Abstract
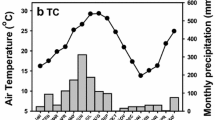
Soil respiration rates were measured monthly (from April 2007 to March 2008) under four adjacent coniferous plantation sites [Oriental spruce (Picea orientalis L.), Austrian pine (Pinus nigra Arnold), Turkish fir (Abies bornmulleriana L.), and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.)] and adjacent natural Sessile oak forest (Quercus petraea L.) in Belgrad Forest—Istanbul/Turkey. Also, soil moisture, soil temperature, and fine root biomass were determined to identify the underlying environmental variables among sites which are most likely causing differences in soil respiration. Mean annual soil moisture was determined to be between 6.3 % and 8.1 %, and mean annual temperature ranged from 13.0°C to 14.2°C under all species. Mean annual fine root biomass changed between 368.09 g/m2 and 883.71 g/m2 indicating significant differences among species. Except May 2007, monthly soil respiration rates show significantly difference among species. However, focusing on tree species, differences of mean annual respiration rates did not differ significantly. Mean annual soil respiration ranged from 0.56 to 1.09 g C/m2/day. The highest rates of soil respiration reached on autumn months and the lowest rates were determined on summer season. Soil temperature, soil moisture, and fine root biomass explain mean annual soil respiration rates at the highest under Austrian pine (R 2 = 0.562) and the lowest (R 2 = 0.223) under Turkish fir.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, M., Bekku, Y. S., Rashidah, W., Okuda, T., & Koizumi, H. (2006). Differences in soil respiration between different tropical ecosystems. Applied Soil Ecology, 34, 258–265.
Binkley, D., & Giardina, C. (1998). Why do tree species affect soils? The Warp and Woof of tree–soil interactions. Biogeochemistry, 42, 89–106.
Brüggemann, N., Rosenkranz, P., Papen, H., Pilegaard, K., & Butterbach-Bahl, K. (2005). Pure stands of temperate forest tree species modify soil respiration and N turnover. Biogeosciences Discussions, 2, 303–331.
Ceccon, C., Panzacchi, P., Scandellari, F., Prandi, L., Ventura, M., Russo, B., et al. (2011). Spatial and temporal effects of soil temperature and moisture and the relation to fine root density on root and soil respiration in a mature apple orchard. Plant and Soil, 342, 195–206.
Coleman, D. C., Hunter, M. D., Hutton, J., Pomeroy, S., & Swift, L. (2002). Soil respiration from four aggrading forested watersheds measured over a quarter century. Forest Ecology and Management, 157, 247–253.
Cook, F. J., & Orchard, V. A. (2008). Relationships between soil respiration and soil moisture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40, 1013–1018.
Epron, D., Nouvellon, Y., Roupsard, O., Mouvondy, W., Mabiala, A., Saint-Andre, L., et al. (2004). Spatial and temporal variations of soil respiration in a Eucalyptus plantation in Congo. Forest Ecology and Management, 202, 149–160.
Fang, C., & Moncrieff, J. B. (2001). The dependence of soil CO2 efflux on temperature. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 155–165.
Gaertig, T., Schack-Kirchner, H., Hildebrand, E. E., & Wilpert, K. V. (2002). The impact of soil aeration on oak decline in southwestern Germany. Forest Ecology and Management, 159, 15–25.
Gough, C. M., & Seiler, J. R. (2004). The influence of environmental, soil carbon, root and stand characteristics on soil CO2 efflux in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantations located on the South Carolina Coastal Plain. Forest Ecology and Management, 191, 353–363.
Hanson, P. J., Edwards, N. T., Garten, C. T., & Andrews, J. A. (2000). Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: a review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry, 48, 115–146.
Joffre, R., Ourcival, J. M., Rambal, S., & Rocheteau, A. (2003). The key role of topsoil moisture on CO2 efflux from a Mediterranean Quercus ilex forest. Annals of Forest Science, 60, 519–526.
Kane, E. S., Valentine, D. W., Schuur, E. A. G., & Dutta, K. (2005). Soil carbon stabilization along climate and stand productivity gradients in black spruce forests of interior Alaska. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 35, 2118–2129.
Keith, H., & Wong, S. C. (2006). Measurement of soil CO2 efflux using soda lime absorption: both quantitative and reliable. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38, 1121–1131.
Khomik, M., Arain, M. A., & McCaughey, J. H. (2006). Temporal and spatial variability of soil respiration in a boreal mixedwood forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 140, 244–256.
Lee, M., Nakane, K., Nakatsubo, T., & Koizumi, H. (2005). The importance of root respiration in annual soil carbon fluxes in a cool-temperate deciduous forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 134, 95–101.
