Abstract
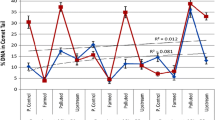
The input of anthropogenic contaminants to the aquatic environment is a major concern for scientists, regulators and the public. This is especially relevant in areas such as the Tamar valley in SW England, which has a legacy of contamination from industrial activity in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Following on from previous laboratory validation studies, this study aimed to assess the relationship between genotoxic and cytotoxic responses and heavy metal concentrations in two bivalve species sampled from locations along the Tamar estuary. Adult cockles, Cerastoderma edule, and blue mussels, Mytilus edulis, were sampled from five locations in the Tamar and one reference location on the south Devon coast. Bivalve haemocytes were processed for comet and neutral red retention (NRR) assays to determine potential genotoxic and cytotoxic effects, respectively. Sediment and soft tissue samples were analysed for metal content by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Sediment concentrations were consistent with the physico-chemical nature of the Tamar estuary. A significant correlation (P = 0.05) was found between total metal concentration in sediment and C. edule soft tissues, but no such correlation was found for M. edulis samples. DNA damage was elevated at the site with highest Cr concentrations for M. edulis and at the site with highest Ni and Pb concentrations for C. edule. Analysis of NRR revealed a slight increase in retention time at one site, in contrast to comet data. We conclude that the comet assay is a reliable indicator of genotoxic damage in the field for both M. edulis and C. edule and discuss reasons for the apparent discrepancy with NRR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D., Dobrzyńska, M. M., & Basaran, N. (1997). Effect of various genotoxins and reproductive toxins in human lymphocytes and sperm in the Comet assay. Teratogenesis Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis, 17(1), 29–43.
Baron, M. G., Purcell, W. M., Jackson, S. K., Owen, S. F., & Jha, A. N. (2012). Towards a more representative in vitro method for fish ecotoxicology: Morphological and biochemical characterisation of three-dimensional spheroidal hepatocytes. Ecotoxicology. doi:10.1007/s10646-012-0965-5.
Beyersmann, D., & Hartwig, A. (2008). Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Archives of Toxicology, 82, 493–512.
Bignell, J. P., Stentiford, G. D., Taylor, N. G. H., & Lyons, B. P. (2011). Histopathology of mussels (Mytilus sp.) from the Tamar estuary, UK. Marine Environmental Research, 72(1–2), 25–32. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.05.004.
Borja, A., Valencia, V., Franco, J., Muxika, I., Bald, J., Belzunce, M. J., et al. (2004). The water framework directive: Water alone, or in association with sediment and biota, in determining quality standards? [doi: DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.04.008]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 8–11.
Canty, M. N., Hutchinson, T. H., Brown, R. J., Jones, M. B., & Jha, A. N. (2009). Linking genotoxic responses with cytotoxic and behavioural or physiological consequences: Differential sensitivity of echinoderms (Asterias rubens) and marine molluscs (Mytilus edulis). Aquatic Toxicology, 94, 68–76.
Cheung, V. V., Wedderburn, R. J., & Depledge, M. H. (1998). Molluscan lysosomal responses as a diagnostic tool for the detection of a pollution gradient in Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong. Marine Environmental Research, 46(1–5), 237–241. doi:10.1016/s0141-1136(97)00104-9.
Cheung, V. V., Depledge, M. H., & Jha, A. N. (2006). An evaluation of the relative sensitivity of two marine bivalve mollusc species using the Comet assay. [Proceedings Paper]. Marine Environmental Research, 62, S301-S305, doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.04.053.
Collins, A. R. (2004). The comet assay for DNA damage and repair—Principles, applications, and limitations. Molecular Biotechnology, 26(3), 249–261.
Company, R., Serafim, A., Lopes, B., Cravo, A., Kalman, J., Riba, I., et al. (2011). Source and impact of lead contamination on delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity in several marine bivalve species along the Gulf of Cadiz. [Article]. Aquatic Toxicology, 101(1), 146–154. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.09.012.
