Abstract
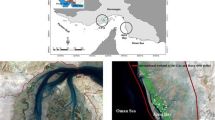
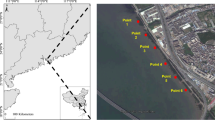
Concentrations of six heavy metals (Cu, Ni, Zn, Cd, Cr, and Pb) in sediments and fine roots, thick roots, branches, and leaves of six mangrove plant species collected from the Futian mangrove forest, South China were measured. The results show that both the sediments and plants in Futian mangrove ecosystem are moderately contaminated by heavy metals, with the main contaminants being Zn and Cu. All investigated metals showed very similar distribution patterns in the sediments, implying that they had the same anthropogenic source(s). High accumulations of the heavy metals were observed in the root tissues, especially the fine roots, and much lower concentrations in the other organs. This indicates that the roots strongly immobilize the heavy metals and (hence) that mangrove plants possess mechanisms that limit the upward transport of heavy metals and exclude them from sensitive tissues. The growth performance of propagules and 6-month-old seedlings of Bruguiera gymnorhiza in the presence of contaminating Cu and Cd was also examined. The results show that this plant is not sufficiently sensitive to heavy metals after its propagule stage for its regeneration and growth to be significantly affected by heavy metal contamination in the Futian mangrove ecosystem. However, older mangrove seedlings appeared to be more metal-tolerant than the younger seedlings due to their more efficient exclusion mechanism. Thus, the effects of metal contamination on young seedlings should be assessed when evaluating the risks posed by heavy metals in an ecosystem.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoramoorthy, G., Chen, F., & Hsu, M. (2008). Threat of heavy metal pollution in halophytic and mangrove plants of Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Pollution, 155, 320–326.
Ahmed, K., Mehedi, Y., Haque, R., & Mondol, P. (2011). Heavy metal concentrations in some macrobenthic fauna of the Sundarbans mangrove forest, south west coast of Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 177, 505–514.
Alberts, J. J., Price, M. Y., & Kania, M. (1990). Metal concentrations in tissues of Spartina alterniflora (Loisel) and sediments of Georgia salt marshes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 30, 47–58.
Arao, T., Ae, N., Sugiyama, M., & Takahashi, M. (2003). Genotypic differences in cadmium uptake and distribution in soybeans. Plant and Soil, 251, 247–253.
Basak, U. C., Das, A. B., & Das, P. (1996). Chlorophylls, carotenoids, proteins and secondary metabolites in leaves of 14 species of mangrove. Bulletin of Marine Science, 58, 654–659.
Chatterjee, M., Massolo, S., Sarkar, S. K., Bhattacharya, A. K., Bhattacharya, B. D., Satpathy, K. K., et al. (2009). An assessment of trace element contamination in intertidal sediment cores of Sunderban mangrove wetland, India for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150, 307–322.
Cheng, H., Liu, Y., Tam, N. F. Y., Wang, X., Li, S. Y., Chen, G. Z., et al. (2010). The role of radial oxygen loss and root anatomy on zinc uptake and tolerance in mangrove seedlings. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1189–1196.
Cuong, D. T., Bayen, S., Wurl, O., Subramanian, K., Wong, K. K. S., Sivasothi, N., et al. (2005). Heavy metal contamination in mangrove habitats of Singapore. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1713–1738.
Dahmani-Muller, H., van Oort, F., Gélie, B., & Balabane, M. (2000). Strategies of heavy metal uptake by three plant species growing near a metal smelter. Environmental Pollution, 109, 231–238.
Das, S., & Vincent, J. R. (2009). Mangroves protected villages and reduced death toll during Indian super cyclone. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106, 7357–7360.
De Filippis, L. F., & Pallaghy, C. K. (1994). Heavy metals: Sources and biological effects. In L. C. Rai, J. P. Caur, & C. J. Soeder (Eds.), Algae and water pollution: Advances in limnology series (pp. 32–77). Stuttgart: Schweizerbart.
