Ecology, 30, 752–758.
Palomares, F., & Delibes, M. (1994). Spatial–temporal ecology and behavior of European genets in southwestern Spain. Journal of Mammalogy, 75, 714–724.
Pinheiro, J., Bates, D., DebRoy, S., Sarkar, D., & the R Development Core Team. (2012). nlme: Linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-103.
Prenda, J., & Granado-Lorencio, C. (1996). The relative influence of riparian habitat structure and fish availability on otter Lutra lutra L. sprainting activity in a small Mediterranean catchment. Biological Conservation, 76, 9–15.
R Development Core Team (2011). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Retrieved April 4, 2012, from http://www.R-project.org/.
Riley, S. P. D., Pollinger, J. P., Sauvajot, R. M., York, E. C., Bromley, C., Fuller, T. K., et al. (2006). A southern California freeway is a physical and social barrier to gene flow in carnivores. Molecular Ecology, 15, 1733–1741.
Rodriguez, A., Crema, G., & Delibes, M. (1996). Use of non-wildlife passages across a high speed railway by terrestrial vertebrates. Journal of Applied Ecology, 33, 1527–1540.
Rosalino, L. M., Macdonald, D. W., & Santos-Reis, M. (2004). Spatial structure and land-cover use in a low density Mediterranean population of Eurasian badgers. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 82, 1493–1502.
Rossell, C., & Velasco, J. M. (2001). Manual de prevenció i correcció dels impactes de les infraestrutures viàries sobre la fauna. Collecció Quaderns Dels Documents De Medi Ambient.
Row, J. R., Blouin-Demer, G., & Weatherhead, P. J. (2007). Demographic effects of road mortality on black ratsnakes (Elaphe obsolete). Biological Conservation, 137, 117–124.
Ruiz-Olmo, J., Saavedra, D., & Jiménez, J. (2001). Testing the surveys and visual and track censuses of Eurasian otters (Lutra lutra). The Zoological Society of London, 253, 359–369.
Santos-Reis, M., Santos, M. J., Lourenço, S., Marques, T., Pereira, I., Pinto, B., et al. (2004). Relationships between stone martens, genets and cork oak woodlands in Portugal. In D. J. Harrison & A. K. Fuller (Eds.), Marten and fishers in human altered landscapes: An international perspective. Massachusetts: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Stewart, P. D., Ellwood, S. A., & Macdonald, D. W. (1997). Remote video-surveillance of wildlife—An introduction from experience with the European badger Meles meles. Mammal Review, 27, 185–204.
Taylor, B. D., & Goldingay, R. L. (2009). Can road-crossing structures improve population viability of an urban gliding mammal? Ecology and Society, 14(2), 13. Retrieved April 2, 2012, from http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol14/iss2/art13/.
van der Ree, R., Heinze, D., McCarthy, M., & Mansergh, I. (2009). Wildlife tunnel enhances population viability. Ecology and Society, 14(2), 7. Retrieved April 2, 2012, from http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol14/iss2/art7/.
van der Ree, R., Jaeger, J. A. G., van der Grift, E., & Clevenger, A. (2011). Effects of roads and traffic on wildlife populations and landscape function: Road ecology is moving toward larger scales. Ecological and Society, 16, 48. Retrieved April 2, 2012, from http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol16/iss1/art48/.
Virgós, E. (2001). Relative value of riparian woodlands in landscapes with different forest cover for medium-sized Iberian carnivores. Biodiversity and Conservation, 10, 1039–1049.
Yanes, M., Velasco, J. M., & Suárez, F. (1995). Permeability of roads and railways to vertebrates: The importance of culverts. Biological Conservation, 71, 217–222.
Zuur, A. F., Ieno, E. N., Walker, N. J., Saveliev, A. A., & Smith, G. M. (2009). Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. USA: Springer.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Brisa—Auto-Estradas de Portugal S.A. for providing the financial and logistical support for this project. Special thanks to Rui Raposo, Alexandre Pirra, Rui Casado, Joaquim Nobre, Pedro Pomar, and Gertrudes Ferro for their help in transporting and setting up the equipment. We would also like to thank all the volunteers that collaborated with us to complete the field work and view the videotapes. C. Grilo was supported by Ph.D. (SFRH/BD/10600/2002) and postdoctoral (SFRH/BPD/64205/2009) grants from the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia. We also would like to thank John A. Bissonette for the valuable critical comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Table 5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serronha, A.M., Mateus, A.R.A., Eaton, F. et al. Towards effective culvert design: monitoring seasonal use and behavior by Mediterranean mesocarnivores. Environ Monit Assess 185, 6235–6246 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3020-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3020-3