Dixon, D. R., Pruski, A. M., Dixon, L. R. J., & Jha, A. N. (2002). Marine invertebrate eco-genotoxicology: A methodological overview. Mutagenesis, 17(6), 495–507. doi:10.1093/mutage/17.6.495.
Emmanouil, C., Sheehan, T. M. T., & Chipman, J. K. (2007). Macromolecule oxidation and DNA repair in mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) gill following exposure to Cd and Cr(VI). Aquatic Toxicology, 82(1), 27–35. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.01.009.
Environment Agency (1996). Tamar estuary and tributaries: Consultation report. (pp. 7). London, UK: Environment Agency.
Everaarts, J. M. (1995). DNA integrity as a biomarker of marine pollution: Strand breaks in sea star (Asterias rubens) and dab (Limand limanda). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4), 431–438.
Fernley, P. W., Moore, M. N., Lowe, D. M., Donkin, P., & Evans, S. (2000). Impact of the Sea Empress oil spill on lysosomal stability in mussel blood cells. Marine Environmental Research, 50(1–5), 451–455. doi:10.1016/s0141-1136(00)00118-5.
Frenzilli, G., Scarcelli, V., Taddei, F., & Nigro, M. (1999). Adaptation of SCGE for monitoring marine ecosystems. Neoplasma, 46(Suppl), 6–7.
Frenzilli, G., Nigro, M., Scarcelli, V., Gorbi, S., & Regoli, F. (2001). DNA integrity and total oxyradical scavenging capacity in the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: A field study in a highly eutrophicasted coastal lagoon. Aquatic Toxicology, 53, 19–32.
Fuerhacker, M. (2009). EU water framework directive and stockholm convention. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16, 92–97.
Fytianos, K. (2001). Speciation analysis of heavy metals in natural waters: A review. Journal of AOAC International, 84(6), 1763–1769.
Hagger, J. A., Lowe, D., Dissanayake, A., Jones, M. B., & Galloway, T. S. (2010). The influence of seasonality on biomarker responses in Mytilus edulis. Ecotoxicology, 19(5), 953–962. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0477-0.
Hasspieler, B. M., Alipour, M., Ali, F. N., Haffner, G. D., & Adeli, K. (1995). Assessment of cyto- and genotoxicity of environmental samples. In F. M. Butterworth, L. D. Corkum, & J. Guzmán-Rincόn (Eds.), Biomonitors and biomarkers as indicators of environmental change: A handbook (pp. 149–168). New York: Plenum Press.
Hilbish, T. J., Carson, E. W., Plante, J. R., Weaver, L. A., & Gilg, M. R. (2002). Distribution of Mytilus edulis, M. galloprovincialis, and their hybrids in open-coast populations of mussels in southwestern England. Marine Biology, 140(1), 137–142. doi:10.1007/s002270100631.
Jha, A. N. (2004). Genotoxicological studies in aquatic organisms: An overview. Mutation Research, Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 552(1–2), 1–17.
Jha, A. N. (2008). Ecotoxicological applications and significance of the Comet assay. Mutagenesis, 23(3), 207–221. doi:10.1093/mutage/gen014.
Jha, A. N., Cheung, V. V., Foulkes, M. E., Hill, S. J., & Depledge, M. H. (2000). Detection of genotoxins in the marine environment: Adoption and evaluation of an integrated approach using the embryo-larval stages of the marine mussel, Mytilus edulis. Mutation Research, Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 464(2), 213–228.
Jung, K., Stelzenmuller, V., & Zauke, G. P. (2006). Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations and biomass indices in Cerastoderma edule Linnaeus (1758) from the German Wadden Sea: An integrated biomonitoring approach. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 338(1), 81–95. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2006.06.036.
Kumaravel, T. S., & Jha, A. N. (2006). Reliable comet assay measurements for detecting DNA damage induced by ionising radiation and chemicals. Mutation Research, Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 605(1–2), 7–16. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.03.002.
