Abstract
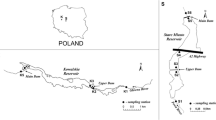
The growing interest in the environmental occurrence of veterinary and human pharmaceuticals is essentially due to their possible health implications to humans and ecosystem. This study assesses the occurrence of human pharmaceuticals in a Malaysian tropical aquatic environment taking a chemometric approach using cluster analysis, discriminant analysis and principal component analysis. Water samples were collected from seven sampling stations along the heavily populated Langat River basin on the west coast of peninsular Malaysia and its main tributaries. Water samples were extracted using solid-phase extraction and analyzed using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for 18 pharmaceuticals and one metabolite, which cover a range of six therapeutic classes widely consumed in Malaysia. Cluster analysis was applied to group both pharmaceutical pollutants and sampling stations. Cluster analysis successfully clustered sampling stations and pollutants into three major clusters. Discriminant analysis was applied to identify those pollutants which had a significant impact in the definition of clusters. Finally, principal component analysis using a three-component model determined the constitution and data variance explained by each of the three main principal components.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Odaini, N. A., Zakaria, M. P., Yaziz, M. I., & Surif, S. (2010). Multi-residue analytical method for human pharmaceuticals and synthetic hormones in river water and sewage effluents by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 1217, 6791–6806.
Bendz, D., Paxeus, N. A., Ginn, T. R., & Loge, F. J. (2005). Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in the environment, a case study: Hoje River in Sweden. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 122, 195–204.
Benotti, M. J., Trenholm, R. A., Vanderford, B. J., Holady, J. C., Stanford, B. D., & Snyder, S. A. (2008). Pharmaceuticals and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in U.S. Drinking Water. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 597–603.
Boyd, G. R., Palmeri, J. M., Zhang, S., & Grimm, D. A. (2004). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in stormwater canals and Bayou St. John in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Science of the Total Environment, 333, 137–148.
Calamari, D., Zuccato, E., Castiglioni, S., Bagnati, R., & Fanelli, R. (2003). Strategic Survey of Therapeutic Drugs in the Rivers Po and Lambro in Northern Italy. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 1241–1248.
Castiglioni, S., Bagnati, R., Fanelli, R., Pomati, F., Calamari, D., & Zuccato, E. (2005). Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Sewage Treatment Plants in Italy. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 357–363.
Christensen, F. M. (1998). Pharmaceuticals in the Environment–A Human Risk? Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 28, 212–221.
Comeau, F., Surette, C., Brun, G. L., & Losier, R. (2008). The occurrence of acidic drugs and caffeine in sewage effluents and receiving waters from three coastal watersheds in Atlantic Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 396, 132–146.
Costanzo, S. D., Murby, J., & Bates, J. (2005). Ecosystem response to antibiotics entering the aquatic environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 218–223.
Cui, C., Ji, S., & Ren, H. (2006). Determination of Steroid Estrogens in Wastewater Treatment Plant of A Controceptives Producing Factory. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121, 407–417.
Glassmeyer, S. T., Hinchey, E. K., Boehme, S. E., Daughton, C. G., Ruhoy, I. S., Conerly, O., Daniels, R. L., Lauer, L., McCarthy, M., Nettesheim, T. G., Sykes, K., & Thompson, V. G. (2009). Disposal practices for unwanted residential medications in the United States. Environment International, 35, 566–572.
Goncalves, C., Esteves Da Silva, J. C. G., & Alpendurada, M. F. (2006). Chemometric interpretation of pesticide occurence in soil samples from an intensive horticulture area in north Portugal. Analytica Chimica Acta, 560, 164–171.
Halling-Sorensen, B., Nors Nielsen, S., Lanzky, P. F., Ingerslev, F., Holten Lutzhoft, H. C., & Jorgensen, S. E. (1998). Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment- A review. Chemosphere, 36, 357–393.
Heberer, T., Schmidt-Bäumler, K., & Stan, H. J. (1998). Occurrence and Distribution of Organic Contaminants in the Aquatic System in Berlin. Part I: Drug Residues and other Polar Contaminants in Berlin Surface and Groundwater. Acta hydrochimica et hydrobiologica, 26, 272–278.
