Abstract
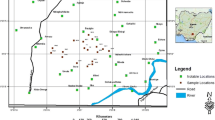
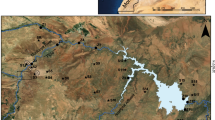
The chemistry of heavy metals in sediments with respect to bio-availability and chemical reactivity is regulated by pH, texture, and organic matter contents of the sediments and specific binding form and coupled reactivity of the metals within. To focus on the metal distribution (Fe, Mn, Pb, Cd, Zn, Co, Cu, and Cr) and behavior in a fresh water aquifer system along with the ecological toxicity parameters, a four-step sequential extraction method was applied on 18 Eastern Ghats’ type sediments from fluorosis-hit Nayagarh district, India. Geo-accumulation index of metals in the sediments indicates that they are practically uncontaminated and/or less contaminated with and Fe, Mn, and Cu; contaminated to moderately contaminated with Pb, Zn, and Cr; and strongly contaminated with Cd. Rather, more than 80 % recovered Cd metal concentration in sediments constitute the labile fractions. Temporal clustering of metal fractions indicates transition metal fraction distribution claiming the sediment pH regulation. Similarly, base metal distribution accounts for organic carbon and soil conductivity due to their greater availability in exchangeable and sulfide fractions. Correlation analysis and factor analysis scores demonstrate lack of inter-relationship between transition group and base metal fractions. High fluoride concentration in ground water is associated with high sodium-bicarbonate-iron affinity with elevated pH values (i.e., >7.0) and high positive factor score with the total iron concentration in ground water.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, H. E., & Hansen, D. J. (1996). The importance of trace metal speciation to water quality criteria. Water Environment Research, 68, 42–54.
Assaad, E., Azzouz, A., Nistor, D., Ursu, A. V., Sajin, T., Miron, D. N., Monette, F., Niquette, P., & Hausler, R. (2007). Metal removal through synergic coagulation–locculation using an optimized chitosan–montmorillonite system. Applied Clay Science, 37, 258–274.
Backes, C. A., McLaren, R. G., Rate, A. W., & Swift, R. S. (1995). Kinetics of cadmium and cobalt desorption from iron and manganese oxides. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 59, 778–785.
Bertin, C., & Bourg, A. C. M. (1995). Trend in the heavy metal content (Cd, Pb, Zn) of river sediment in the drainage basin of smelting activities. Water Research, 29, 1729–1736.
Camusso, M., Galassi, S., & Vignati, D. (2002). Assesment of river Po sediment quality by micropollutant analysis. Water Research, 36, 2491–2504.
Copeland, R. A., & Ayers, J. C. (1972). Trace element distribution in water, sediment, phytoplankton, zooplankton and benthos of Lake Michigan: a base line study with calculation of concentration factors and build up of radioisotopes in the food web. Ann Arbor: Environmental Research Group.
Forstner, U. (1985). Chemical forms and reactivities of metals in sediments. In R. Leschber, R. D. Davis, & P. L’Hermite (Eds.), Chemical methods for assessing bioavailable metals in sludge and soils (pp. 1–30). London: Elsevier.
Forstner, U., & Muller, G. (1973). Heavy metal accumulation in river sediment: a response to environmental pollution. Geoforum, 14, 53–61.
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Berlin: Springer.
Goncalves, E. P. R., Boaventura, R. A. R., & Mouvet, C. (1992). Sediments and aquatic mosses as pollution indicators for heavy metals in the Ave River basin (Portugal). Science of the Total Environment, 142, 143–156.
Gupta, G. C., & Harrison, F. L. (1981). Effect of cations on copper adsorption by kaoline. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 15, 323–339.
Han, F. X., Banin, A., Kingery, W. L., Triplett, G. B., Zhou, L. X., Zheng, S. J., & Ding, W. X. (2003). New approach to studies of heavy metal redistribution in soil. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 113–120.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J.M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial (Piseuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34, 807–816.