Deng, H., Ye, Z. H., & Wong, M. H. (2004). Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environmental Pollution, 132, 29–40.
Essien, J. P., Antai, S. P., & Olajire, A. A. (2009a). Distribution, seasonal variations and ecotoxicological significance of heavy metals in sediments of Cross River Estuary mangrove swamp. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 197, 91–105.
Essien, J. P., Essien, V., & Olajire, A. A. (2009b). Heavy metal burdens in patches of asphyxiated swamp areas within the Qua Iboe estuary mangrove ecosystem. Environmental Research, 109, 690–696.
Frías-Espericueta, M. G., Osuna-López, J. I., López-López, G., Izaguirre-Fierro, G., & Muy-Rangel, M. D. (2008). The metal content of bivalve molluscs of a coastal lagoon of NW Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80, 90–92.
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds: A sink and source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17, 246–250.
Inskeep, W. P., & Bloom, P. R. (1985). Extinction coefficients of chlorophyll a and b in N,N-dimethylformamide and 80 % acetone. Plant Physiology, 77, 483–485.
Lefèvre, I., Marchal, G., Corréal, E., Zanuzzi, A., & Lutts, S. (2009). Variation in response to heavy metals during vegetative growth in Dorycnium pentaphyllum Scop. Plant Growth Regulation, 59, 1–11.
Liu, X. L., Zhang, S. Z., Shan, X. Q., & Zhu, Y. G. (2005). Toxicity of arsenate and arsenite on germination, seedling growth and amylolytic activity of wheat. Chemosphere, 61, 293–301.
Liu, Y., Tam, N. F. Y., Yang, J. X., Pi, N., Wong, M. H., & Ye, Z. H. (2009). Mixed heavy metals tolerance and radial oxygen loss in mangrove seedlings. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 1843–1849.
Lugo, A., & Snedaker, S. C. (1974). The ecology of mangroves. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 5, 39–64.
Macfarlane, G. R., & Burchett, M. D. (2001). Photosynthetic pigments and peroxidase activity as indicators of heavy metal stress in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42, 233–240.
Macfarlane, G. R., Koller, C. E., & Blomberg, S. P. (2007). Accumulation and partitioning of heavy metals in mangroves: A synthesis of field-based studies. Chemosphere, 69, 1454–1464.
Marchand, C., Lallier-Vergès, E., Baltzer, F., Albéric, P., Cossa, D., & Baillif, P. (2006). Heavy metals distribution in mangrove sediments along the mobile coastline of French Guiana. Marine Chemistry, 98, 1–17.
Marchand, C., Allenbach, M., & Lallier-Vergès, E. (2011). Relationships between heavy metals distribution and organic matter cycling in mangrove sediments (Conception Bay, New Caledonia). Geoderma, 160, 444–456.
Moura, D. J., Péres, V. F., Jacques, R. A., & Saffi, J. (2012). Heavy metal toxicity: Oxidative stress parameters and DNA repair. In D. K. Gupta & L. M. Sandalio (Eds.), Metal toxicity in plants: Perception, signaling and remediation (pp. 187–205). Berlin: Springer.
Munns, R. (2005). Genes and salt tolerance: Bringing them together. New Phytologist, 167, 645–663.
Nobi, E. P., Dilipan, E., Thangaradjou, T., Sivakumar, K., & Kannan, L. (2010). Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of different coastal ecosystems of Andaman Islands, India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 87, 253–264.
Ong Che, R. G. (1999). Concentration of 7 heavy metals in sediments and mangrove root samples from Mai Po, Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 39, 269–279.
Page, A. L., Miller, R. H., & Keeney, D. R. (Eds.), (1982). Methods of Soil Analysis. Madison, Wisconsin: ASA and SSSA.
