Abstract
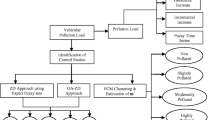
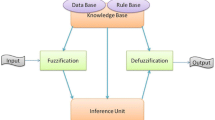
Proper assessment of air quality status in an atmosphere based on limited observations is an essential task for meeting the goals of environmental management. A number of classification methods are available for estimating the changing status of air quality. However, a discrepancy frequently arises from the quality criteria of air employed and vagueness or fuzziness embedded in the decision making output values. Owing to inherent imprecision, difficulties always exist in some conventional methodologies like air quality index when describing integrated air quality conditions with respect to various pollutants parameters and time of exposure. In recent years, the fuzzy logic-based methods have demonstrated to be appropriated to address uncertainty and subjectivity in environmental issues. In the present study, a methodology based on fuzzy inference systems (FIS) to assess air quality is proposed. This paper presents a comparative study to assess status of air quality using fuzzy logic technique and that of conventional technique. The findings clearly indicate that the FIS may successfully harmonize inherent discrepancies and interpret complex conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, R. O., & Church, R. L. (1980). Water quality indexing and scoring. Journal of the Environmental Engineering Division, 106(4), 757–771.
Bardalo, A. A., Nilsumranchit, W., & Chalermwat, K. (2001). Water quality and uses of the Bangpakong river, Eastern Thailand. Water Research, 35(15), 3635–3642.
Brown, R. M., McClelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index—Do we dare? Water & Sewage Works, 117(10), 339–343.
Dee, N., Baker, J., Drobny, N., Duke, K. M., Whitman, I., & Fahringer, D. (1973). An environmental evaluation system for water resource planning. Water Resources Research, 9(3), 523–535.
Dinius, S. H. (1972). Social accounting system for evaluating water resources. Water Resources Research, 8(5), 1159–1177.
Egborge, A. B. M., & Coker, J. B. (1986). Water quality index: Application in the Warri River, Nigeria. Journal of Environmental Pollution (Series B), 12(1), 27–40.
Giljanovic, N. S. (1999). Water quality evaluation by index in Dalmatia. Water Research, 33(16), 3423–3440.
GVAQI (1997) Greater Vancouver Regional District Air Quality and Source Control Department, Burnaby, BC, Canada
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 37(3), 300–306.
Inhaber, H. (1974). A set of suggested air quality indices for Canada. Atmospheric Environment, 9(3), 353–364.
Kumar, D., & Alappat, B. J. (2004). Selection of the appropriate aggregation function for calculating leachate pollution index. Practical Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Management, 8(4), 253–264.
Malaysia. (1997). A guide to air pollutant index in Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur: Department of Environment.
Ontario (1991). A Guideline to the Ontario Air Quality Index System. Ontario Ministry of the Environment, Toronto, Ont. Canada ISBN 0-7729-8230-9 Air Resource Branch
ORAQI. (1970). Oak Ridge Air Quality Index. In W. R. Ott (Ed.), Environmental indices theory and practice. Mich: Ann Arbor Science.
Ott, W. R. (1978). Environmental indices: Theory and practice. Ann Arbor: Ann Arbor Science.
Prasad, B., & Bose, J. M. (2001). Evaluation of the heavy metal pollution index for surface and spring water near a lime stone mining area of the lower Himalayas. Environmental Geology, 41, 183–188.
Prati, L., Pavanello, R., & Pesarin, F. (1971). Assessment of surface water quality by a single index of pollution. Water Research, 5, 741–751.
Saaty T. L. (1980). The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw-Hill
Sugeno, M., & Kang, G. (1988). Structure identification of fuzzy model. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 26(1), 15–33.
U.K. (1998). Air Pollution - what it means for your health. Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions. PO BOX No 236, Wetherby LS23 7NB, U.K.
USEPA. (1976). Federal Register, 41(174). Tuesday, September 7, 1976.
USEPA. (1998). Federal Register, 63(236). Wednesday, December 9, 1998
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the Vice Chancellor of the Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra for providing the required facility to carry out the work successfully. The authors also thank to W.B. State Pollution Control Board to provide the air pollution monitoring data in the web site for public use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, T., Gorai, A.K. & Pathak, G. Development of fuzzy air quality index using soft computing approach. Environ Monit Assess 184, 6187–6196 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2412-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2412-0