ISI. (1991). Indian Standard Specification for Drinking Water IS:10500. India: Indian Standard Institute.
Jenne, F. A. (1968). Controls of Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn concentrations in soils and water: the significance of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides. American Chemical Society, Advances in Chemistry Series, 73, 337–387.
Kemp, A. L. W., & Thomas, R. L. (1976). Impact of man’s activities on the chemical composition in the sediments of Lakes Ontario, Erie and Huron. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 5, 469–490.
Lim, T. T., Tay, J. H., & Wang, J. Y. (2004). Chelating-agent-enhanced heavy metal extraction from a contaminated acidic soil. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 130, 59–66.
Liu, W. X., Li, X. D., Shen, Z. G., Wang, D. C., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y. S. (2003). Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 121, 377–388.
Middelburg, J. J., Correlis, H., Weijdew, V. D., & Woittiez, J. R. W. (1988). Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chemical Geology, 68, 253–273.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediment des Rheins,Veranderungem Seit 1971. Umschau, 79, 778–783.
Nolting, R. F., Ramkema, A., & Everaats, J. M. (1999). The geochemistry of Cu, Cd, Zn, Ni and Pb in sediment cores from the continental slope of the Banc d’Arguin (Mauritania). Continental Shelf Research, 19, 665–691.
Nriagu, J. O. (1979). Copper in the environment. Part I: ecological cycling (p. 217). New York: Wiley.
Pati, G.C. (2009). Ground water resource scenario of Orissa, Workshop on Ground Water Scenario and Quality in Orissa, 6th &7th March, Bhubaneswar.
Prasad, M. B. K., Ramanathan, A. L., Shrivastav, S. K. R., Anshumali, & Saxena, R. (2006). Metal fractionation studies in surfacial and core sediments in the Achankovil river basin in India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121, 77–102.
Rauret, G. (1998). Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta, 46(3), 449–455.
Riemer, D. N., & Toth, S. J. (1970). Chemical composition of five species of nymphaeaceae. American Water Works Association, 62, 195–208.
Sawyer, E. W. (1986). The influence of source rock type, chemical weathering and sorting on the geochemistry of clastic sediments from the Quetico Metasedimentary Belt, superior Province, Canada. Chemical Geology, 55, 77–95.
Shilla, D., Qadah, D., & Kalibbala, M. (2008). Distribution of heavy metals in dissolved, particulate and biota in the Scheldt estuary, Belgium. Chemical Ecology, 24(1), 1–14.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., Anthemidis, A., Sofoniou, M., & Kouimtzis, T. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Stumm, W., & Morgan, J. J. (1981). Aquatic chemistry (p. 780). New York: Wiley.
Tomilson, D. C., Wilson, D. J., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problem in assessment of heavy metals in estuaries and the formation of pollution index. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1–4), 566–575.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72(2), 175–192.
Vogel, A.I. (2000). A text book of quantitative inorganic analysis (pp 556–579). New York: Longmans Green.
Wunderlin, D. A., Diaz, M. D. P., Ame, M. V., Pesce, S. F., Hued, A. C., & Bistoni, M. D. (2001). Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba Argentina). Water Research, 35, 2881–2894.
Zhang, J. (1995). Geochemistry of trace metals from Chinese river/estuary systems: an overview. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 41, 631–658.
Zhou, F., Guo, H. C., Liu, Y., & Jiang, Y. M. (2007). Chemometrics data analysis of marine water quality and source identification in Southern Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54, 745–756.
Acknowledgment
The authors express their sincere thanks to the Director, Institute of Minerals and Materials Technology (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research), Bhubaneswar for his kind permission to publish the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harichandan, R., Routroy, S., Mohanty, J.K. et al. An assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils of fresh water aquifer system and evaluation of eco-toxicity by lithogenic implications. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3503–3516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2806-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2806-7