Abstract
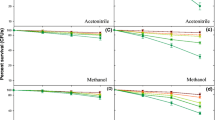
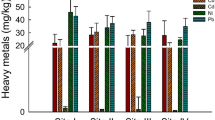
In the industrial area of Chinhat, Lucknow (India) wastewater coming from pesticide manufacturing and other industries is used to irrigate the agricultural crops. This practice has been polluting the soil and pollutants might reach the food chain. Gas chromatographic analysis revealed the presence of certain organochlorine pesticides in soil samples. Samples were extracted using different solvents, i.e., hexane, acetonitrile, methanol, chloroform, and acetone (all were HPLC-grade, SRL, India). Soil extracts were assayed for mutagenicity using Ames Salmonella/mammalian microsome test. Mutagenicity was observed in the test samples and TA98 was the most responsive strain for all the soil extracts (irrigated with wastewater) in terms of mutagenic index in the presence (+S9) and absence (−S9) of metabolic activation. In terms of slope (m) of linear dose–response curve for the most responsive strain TA98 exhibited highest sensitivity against the soil extracts in the presence and absence of S9 fraction. Hexane-extracted soil sample (wastewater) exhibited maximum mutagenicity in terms of net revertants per gram of soil in the presence and absence of S9 mix as compared to the other soil extracts. Groundwater-irrigated soil extracts displayed low level of mutagenicity as compared to wastewater-irrigated soil. The soil is accumulating a large number of pollutants due to wastewater irrigation and this practice of accumulation has an adverse impact on soil health.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhilash, P. C., & Singh, N. (2010). Withania somnifera Dunal-mediated dissipation of lindane from simulated soil: Implications for rhizoremediation of contaminated soil. Journal of Soils Sediments, 10, 272–282.
Aleem, A., & Malik, A. (2003). Genotoxic hazarads of long-term application of wastewater on agricultural soil. Mutation Research, 538, 145–154.
Alexander, R. R., Tang, J., & Alexander, M. (2002). Genotoxicity is unrelated to total concentration of priority carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils undergoing biological treatment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 150–154.
Ames, B. N. (1971). The detection of chemical mutagens with enteric bacteria. In A. Hollaender (Ed.), Chemical mutagens: Principles and methods for their detection (Vol. 1, pp. 267–282). New York: Plenum.
Ansari, M. I., & Malik, A. (2009). Genotoxicity of wastewaters used for irrigation of food crops. Environmental Toxicology, 24, 103–115.
Asita, A. O., & Makhalemele, R. (2008). Genotoxicity of chlorpyrifos, Alpha-thrin, Efekto virikop and Springbok to onion root tips cells. African Journal of Biotechnology, 23, 4244–4250.
Barbee, G. C., Brown, K. W., & Donnelly, K. C. (1992). Fate of mutagenic chemicals in soil amended with petroleum and wood preserving sludges. Waste Management Research, 10, 73–85.
Barra, R., Popp, P., Quiroz, R., Bauer, C., Cid, H., & von Tumpling, W. (2005). Persistent toxic substances in soils and waters along an altitudinal gradient in the Laja River Basin, Central Southern Chile. Chemosphere, 58, 905–915.
Celik, A., Mazmanci, B., Camlica, Y., & Aslin, A. (2003). Cytogenetic effects of lambda-cyhalothrin on Wistar rat bone marrow. Mutation Research, 539, 91–97.
Chakraborty, D., & Konar, S. K. (2002). Ecological study on the status of pollution by steel plant waste on river Damodar at Barnpur, West Bengal. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 44, 50–57.
Chen, G., & White, P. A. (2004). The mutagenic hazards of aquatic sediments: A review. Mutation Research, 567, 151–225.
Chenon, P., Gauthier, L., Loubieres, P., Severac, A., & Delpoux, M. (2003). Evaluation of the genotoxic and teratogenic potential of a municipal sludge and sludge amended soil using the amphibian Xenopus laevis and the tobacco: Nicotiana tabacum L. var xanthi dulieu. Science of the Total Environment, 301, 139–150.
Claxton, L., & George S. (2002). Challenges and approaches for identifying carcinogens in contaminated media. In G. Sunahara, A. Renoux, C. Thellen, & A. Pilon (Eds.), Environmental analysis of contaminated sites (pp. 73–93). West Sussex: Wiley.
Claxton, L. D., Stead, A. G., & Walsh, D. (1988). An analysis by chemical class of Salmonella mutagenicity tests as predictors of animal carcinogenicity. Mutation Research, 205, 197–225.
Claxton, L. D., Douglas, G., Krewski, D., Lewtas, J., Matsushita, H., & Rosenkranz, H. (1992). Overview, conclusions, and recommendations of the IPCS collaborative study on complex mixtures. Mutation Research, 276, 61–80.