IWK (2010). Indah Water Konsortium Sdn Bhd. Retrieved May 2010 from http://www.iwk.com.my/
Johnson, R. A., & Wichern, D. W. (2007). Applied multivariate statitical analysis. New Jersey, USA: Pearson Education Inc.
Jones, O. A., Voulvoulis, N., & Lester, J. N. (2002). Aquatic environmental assessment of the top 25 English prescription pharmaceuticals. Water Research, 36, 5013–5022.
Jones, O. A., Lester, J. N., & Voulvoulis, N. (2005). Pharmaceuticals: a threat to drinking water? Trends in Biotechnology, 23, 163–167.
Juahir, H., Zain, S. M., Aris, A. Z., Yusoff, M. K., & Mokhtar, M. B. (2009). Spatial assessment of Langat river water quality using chemometrics. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 12, 287–295.
Juahir, H., Zain, S. M., Yusoff, M. K., Hanidza, T. I. T., Armi, A. S. M., Toriman, M. E., & Mokhtar, M. (2010). Spatial water quality assessment of Langat River Basin (Malaysia) using environmetric techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173, 1–17.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2009a). Illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment - Forensic applications of environmental data, Part 2: Pharmaceuticals as chemical markers of faecal water contamination. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1778–1786.
Kasprzyk-Hordern, B., Dinsdale, R. M., & Guwy, A. J. (2009b). Illicit drugs and pharmaceuticals in the environment - Forensic applications of environmental data. Part 1: Estimation of the usage of drugs in local communities. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1773–1777.
Kim, J.-W., Jang, H.-S., Kim, J.-G., Ishibashi, H., Hirano, M., Nasu, K., Ichikawa, N., Takao, Y., Shinohara, R., & Arizono, K. (2009). Occurrence of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in Surface Water from Mankyung River, South Korea. Journal of Health Science, 55, 249–258.
Kolpin, D. W., Furlong, E. T., Meyer, M. T., Thurman, E. M., Zaugg, S. D., Barber, L. B., & Buxton, H. T. (2002). Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, and Other Organic Wastewater Contaminants in U.S. Streams, 1999–2000: A National Reconnaissance. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 1202–1211.
Kosjek, T., Heath, E., & Krbavcic, A. (2005). Determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDs) residues in water samples. Environment International, 31, 679–685.
Kruawal, K., Sacher, F., Werner, A., Muller, J., & Knepper, T. P. (2005). Chemical water quality in Thailand and its impacts on the drinking water production in Thailand. Science of the Total Environment, 340, 57–70.
KTA Tenaga, S.B. (2005). Sungai Langat Integrated River Basin Management Study. M. o. N. R. a. Environment: Kuala Lumpur.
Langford, K. H., & Thomas, K. V. (2009). Determination of pharmaceutical compounds in hospital effluents and their contribution to wastewater treatment works. Environment International, 35, 766–770.
Liu, C.-W., Lin, K.-H., & Kuo, Y.-M. (2003). Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 313, 77–89.
Loos, R., Gawlik, B. M., Locoro, G., Rimaviciute, E., Contini, S., & Bidoglio, G. (2009). EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environmental Pollution, 157, 561–568.
Mas, S., de Juan, A., Tauler, R., Olivieri, A. C., & Escandar, G. M. (2010). Application of chemometric methods to environmental analysis of organic pollutants: A review. Talanta, 80, 1052–1067.
Mendiguchia, C., Moreno, C., Galindo-Riano, M. D., & Garcia-Vargas, M. (2004). Using chemometric tools to assess anthropogenic effects in river water: A case study: Guadalquivir River (Spain). Analytica Chimica Acta, 515, 143–149.
Nakada, N., Tanishima, T., Shinohara, H., Kiri, K., & Takada, H. (2006). Pharmaceutical chemicals and endocrine disrupters in municipal wastewater in Tokyo and their removal during activated sludge treatment. Water Research, 40, 3297–3303.
