Abstract
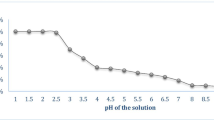
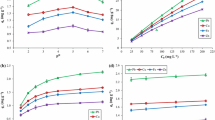
The abundantly available industrial waste product Morus alba L. pomace (MAP) is one of the cost-effective biosorbent for removal of metal ions from aqueous solutions. Hence, in the present study, we aimed to test the ability of MAP to remove Cd(II) ions through batch biosorption process. Firstly, MAP was characterized using several techniques, and then the influence of various experimental parameters such as initial pH of the aqueous solution, initial Cd(II) concentration, contact time, MAP concentration, and temperature were evaluated upon the biosorption process. It was found that the maximum uptake of Cd(II) ions occurred at initial pH 6.0 and optimum contact time was observed as 60 min. Cd(II) ions adsorption on MAP analyzed by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models and the maximum monolayer biosorption capacity of MAP was found to be 21.69 mg g−1 by using the Langmuir isotherm model. The pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, Elovich, and intraparticle diffusion models were employed to describe the biosorption kinetics. In order to investigate the thermodynamic properties of the biosorption process, the changes in the Gibbs free energy (∆G), enthalpy (∆H), and entropy (∆S) were also evaluated and it has been concluded that the process was feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic in the temperature range of 5–40 °C.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aci, F., Nebioglu, M., Arslan, M., Imamoglu, M., Zengin, M., & Kucukislamoglu, M. (2008). Preparation of activated carbon from sugar beet molasses and adsorption of methylene blue. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 17(8A), 997–1001.
Ahluwalia, S. S., & Goyal, D. (2007). Microbial and plant derived biomass for removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2243–2257.
Akar, T., Kaynak, Z., Ulusoy, S., Yuvaci, D., Ozsari, G., & Tunali-Akar, S. (2009). Enhanced biosorption of nickel(II) ions by silica-gel-immobilized waste biomass: biosorption characteristics in batch and dynamic flow mode. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 1134–1141.
APHA, American Public Health Association. (1985). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (18th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Association.
Asma, S., Waheed, A. M., & Muhammed, I. (2005). Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using papaya wood as a new biosorbent. Separation and Purification Technology, 45, 25–31.
ATSDR. (1999). Agency for toxic substances and disease registry, toxicological profiles. Atlanta: Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service.
Bhat, S. V., Melo, J. S., Chaugule, B. B., & D’Souza, S. F. (2008). Biosorption characteristics of uranium (VI) from aqueous medium onto Catenella repens, a red alga. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 158, 628–635.
Boehm, H. P. (2002). Surface oxides on carbon and their analysis: a critical assessment. Carbon, 40, 145–149.
Briand, L. E., Farneth, W. E., & Wachs, I. E. (2000). Quantitative determination of the number of active surface sites and the turnover frequencies for methanol oxidation over metal oxide catalysts: I. Fundamentals of the methanol chemisorption technique and application to monolayer supported molybdenum oxide catalysts. Catalysis Today, 62, 219–229.
Cheung, C. W., Porter, J. F., & McKay, G. (2001). Sorption kinetic analysis for the removal of cadmium ions from effluents using bone char. Water Research, 35, 605–612.
Chong, K. H., & Volesky, B. (1995). Description of two-metal biosorption equilibria by Langmuir-type models. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 47, 1–10.
Elouear, Z., Bouzid, J., & Boujelben, N. (2009). Removal of nickel and cadmium from aqueous solutions by sewage sludge ash: study in single and binary systems. Environmental Technology, 30, 561–570.
Forstner, U., & Wittman, C. T. W. (1981). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. New York: Springer.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Über die adsorption in lösungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Ghodbane, I., Nouri, L., Hamdaoui, O., & Chiha, M. (2008). Kinetic and equilibrium study for the sorption of cadmium(II) ions from aqueous phase by eucalyptus bark. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152(1), 148–158.
Guillen-Jimenez, F. M., Netzahuatl-Munoz, A. R., Morales-Barrera, L., & Cristiani-Urbina, E. (2009). Hexavalent chromium removal by Candida sp. in a concentric drafttube airlift bioreactor. Water Air Soil Pollution, 204, 43–51.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34, 451–465.
Khan, M. N., & Wahab, M. F. (2007). Characterization of chemically modified corncobs and its application in the removal of metal ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 141, 237–244.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substance. Kung Sven. Veten. Hand., 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403.
Li, X., Tang, Y., Cao, X., Lu, D., Luo, F., & Shao, W. (2008). Preparation and evaluation of orange peel cellulose adsorbents for effective removal of cadmium, zinc, cobalt and nickel. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 317, 512–521.
Liu, Y. G., Wang, X., Zeng, G. M., Qu, D., Gu, J. J., Zhou, M., & Chai, L. Y. (2007). Cadmium-induced oxidative stress and response of the ascorbate–glutathione cycle in Bechmeria nivea (L.) Gaud. Chemosphere, 69, 99–107.
Masamune, S., & Smith, J. M. (2004). Adsorption of ethyl alcohol on silica gel. AICHE Journal, 11(1), 41–45.
Megateli, S., Semsari, S., & Couderchet, M. (2009). Toxicity and removal of heavy metals (cadmium, copper, and zinc) by Lemna gibba. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 1774–1780.
Nagpal, U. M. K., Bankar, A. V., Pawar, N. J., Kapadnis, B. P., & Zinjarde, S. S. (2011). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of heavy metals by leaf powder of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 215, 177–188.
Ozcan, A., Ozcan, A. S., Tunali, S., Akar, T., & Kiran, I. (2005). Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of copper(II) ions onto seeds of Capsicum annuum. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 124, 200–208.
Ozdes, D., Duran, C., & Senturk, H. B. (2011). Adsorptive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by using Turkish illitic clay. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 3082–3090.
Ozer, C., Imamoglu, M., Turhan, Y., & Boysan, F. (2012). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using phosphoric acid activated carbon produced from hazelnut husks. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 94, 1283–1293.
Rehman, A., & Anjum, M. S. (2011). Multiple metal tolerance and biosorption of cadmium by Candida tropicalis isolated from industrial effluents: glutathione as detoxifying agent. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174, 585–595.
Reddad, Z., Gerente, C., Andres, Y., & Le Cloirec, P. (2002). Adsorption of several metal ions onto a low-cost biosorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(9), 2067–2073.
Smith, J. M., & Van Ness, H. C. (1987). Introduction to chemical engineering thermodynamics (4th ed.). Singapore: McGraw-Hill.
Verougstraete, V., Lison, D., & Hotz, P. (2002). A systematic review of cytogenetic studies conducted in human populations exposed to cadmium compounds. Mutation Research, 511, 15–43.
Vimala, R., & Das, N. (2009). Biosorption of cadmium(II) and lead(II) from aqueous solutions by using mushrooms: a comparative study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 376–382.
Walker, G. M., & Weatherley, L. R. (2001). Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution—the effect of adsorbent pore size distribution and dye aggregation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 83, 201–206.
Weber, W. J., Jr., & Morriss, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of Sanitary Engineering Division, American Society of Civil Engineers, 89, 31–60.
World Health Organization. (1993). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, second ed., vol. 1., Geneva.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serencam, H., Ozdes, D., Duran, C. et al. Biosorption properties of Morus alba L. for Cd (II) ions removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Monit Assess 185, 6003–6011 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3001-6