Parvaresh, H., Abedi, Z., Farshchi, P., Karami, M., Khorasani, N., & Karbassi, A. (2011). Bioavailability and concentration of heavy metals in the sediments and leaves of grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh, in Sirik Azini creek, Iran. Biological Trace Element Research, 143, 1121–1130.
Pekey, H. (2006). The distribution and sources of heavy metals in Izmit Bay surface sediments affected by a polluted stream. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, 1197–1208.
Polidoro, B. A., Carpenter, K. E., Collins, L., Duke, N. C., Ellison, A. M., Ellison, J. C., et al. (2010). The loss of species: Mangrove extinction risk and geographic areas of global concern. PLoS One, 5, e10095.
Ray, A. K., Tripathy, S. C., Patra, S., & Sarma, V. V. (2006). Assessment of Godavari estuarine mangrove ecosystem through trace metal studies. Environment International, 32, 219–223.
Shriadah, M. M. A. (1999). Heavy metals in mangrove sediments of the United Arab Emirates shoreline (Arabian Gulf). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 116, 523–534.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, Y. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–205.
Tam, N. F. Y., Li, S. H., Lan, C. Y., Chen, G. Z., Li, M. S., & Wong, Y. S. (1995). Nutrients and heavy metal contamination of plants and sediments in Futian mangrove forest. Hydrobiologia, 295, 149–158.
Wang, Y. T., Qiu, Q., Yang, Z. Y., Hu, Z. J., Tam, N. F. Y., & Xin, G. R. (2010). Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in two mangroves in South China. Plant and Soil, 331, 181–191.
Wang, Y. T., Huang, Y. L., Qiu, Q., Xin, G. R., Yang, Z. Y., & Shi, S. H. (2011). Flooding greatly affects the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi communities in the roots of wetland plants. PLoS One, 6, e24512.
Yan, Z. Z., Ke, L., & Tam, N. F. Y. (2010). Lead stress in seedlings of Avicennia marina, a common mangrove species in South China, with and without cotyledons. Aquatic Botany, 92, 112–118.
Yang, Q., Tam, N. F. Y., Wong, Y. S., Luan, T. G., Su, W. S., Lan, C. Y., et al. (2008). Potential use of mangrove as constructed wetland for municipal sewage treatment in Futian, Shenzhen, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57, 735–743.
Yeh, H. C., Chen, I. M., Chen, P., & Wang, W. H. (2009). Heavy metal concentrations of the soldier crab (Mictyris brevidactylus) along the inshore area of Changhua, Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 153, 103–109.
Young, L., & Melville, D. S. (1993). Conservation of the Deep Bay environment. In B. Morton (Ed.), The marine biology of the South China Sea (pp. 211–231). Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press.
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Ouyang, Y., Liao, B., & Zhao, B. (2010). Removal of nutrients and heavy metals from wastewater with mangrove Sonneratia apetala Buch-Ham. Ecological Engineering, 36, 807–812.
Zheng, W. J., Chen, X. Y., & Lin, P. (1997). Accumulation and biological cycling of heavy metal elements in Rhizophora stylosa mangroves in Yingluo Bay, China. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 159, 293–301.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30871475 and 31071357), the Project of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (2010B020311005), and the Reserve Key Project of Sun Yat-sen University, Foundation for Distinguished Young Talents in Higher Education of Guangdong, China (C10438), and Foundation from Key Laboratory of Biodiversity Dynamics and Conservation of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Sun Yat-sen University (KLB11006), and the Open Research Fund Program from the Guangdong Key Laboratory of Plant Resources (plant01k15). We thank Li Meng-ying and Wang Xin-ya (Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China) for their generous help in sampling and analyzing heavy metals. We also thank Prof. Lars Olof Björn (Lund University, Sweden) and the anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful advice regarding our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Qiu, Q., Xin, G. et al. Heavy metal contamination in a vulnerable mangrove swamp in South China. Environ Monit Assess 185, 5775–5787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2983-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2983-4