Kumaravel, T. S., Vilhar, B., Faux, S. P., & Jha, A. N. (2009). Comet assay measurements: A perspective. Cell Biology and Toxicology, 25(1), 53–64. doi:10.1007/s10565-007-9043-9.
Langston, W. J., Chesman, B. S., Burt, G. R., Hawkins, S. J., Readman, J., & Worsfold, P. J. (2003). Characterisation of the South West European Marine Sites. Plymouth Sound and Estuaries cSAC, SPA. Plymouth: Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.
Law, R. J., Dawes, V. J., Woodhead, R. J., & Mattiessen, P. (1997). Polcyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in seawater around England and Wales. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 34(5), 306–322.
Lindsay, P., & Bell, F. G. (1997). Contaminated sediment in two United Kingdom estuaries. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience, 3(3), 375–387.
Liu, Y. P., Millward, G. E., & Harris, J. R. W. (1998). Modelling the distributions of dissolved Zn and Ni in the Tamar Estuary using hydrodynamics coupled with chemical kinetics. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 47(5), 535–546. doi:10.1006/ecss.1998.0372.
Lobo, J., Costa, P., Caeiro, S., Martins, M., Ferreira, A., Caetano, M., et al. (2010). Evaluation of the potential of the common cockle (Cerastoderma edule L.) for the ecological risk assessment of estuarine sediments: Bioaccumulation and biomarkers. Ecotoxicology, 19(8), 1496–1512. doi:10.1007/s10646-010-0535-7.
Lowe, D. M. (1988). Alterations in cellular structure of Mytilus edulis resulting from exposure to environmental contaminants under field and experimental conditions. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 46, 91–100.
Lowe, D. M., & Pipe, R. K. (1994). Contaminant induced lysosomal membrane damage in marine mussel digestive cells: An in vitro study. Aquatic Toxicology, 30(4), 357–365. doi:10.1016/0166-445x(94)00045-x.
Lowe, D. M., Fossato, V. U., & Depledge, M. H. (1995). Contaminant-induced lysosomal membrane damage in blood cells of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Venice Lagoon: An in vitro study. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 129(1–3), 189–196.
Lyons, B. P., Thain, J. E., Stentiford, G. D., Hylland, K., Davies, I. M., & Vethaak, A. D. (2010). Using biological effects tools to define good environmental status under the European Union marine strategy framework directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(10), 1647–1651. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.06.005.
Millward, G. E., Kadam, S., & Jha, A. N. (2012). Tissue-specific assimilation, depuration and toxicity of nickel in Mytilus edulis. Environmental Pollution, 162, 406–412. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.034.
Money, C., Braungardt, C. B., Jha, A. N., Worsfold, P. J., & Achterberg, E. P. (2011). Metal speciation and toxicity of Tamar Estuary water to larvae of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Marine Environmental Research, 72(1–2), 3–12. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.05.001.
Moore, M. N., & Lowe, D. (2004). ICES techniques in marine environmental sciences. No. 36. Biological effects of contaminants: Measurement of lysosomal membrane stability. Copenhagen: International Council for Exploration of the Sea.
Moore, M. N., Widdows, J., Cleary, J. J., Pipe, R. K., Salkeld, P. N., Donkin, P., et al. (1984). Responses of the mussel Mytilus edulis to copper and phenanthrene: Interactive effects. Marine Environmental Research, 14, 147–183.
Moore, M. N., Depledge, M. H., Readman, J. W., & Paul Leonard, D. R. (2004). An integrated biomarker-based strategy for ecotoxicological evaluation of risk in environmental management. Mutation Research, Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 552(1–2), 247–268. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.06.028.
Nacci, D. E., & Jackim, E. (1989). Using the DNA alkaline unwinding assay to detect DNA damage in laboratory and environmentally exposed cells and tissues. Marine Environmental Research, 29, 333–337.