Li, Y., Xua, M., Sunb, O. J., & Cui, W. (2004). Effects of root and litter exclusion on soil CO2 efflux and microbial biomass in wet tropical forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 2111–2114.
Liu, X., Wan, S., Su, B., Hui, D., & Luo, Y. (2002). Response of soil CO2 efflux to water manipulation in a tallgrass prairie ecosystem. Plant and Soil, 240, 213–223.
Luo, Y., & Zhou, X. (2006). Soil respiration and environment. London: Elsevier.
Raich, J. W. (1998). Aboveground productivity and soil respiration in three Hawaiian rain forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 107, 309–318.
Raich, J. W., & Tufekcioglu, A. (2000). Vegetation and soil respiration: correlations and controls. Biogeochemistry, 48, 71–90.
Raich, J. W., Potter, C. S., & Bhagawati, D. (2002). Interannual variability in global soil respiration, 1980–94. Global Change Biology, 8, 800–812.
Rey, A., Pegoraro, E., Tedeschi, V., Parri, I., Jarvis, P. G., & Valentin, R. (2002). Annual variation in soil respiration and its components in a coppice oak forest in Central Italy. Global Change Biology, 8, 851–866.
Rey, A., Pegoraro, E., Oyonarte, C., Were, A., Escribano, P., & Raimundo, J. (2011). Impact of land degradation on soil respiration in a steppe (Stipa tenacissima L.) semi-arid ecosystem in the SE of Spain. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43, 393–403.
SPSS Institute Inc. (2003). SPSS Base 12.0 User’s Guide. 703 pp
Tang, X., Zhou, G., Liu, S., Zhang, D., Liu, S., Li, J., et al. (2006). Dependence of soil respiration on soil temperature and soil moisture in successional forests in Southern China. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 48(6), 654–663.
Tufekcioglu, A., & Kucuk, M. (2004). Soil respiration in young and old oriental spruce stands and in adjacent grasslands in Artvin, Turkey. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 28, 429–434.
Tufekcioglu, A., Raich, J. W., Isenhart, T. M., & Schultz, R. C. (2001). Soil respiration within riparian buffers and an adjacent crop field. Plant and Soil, 229, 117–124.
Tufekcioglu, A., Raich, J. W., Isenhart, T. M., & Schultz, R. C. (2003). Biomass, carbon and nitrogen dynamics of multi-species riparian buffers within an agricultural watershed in Iowa, USA. Agroforestry Systems, 57, 187–198.
Vanhala, P. (2002). Seasonal variation in the soil respiration rate in coniferous forest soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 1375–1379.
Veenendaal, E. M., Kolle, O., & Lloyd, J. (2004). Seasonal variation in energy fluxes and carbon dioxide exchange for a broad-leaved semi-arid savanna (Mopane woodland) in Southern Africa. Global Change Biology, 10, 318–328.
Vesterdal, L., Schmidt, I. K., Callesen, I., Nilsson, L. O., & Gundersen, P. (2008). Carbon and nitrogen in forest floor and mineral soil under six common European tree species. Forest Ecology and Management, 255(1), 35–48.
Vincent, G., Shahriari, A. R., Lucot, E., Badot, P., & Epron, D. (2006). Spatial and seasonal variations in soil respiration in a temperate deciduous forest with fluctuating water table. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38, 2527–2535.
Wang, W., Ohse, K., Liu, J., Mo, W., & Oikawa, T. (2005). Contribution of root respiration to soil respiration in a C3/C4 mixed grassland. Journal of Biosciences, 30(4), 507–514.
WRB (2006). IUSS Working Group, World reference base for soil resources 2006. 2nd edition. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103. FAO, Rome. ISBN 92-5-105511-4, pp.145.
Yi, Z., Fu, S., Yi, W., Zhou, G., Mo, J., Zhang, D., et al. (2007). Partitioning soil respiration of subtropical forests with different successional stages in south China. Forest Ecology and Management, 243, 178–186.
Yohannes, Y., Shibistova, O., Abate, A., Fetene, M., & Guggenberger, G. (2011). Soil CO2 efflux in an Afromontane forest of Ethiopia as driven by seasonality and tree species. Forest Ecology and Management, 261, 1090–1098.
Zheng, D., Chen, J., LeMoine, J. M., & Euskirchen, E. S. (2005). Influences of land-use change and edges on soil respiration in a managed forest landscape, WI, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 215, 169–182.
Acknowledgments
Manuscript partly contains some results presented in Master of Science Thesis of Serdar Akburak in advisory of Ender Makineci completed in 2008 at Istanbul University, Science Institute. This work was supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Istanbul University, project number T1410/070807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akburak, S., Makineci, E. Temporal changes of soil respiration under different tree species. Environ Monit Assess 185, 3349–3358 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2795-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2795-6