Nakada, N., Kiri, K., Shinohara, H., Harada, A., Kuroda, K., Takizawa, S., & Takada, H. (2008). Evaluation of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products as Water-soluble Molecular Markers of Sewage. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 6347–6353.
NMUS. (2006). Malaysian Statistics on Medicine. Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Health Malaysia.
Petrovic, M., Gonzalez, S., & Barceló, D. (2003). Analysis and removal of emerging contaminants in wastewater and drinking water. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 22, 685–696.
Quintana, J. B., & Reemtsma, T. (2004). Sensitive determination of acidic drugs and triclosan in surface and wastewater by ion-pair reverse-phase liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 18, 765–774.
Rodgers-Gray, T. P., Jobling, S., Morris, S., Kelly, C., Kirby, S., Janbakhsh, A., Harries, J. E., Waldock, M. J., Sumpter, J. P., & Tyler, C. R. (2000). Long-Term Temporal Changes in the Estrogenic Composition of Treated Sewage Effluent and Its Biological Effects on Fish. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 1521–1528.
Rodriguez-Mozaz, S., Lopez de Alda, M. J., & Barcelo, D. (2004). Picogram per Liter Level Determination of Estrogens in Natural Waters and Waterworks by a Fully Automated On-Line Solid-Phase Extraction-Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method. Analytical Chemistry, 76, 6998–7006.
Saim, N., Osman, R., Sari Abg Spian, D. R., Jaafar, M. Z., Juahir, H., Abdullah, M. P., & Ghani, F. A. (2009). Chemometric approach to validating faecal sterols as source tracer for faecal contamination in water. Water Research, 43, 5023–5030.
Stumpf, M., Ternes, T. A., Wilken, R.-D., Silvana Vianna, R., & Baumann, W. (1999). Polar drug residues in sewage and natural waters in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 225, 135–141.
Thompson, R. E., Voit, E. O., & Scott, G. I. (2000). Statistical modeling of sediment and oyster PAH contaminant data collected at a south Carolina Estuary (complete and left-censored samples). Environmetrics, 11, 99–119.
Weigel, S., Bester, K., & Huhnerfuss, H. (2001). New method for rapid solid-phase extraction of large-volume water samples and its application to non-target screening of North Sea water for organic contaminants by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography. A, 912, 151–161.
Werner, J. J., McNeill, K., & Arnold, W. A. (2005). Environmental photodegradation of mefenamic acid. Chemosphere, 58, 1339–1346.
Wiegel, S., Aulinger, A., Brockmeyer, R., Harms, H., Loffler, J., Reincke, H., Schmidt, R., Stachel, B., von Tumpling, W., & Wanke, A. (2004). Pharmaceuticals in the river Elbe and its tributaries. Chemosphere, 57, 107–126.
Yamamoto, H., Nakamura, Y., Moriguchi, S., Nakamura, Y., Honda, Y., Tamura, I., Hirata, Y., Hayashi, A., & Sekizawa, J. (2009). Persistence and partitioning of eight selected pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: Laboratory photolysis, biodegradation, and sorption experiments. Water Research, 43, 351–362.
Ying, G.-G., Kookana, R. S., & Ru, Y.-J. (2002). Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environment International, 28, 545–551.
Yu, C.-P., & Chu, K.-H. (2009). Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products along the West Prong Little Pigeon River in east Tennessee, USA. Chemosphere, 75, 1281–1286.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by funding from Malaysia’s Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI) under the Science Fund (project number 5450100). The authors would like to thank the Public Health Lab of the Veterinary Department under the Ministry of Agriculture and Agro-Based Industry and Fisheries for their generous support in the performance of the LC-MS/MS procedures. The authors are grateful to the Sewage Service Department for providing the sewage information in the Langat basin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Odaini, N.A., Zakaria, M.P., Zali, M.A. et al. Application of chemometrics in understanding the spatial distribution of human pharmaceuticals in surface water. Environ Monit Assess 184, 6735–6748 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2454-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2454-3