Claxton, L. D., Houk, V. S., & Hughes, T. J. (1998). Genotoxicity of industrial wastes and effluents. Mutation Research, 410, 237–243.
Cotelle, S., Masfaraund, J. F., & Férard, J. F. (1999). Assessment of the genotoxicity of contaminated soil with Allium/Vicia-micronucleus and the Tradescantia-micronucleus assays. Mutation Research, 426, 167–171.
Courty, B., Curieux, F. L., Milon, V., & Marzin, D. (2004). Influence of extraction parameters on the mutagenicity of soil samples. Mutation Research, 565, 23–34.
Courty, B., Curieux, F. L., Belkessam, L., Laboudigue, A., & Marzin, D. (2008). Mutagenic potency in Salmonella typhimurium of organic extracts of soil samples originating from urban, suburban, agricultural, forest and natural areas. Mutation Research, 653, 1–5.
Covacia, A., Gheorgheb, A., Voorspoelsa, S., Maervoeta, J., Redekerc, E. S., Blustc, R., et al. (2005). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in sediment cores from the Western Scheldt River (Belgium): Analytical aspects and depth profiles. Environmental International, 31, 367–375.
Davol, P., Donnelly, K. C., Brown, K. W., Thomas, J. C., Estiri, M., & Jones, D. H. (1989). Mutagenic potential of runoff water from soils amended with three hazardous industrial wastes. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 8, 189–200.
DeMarini, D. M., Houk, V. S., Kornel, A., & Rogers, C. J. (1992). Effect of a base-catalyzed dechlorination process on the genotoxicity of PCB-contaminated soil. Chemosphere, 24, 1713–1720.
Donnelly, K. C., Brown, K. W., & DiGiullio, D. G. (1988). Mutagenic characterization of soil and water samples from a superfund site. Nuclear and Chemical Waste Management, 8, 135–141.
Donnelly, K. C., Brown, K. W., Anderson, C. S., Thomas, J. C., & Scott, B. R. (1991). Bacterial mutagenicity and acute toxicity of solvent and aqueous extracts of soil samples from an abandoned chemical manufacturing site. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 10, 1123–1132.
Edenharder, R., Ortseifen, M., Koch, M., & Wesp, H. F. (2000). Soil mutagens are airborne mutagens: Variation of mutagenic activities induced in Salmonella typhimurium TA98 and TA100 by organic extracts of agricultural and forest soils in dependence on location and season. Mutation Research, 472, 23–36.
Ehrlichmann, H., Dott, W., & Eisentraeger, A. (2000). Assessment of the water-extractablegenotoxic potential of soil samples from contaminated sites. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 46, 73–80.
Felton, J. S., & Wu, R. W. (2004). Ames/Salmonella assay: A bacterial test for mutagens. In Encyclopedia of life science. Wiley. doi:10.1038/npg.els.0001413.
Gan, J., Papiernik, S. K., Koskinen, W. C., & Yates, S. K. (1999). Evaluation of accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) for analysis of pesticide residues in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 333, 249–3253.
Hans, R. K., Farooq, M., Babu, G. S., Srivastava, S. P., Joshi, P. C., & Viswanathan, P. N. (1999). Agricultural produce in the dry bed of the River Ganga in Kanpur, India: A new source of pesticide contamination in human diets. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 37, 847–852.
Karabay, N. U., & Oguz, M. G. (2005). Cytogenetic and genetic effects of the insecticides, imidacloprid and methamidophos. Genetics and Molecular Research, 4, 653–662.
Knize, M. G., Takemoto, B. T., Lewis, P. R., & Felton, J. S. (1987). The characterization of the mutagenic activity of soil. Mutation Research, 192, 23–30.
Lah, B., Vidic, T., Glasencnik, E., Cepeljnik, T., Gorjanc G., & Marinsek-Logar, R. (2008). Genotoxicity evaluation of water soil leachates by Ames test, comet assay, and preliminary Tradescantia micronucleus assay. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 13, 9107–118.
Maron, D. M., & Ames, B. N. (1983). Revised methods for Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutation Research, 101, 173–215.
Malik, A., & Ahmad, M. (1995). Genotoxicity of some wastewaters in India. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 10, 287–293.
Martin, F. L., Piearce, T. G., Hewer, A., Phillips, D. H., & Semple, K. T. (2005). A biomarker model of sublethal genotoxicity (DNA single-strand breaks and adducts) using the sentinel organism Aporrectodea longa in spiked soil. Environmental Pollution, 138, 307–315.