Nacci, D. E., Kohan, M., Pelletier, M., & George, E. (2002). Effects of benzo[a]pyrene exposure on a fish population resistant to the toxic effects of dioxin-like compounds. Aquatic Toxicology, 57(4), 203–215.
Nevo, E., Noy, R., Lavie, B., Beiles, A., & Muchtar, S. (1986). Genetic diversity and resistance to marine pollution: Theory and practice. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 29, 139–144.
Papis, E., Davies, S. J., & Jha, A. N. (2011). Relative sensitivity of fish and mammalian cells to the antibiotic, trimethoprim: Cytotoxic and genotoxic responses as determined by neutral red retention, Comet and micronucleus assays. Ecotoxicology, 20, 208–217.
Phillips, D. J. H. (1977). The use of biological indicator organisms to monitor trace metal pollution in marine and estuarine environments—A review. Environmental Pollution, 13, 281–317. doi:10.1016/0013-9327(77)90047-7.
Pipe, R. K., Porte, C., & Livingstone, D. R. (1993). Antioxidant enzymes associated with the blood cells and haemolymph of the mussel Mytilus edulis. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 3(3), 221–233. doi:10.1006/fsim.1993.1022.
Rank, J., Jensen, K., & Jespersen, P. H. (2005). Monitoring DNA damage in indigenous blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) sampled from coastal sites in Denmark. Mutation Research, Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 585(1–2), 33–42. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2005.04.008.
Sasaki, Y. F., Izumiyama, F., Nishidate, E., Ishibashi, S., Tsuda, S., Matsusaka, N., et al. (1997). Detection of genotoxicity of polluted sea water using shellfish and the alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCE) assay: A preliminary study. Mutation Research, 393(1–2), 133–139.
Shaw, J. P., & Moore, M. N. (2011). Introduction to the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) PREDICT 2 Tamar Estuary Research Workshop: Pathological risk evaluation using “health status-related” biomarkers. Marine Environmental Research, 72(1–2), 1–2. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.05.002.
Shaw, J. P., Dondero, F., Moore, M. N., Negri, A., Dagnino, A., Readman, J. W., et al. (2011). Integration of biochemical, histochemical and toxicogenomic indices for the assessment of health status of mussels from the Tamar Estuary, U.K. Marine Environmental Research, 72(1–2), 13–24. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.05.003.
Steinert, S. A., Streib-Montee, R., Leather, J. M., & Chadwick, D. B. (1998). DNA damage in mussels at sites in San Diego Bay. Mutation Research, 399, 65–85.
Sternlieb, I., & Goldfischer, S. (1976). Heavy metals and lysosomes. Frontiers in Biology, 45, 185–200.
Viarengo, A. (1985). Biochemical effects of trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 16(4), 153–158.
Webb, M. (1979). The chemistry, biochemistry and biology of cadmium. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Wedderburn, J., Cheung, V., Bamber, S., Bloxham, M., & Depledge, M. H. (1998). Biomarkers of biochemical and cellular stress in Carcinus maenas: An in situ field study. Marine Environmental Research, 46(1–5), 321–324. doi:10.1016/s0141-1136(98)00016-6.
Woodhead, R. J., Law, R. J., & Mattiessen, P. (1999). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments around England and Wales, and their possible biological significance. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38(9), 773–790.
Wootton, E. C., Dyrynda, E. A., & Ratcliffe, N. A. (2003). Bivalve immunity: Comparisons between the marine mussel (Mytilus edulis), the edible cockle (Cerastoderma edule) and the razor-shell (Ensis siliqua). Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 15(3), 195–210. doi:10.1016/s1050-4648(02)00161-4.
Acknowledgment
Partial financial support from European Regional Development Fund, INTERREG IVA (grant no. 4059) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dallas, L.J., Cheung, V.V., Fisher, A.S. et al. Relative sensitivity of two marine bivalves for detection of genotoxic and cytotoxic effects: a field assessment in the Tamar Estuary, South West England. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3397–3412 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2800-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2800-0