McDaniels, A. E., Reyes, A. L., Wymer, L. J., Rankin, C. C., & Stelma Jr., G. N. (1993). Genotoxic activity detected in soils from a hazardous waste site by the Ames test and an SOS colorimetric test. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 22, 115–122.
Mouchet, F., Gauthier, L., Mailhes, C., Jourdain, M. J., Ferrier, V., & Triffault, G. (2006). Biomonitoring of the genotoxic potential of aqueous extracts of soils and bottom ash resulting from municipal solid waste incineration using the comet and micronucleus tests on amphibian (Xenopus laevis) larave and bacterial assays (Mutatox® and Ames tests). Science of the Total Environment, 355, 232–246.
Pagano, D. A., & Zeiger, E. (1992). Conditions for detecting the mutagenicity of divalent metals in Salmonella typhimurium. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 19, 136–146.
Prakash, O., Suar, M., Raina, V., Pal, C. D. R., & Lal, R. (2004). Residues of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in soil and water samples from Delhi and adjoining areas. Current Science, 87, 73–77.
Randerath, K., Zhou, G. D., Donnelly, K. C., Safe, S. H., & Randerath, E. (1994). DNA damage induced by wood preserving waste extracts in vitro without metabolic activation, as assayed by P32 postlabeling. Cancer Letter, 83, 123–128.
Ruiz, M. J., & Marzin, D. (1996). Genotoxicity of six pesticides by Salmonella mutagenicity test and SOS chromotest. Mutation Research, 390, 245–255.
Sanghi, R., & Sasi, K. S. (2001). Pesticides and heavy metals in agricultural soils of Kanpur, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 67, 446–454.
Šašek, V., Glaser, J. A., & Baveye, P. (2003). Genotoxicity estimation in soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons after biodegradation NATO Science Series IV. Earth and Environmental Sciences, 19, 211–215.
Shukla, Y., Taneja, P., Arora, A., & Sinha, N. (2004). Mutagenic potential of mancozeb in Salmonella typhimurium. Journal of Environmental Pathology Toxicology Oncology, 23, 60–65.
Singh, K. P., Takroo, R., & Ray, P. K. (1987). Analysis of pesticide residues in water. UP: Industrial Toxicology Research Centre Lucknow. ITRC manual no. 1.
Siroki, O., Underger, U., Institoris, L., & Nehez, M. (2001). A study on geno- and immunotoxicological effects of subacute propoxur and pirimicab exposure in rats. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 50, 76–81.
Steckert, A. V., Schnack, C. K., Sivano, J., Dal-Pizzol, F., & Andrade, V. M. (2009). Markers of pesticide exposure in irrigated rice culture. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 57, 11441–11445.
Tzoneva, M., Kappas, A., Georgieva, V., Vachkova, R., & Tziolas, V. (1985). On the genotoxicity of the pesticides Endodan and Kilacar in 6 different test systems. Mutation Research, 157, 13–22.
Vargas, V. M. F., Motta, V. E. P., & Henriques, J. A. P. (1993). Mutagenic activity detected by the Ames test in river water under the influence of petrochemical industries. Mutation Research, 319, 31–45.
Vargas, V. M. F., Guidobono, R. R., Jordao, C., & Henriques, J. A. P. (1995). Use of two short-term tests to evaluate the genotoxicity of river water treated with different concentration/extraction procedures. Mutation Research, 343, 31–52.
Watanabe, T., & Hirayama, T. (2001). Genotoxicity of soil. Journal of Health Science, 47, 433–438.
Watanabe, T., Wannee, K. R., Asanoma, M., Tepsuwan, A., Tantasri, N., Meesiripan, N., et al. (2005). Mutagenicity of surface soils in urban areas of Aichi prefecture, Japan, and Bangkok, Thailand. Journal of Health Science, 51, 645–657.
Watanabe, T., Takahashi, K., Konishi, E., Hoshino, Y., Hasei, T., Asanoma, M., et al. (2008). Mutagenicity of surface soil from residential areas in Kyoto city, Japan, and identification of major mutagens. Mutation Research, 649, 201–212.
White, P. A., & Claxton, L. D. (2004). Mutagens in contaminated soil: A review. Mutation Research, 567, 227–345.
Zemanek, M. G., Pollard, S. J., Kenefick, S. L., & Hrudey, S. (1997). Toxicity and mutagenicity of component classes of oils isolated from soils at petroleum- and creosole-contaminated. Journal of Air Waste Management Association, 47, 1250–1258.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly financed by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi vide letter F.No.: 36-12/2008 (SR). The Central Pollution Control Board, Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi is gratefully thanked for providing the Gas Chromatography facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anjum, R., Malik, A. Mutagenicity assessment of contaminated soil in the vicinity of industrial area. Environ Monit Assess 184, 3013–3026 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2167-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2167-7